Defi Infrastructure 101 - Aperçu et paysage du marché
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is redefining the future of finance. There is a major shift going on in the underlying infrastructure powering financial applications, and it’s changing the way we think about permission and control, transparency, and risks.
DeFi est un secteur de marché en développement à l’intersection des technologies blockchain, des actifs numériques et des services financiers. Selon DeFi Pulse, the value of digital assets locked into Defi applications grew 10X from less than $1 billion in 2019 to over $10 billion in 2020, and over $80 billion at its peak thus far in 2021. Yet the DeFi applications and underlying infrastructure are still in its nascent stage of development.
The goal of this report is to provide an introduction of the new emerging area of DeFi infrastructure powering DeFi apps today. While it’s easy to get caught up in the hype and speculation within the space, I’ll focus on the key components of Defi applications, their key differentiation compared to traditional finance, potential risks, and longer-term implications these Defi apps are causing.
Major Structural Commonalities Across DeFi Apps
DeFi apps are financial applications with no central counterparties. In practice, this means there is no institution (e.g. banks) you are interfacing with to access these financial applications; instead users interface directly with the programs (e.g. smart contracts) on top of the protocol itself. For more of a DeFi 101 primer, I highly recommend ce rapport.
Les principales catégories d'applications DeFi comprennent les échanges décentralisés, les plateformes de prêt, les pièces stables, les actifs synthétiques, l'assurance, entre autres. Bien que de portée diverse, toutes ces applications DeFi partagent un ensemble majeur de points communs, notamment :
- Utiliser les blockchains sous-jacentes comme registre principal
- Open source et transparent par défaut
- Interopérable et programmable (composabilité)
- Ouvert et accessible à tous (sans autorisation)
Utiliser les blockchains sous-jacentes comme registre principal
Compared to traditional financial applications which use core banking systems (Fiserv, Jack Henry, FIS, etc.) as the underlying ledgers of record, Defi apps use blockchains as their underlying core ledger.
A few of the most prominent blockchains used to build Defi apps include Ethereum, Solana, and Binance Chain, etc. These underlying blockchains store the ledger state of what is deposited into the DeFi apps, what is stored within the smart contracts, all of the transactions, and withdrawals.
All of the core accounting functions to ensure matching inputs and outputs are handled by the blockchain itself, the Defi apps don’t need to create external systems to reconcile balances, because all of the transactions are queryable across the various block explorers.
De plus, par rapport au système traditionnel, il n’existe pas de processus distinct de règlement et de compensation des transactions. Le traitement, la compensation et le règlement de la transaction se produisent tous en même temps lorsque la transaction est diffusée. Bien qu'il soit conseillé d'attendre environ 21 blocs ou plus pour garantir la finalité sur la blockchain elle-même.
Open Source et Transparent par défaut
Compared to traditional financial applications which are all closed-source and built on top of proprietary systems, Defi applications are typically entirely open-sourced and built on top of open underlying blockchains.

Cela provoque trois propriétés intéressantes :
- Composabilité — L'application DeFi elle-même peut être dupliquée, remixée et réutilisée dans de nombreuses autres applications (plus d'informations ci-dessous).
- Transparence — Étant donné que l'application DeFi est open source, il est entièrement vérifiable de savoir exactement ce que fait le contrat intelligent en termes de fonctions, d'autorisations utilisateur et de données utilisateur.
- Auditabilité — Étant donné que la blockchain sous-jacente elle-même est open source, l'ensemble du flux de fonds est entièrement vérifiable, y compris les garanties dans le système, le volume des transactions, les défauts, etc.
Contrairement au système financier traditionnel (qui est opaque), fonctionne sur un système de réserves fractionnaires et est sujet aux chocs du marché – le système DeFi est complètement transparent et sur-garanti – ce qui permet aux entreprises DeFi de résister beaucoup plus efficacement aux ralentissements.
Interopérable et programmable
Afin que les développeurs gagnent la confiance des utilisateurs, la majorité des applications DeFi sont entièrement open source, y compris le front-end et les contrats intelligents eux-mêmes. De plus, étant donné que les applications DeFi fonctionnent toutes sur une plate-forme commune (la blockchain sous-jacente), ces applications DeFi sont totalement interopérables les unes avec les autres et peuvent être programmées pour fonctionner avec n'importe quelle autre application DeFi de l'écosystème.
Ceci est communément appelé le «legos d'argentoucomposabilité» aspects de DeFi. Toutes ces applications DeFi sont comme des pièces de Lego individuelles qui peuvent être remixées pour fonctionner avec d'autres pièces de Lego afin de construire quelque chose de nouveau.
Comparez cela au système financier traditionnel où :
- Fragmentation des infrastructures — Les applications financières traditionnelles ne reposent pas sur une infrastructure commune.
- Applications cloisonnées — Les applications financières traditionnelles sont généralement la propriété d'une seule institution bancaire. Par exemple, toutes les « applications fintech » de Wells Fargo fonctionnent ensemble, mais pas entre différentes institutions bancaires.
- Développeur peu convivial — Les applications financières traditionnelles ne sont pas conçues pour que d'autres développeurs puissent créer des services par-dessus.
Le système financier traditionnel a des normes communes ; Cependant, il est extrêmement difficile de parvenir à un consensus entre les acteurs du marché, car les institutions financières considèrent leurs logiciels comme leur avantage concurrentiel au lieu d'utiliser les produits comme un facteur de différenciation.
L'une des principales raisons pour lesquelles nous avons vu tant d'innovation dans l'espace DeFi est que les systèmes sont interopérables, ce qui permet à l'écosystème des développeurs d'avoir une expression plus créative sur les produits et services qu'ils créent. De plus, les développeurs n'ont pas besoin de perdre du temps à réinventer la roue, mais peuvent plutôt s'appuyer sur des cadres communs et se concentrer sur les éléments qui rendent leurs produits spéciaux.
Ouvert et accessible à tous
Avec les applications financières traditionnelles, les nouveaux utilisateurs doivent généralement passer par un long processus d'intégration, des vérifications de revenus, des vérifications de crédit ou même des réunions en personne, juste pour pouvoir utiliser un produit financier donné.
En raison de ces règles arbitraires fixées par les institutions financières, ces processus d'intégration sont sujet aux préjugés comme discrimination en matière de prêt, refus des services bancaires de base, ouverture de lignes de crédit sans consentement, facturer des frais illégaux, etc.
Avec les applications DeFi, tout ce dont vous avez besoin est une adresse de portefeuille pour interagir avec ces systèmes. Les applications DeFi ne demandent pas de vérification des revenus, elles n'ont pas besoin de vérifications de crédit et, dans la plupart des cas, elles n'ont même pas besoin de savoir qui vous êtes en dehors de l'adresse du portefeuille que vous utilisez.
Ceci est communément appelé les applications DeFi étant sans permission. Si vous disposez des fonds dans votre portefeuille pour la transaction que vous souhaitez effectuer, vous pouvez le faire. Il n'y a aucune institution ou intermédiaire pour arrêter ou vous refuser le service. Peu importe votre origine ou votre pays d'origine, les applications DeFi ne font aucune discrimination.
C'est l'un des aspects les plus sous-estimés des produits DeFi.
Traditional Fintech Architectures vs. DeFi Architecture
Voici un schéma plus architectural sur les principales différences techniques entre une application fintech traditionnelle et une application DeFi (simplifié par souci de concision) :
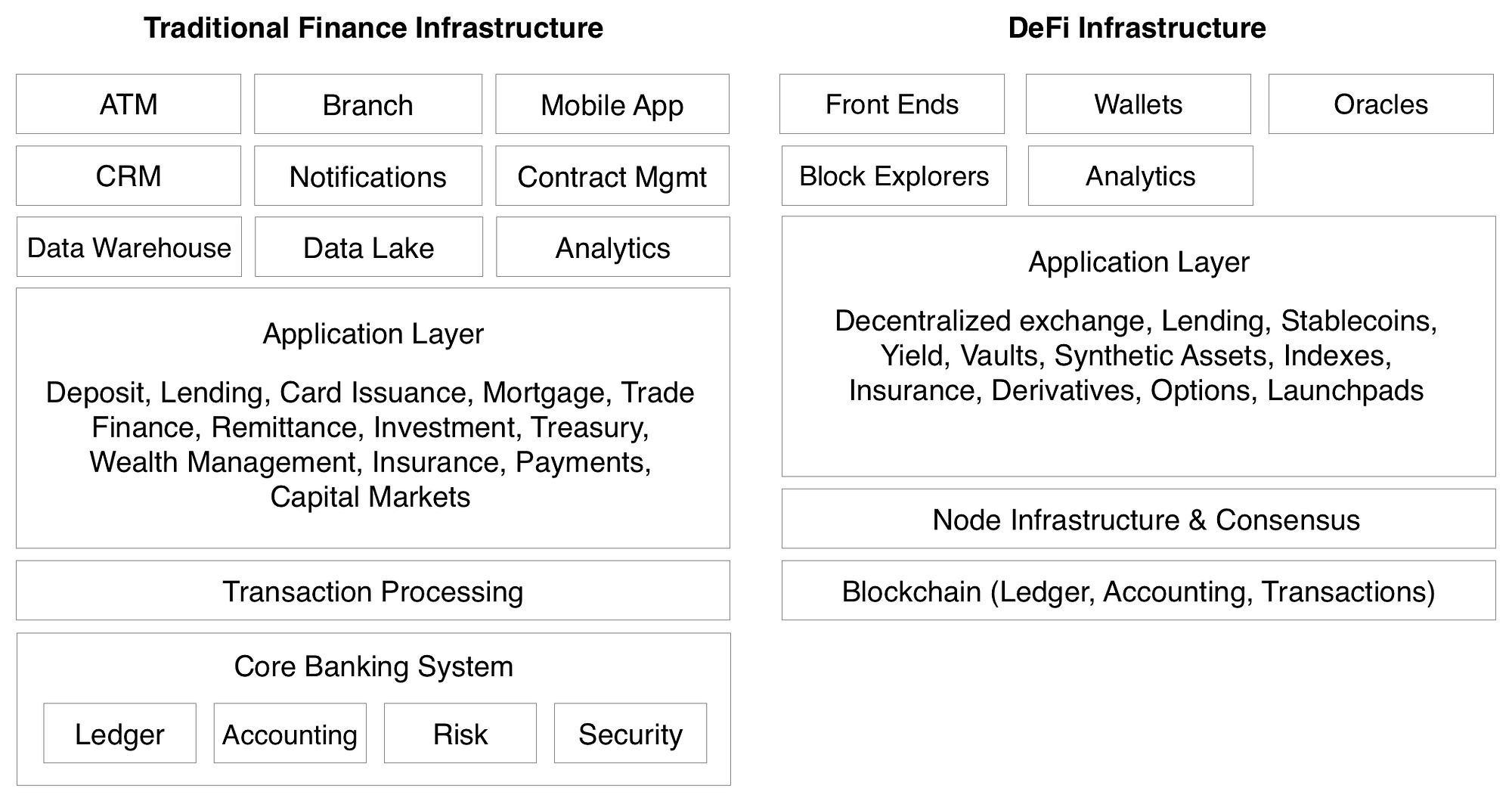
Here is a more direct comparison chart on some of the key differences between centralized and decentralized financial applications:

DeFi Infrastructure — Market Map
Below is a market map of two different DeFi ecosystems, one built on the Solana ecosystem and the other built on the Ethereum ecosystem.
The reason why I am picking these two ecosystems to focus on is to show the breadth of DeFi apps being built across two different underlying protocols. I also believe Solana is the most interesting new layer one protocol because of its high transaction throughput (50K+ transactions per second), sub second latency & transaction confirmation times, and fast growing ecosystem of developers building DeFi apps on top of the Solana protocol.
While similar in structure, each underlying protocol has its own ecosystem built on top which is largely independent of the other. Below are some of the further explanations of each layer and the tradeoffs between them.

Base Layer (Layer One)
The base layer is the blockchain in which the core ledger itself sits. Ethereum is the most dominant layer one today, and Solana is the most promising new entrant with faster transaction speeds, more throughput, and cheaper transactions.
Node Infrastructure
A never ending amount of data needs to be queried about the underlying ledger (retrieving blocks, finding transactions, syncing data, writing transactions, etc). In the Ethereum ecosystem, a whole industry sprung up to solve this need (Infura, Alchemy, etc.).
Contrast this with Solana where the underlying ledger is fast enough and in sync enough that teams can just query Solana’s RPC nodes directly (this might not last forever though).
Couche deux
On Ethereum, there are various layer two solutions primarily used for scaling since Etheruem itself cannot handle all of the transactions on itself. Two of the promising scaling solutions include Matic, Optimism, among others.
On Solana, since there is only one layer to build upon (no layer 2 scaling solution needed) there are no specialized integrations needed and no mismatches with the underlying ledger which is processing settlement.
Order Book Aggregation
Unique to Solana, there is an additional layer occupied by a DeFi project named Sérum which provides a CLOB (Central limit order book) that is used by all of the DeFi projects built on top.
When new DeFi projects are built on top of Solana (DEX, AMM, Options, etc.), they can pull orders from Serum and push orders back into Serum, greatly reducing the cold start challenge most new financial applications face.
The best way to think about it is to think of it as “networked liquidity” and an “order management” system which is used by the majority of projects within the Solana ecosystem.
One of the more innovative examples of combining a CLOB (Serum) and an AMM is Raydium (very similar to Uniswap v3). The combining of these systems allows for passive LPs with active market making using Serum.
DeFi Toolset
There are a set of common tools needed to operate most of these DeFi apps, either from the perspective of developers or end users. These services don’t have direct traditional finance analogies but they include:
- Portefeuilles — The main interface people use to store assets & interface with DeFi apps.
- Oracles — On-chain data feeds DeFi apps use to reference prices and execute transactions against (example: liquidations).
- Block Explorers & Analytics — Tools like Block Explorers were created to allow people to query the blockchain ledger itself directly. These are used most often when verifying transactions.
- Stablecoins — The two main assets used in DeFi ecosystems include the underlying native protocol token (ETH or SOL) and ideally on-chain stablecoins (USDC, Dai, or Pai).
- Front-Ends — A new emerging layer which creates easy to use front-end applications to interact with multiple DeFi projects at once, or to simplify transactions. This includes both Zapper.fi within the Ethereum Ecosystem or Step Finance within the Solana ecosystem.
Applications DeFi
The DeFi apps themselves are composed of all of the core financial applications which can be used directly, or embedded into other various apps within the crypto ecosystem.

Potential Missing Pieces of DeFi Infrastructure
When comparing and contrasting DeFi infrastructure with traditional financial infrastructure, there were a few pieces that don’t exist yet in the decentralized world that could be interesting to explore.
A few to highlight below:
- Applications grand public — In the traditional financial world, consumers typically act with consumer apps (ex. Robinhood, Chime, Transferwise) not the underlying protocols themselves. The front-ends of the DeFi space could be greatly improved and intermediate much more of the total consumer experience. In general, the UI/UX of most DeFi apps are still very difficult to use from a consumer perspective.
- CRM — The DeFi space doesn’t really have a concept of customer relationship management nor typically collects any amount of consumer data. While great from a privacy perspective, there is great value in understanding the customer better.
- Notifications — Notifications or alerts don’t really exist at all in the DeFi space at all. On a more broader level there aren’t any great methods to communicate with users either.
- Analyse des produits — There are tools to measure blockchain activity, but not to measure engagement within DeFi applications.
- Sécurité - DeFi products do typically conduct security audits; however, none of the security audits guarantee the most common protections consumers are accustomed to in the traditional financial world. On top of this, the demand for security auditors outstrips the supply, so it’s a big bottleneck.
- Transaction Rollbacks — In traditional finance, if you make a mistake, a financial institution can initiate a rollback of the transaction. This does not yet exist in DeFi.
- Garde — Right now, most DeFi projects need to be interacted with from an individual wallet perspective. None of the custodians allow you to interact with DeFi apps.
- Plateformes de développement — Most of the developers in the crypto space are building right on top of the layer one protocol itself. There are no concepts of developer platforms or middleware just yet.
- Embeddable Wallets — Wallets are seen as these external services, there aren’t any offerings of white-label wallets to embed these directly into the DeFi apps themselves. There are several initiatives such as Torus, but these are still in its infancy.
- Active — One of the biggest complaints from the traditional finance world about DeFi is the pseudonymity of users. Ideally there needs to be a way to keep out the bad actors while persevering consumer privacy.
Future of Financial Applications
After meeting hundreds of founders and seeing progress teams are making, one thing is very clear — the pace of innovation in DeFi is 10x faster vs. that of traditional fintech apps.
In traditional finance:
- The underlying ledgers are not open source nor developer friendly.
- There are a whole host of “banking as a service” applications just to wrap underlying partner banks in developer friendly platforms.
- Fintech apps are very challenging regulatory wise and typically take years of development before releasing a single product.
Contrast that to DeFi where:
- Everything is open source including the ledger itself.
- All of the transactions are public.
- Everything is built from the perspective of developers building applications on top of protocols.
- New DeFi apps are built and released in weeks, not years.
We at Race Capital believe that DeFi developers will forever change how the finance world works. We are incredibly bullish about the DeFi infrastructure stack and community.
If you are building the horizontal infrastructure layers of the new open source financial stack including: trading, lending, borrowing, and/or any horizontal tools all new DeFi projects will rely upon in the future, we want to chat with you. Send me a message > chris@race.capital
Merci !
A big thank you to Bartosz Lipinski, Kas Vardhanabhuti, George Harrap, Dylan Macalinao, Anmol Singh, Edith Yeung, and Kim McCann for helping to review and provide feedback on this post.
Disclaimer: I’m a proud seed investor in Laboratoires Solana.
