Decemberben 2020, Az AWS bejelentette - a Amazon SageMaker JumpStart, képessége Amazon SageMaker amely segít gyorsan és egyszerűen elkezdeni a gépi tanulást (ML). A JumpStart az előre betanított modellek széles skálájának egy kattintással történő finomhangolását és telepítését biztosítja a népszerű ML-feladatok között, valamint a gyakori üzleti problémákat megoldó végpontok közötti megoldások választékát. Ezek a funkciók eltávolítják az ML folyamat minden egyes lépéséből adódó nehézségeket, megkönnyítve a kiváló minőségű modellek fejlesztését, és lerövidítve a telepítéshez szükséges időt.
This post is the third in a series on using JumpStart for specific ML tasks. In the első poszt, we showed how you can run image classification use cases on JumpStart. In the második bejegyzés, we showed how you can run text classification use cases on JumpStart. In this post, we provide a step-by-step walkthrough on how to fine-tune and deploy an image segmentation model, using trained models from MXNet. We explore two ways of obtaining the same result: via JumpStart’s graphical interface on Amazon SageMaker Studio, és programozottan keresztül JumpStart API-k.
If you want to jump straight into the JumpStart API code we explain in this post, you can refer to the following sample Jupyter notebooks:
JumpStart áttekintése
JumpStart helps you get started with ML models for a variety of tasks without writing a single line of code. At the time of writing, JumpStart enables you to do the following:
- Telepítsen előre betanított modelleket a gyakori ML-feladatokhoz – A JumpStart lehetővé teszi a gyakori ML-feladatok megoldását fejlesztési erőfeszítések nélkül azáltal, hogy könnyen telepítheti a nagy, nyilvánosan elérhető adatkészleteken előre betanított modelleket. Az ML-kutató közösség nagy erőfeszítéseket tett annak érdekében, hogy a közelmúltban kifejlesztett modellek többségét nyilvánosan elérhetővé tegye. A JumpStart több mint 300 modellből álló gyűjteményt tartalmaz, amelyek a 15 legnépszerűbb ML-feladatot ölelik fel, mint például az objektumészlelés, a szövegosztályozás és a szöveggenerálás, így a kezdők is könnyen használhatják őket. Ezek a modellek olyan népszerű modellközpontokból származnak, mint a TensorFlow, PyTorch, Hugging Face és MXNet.
- Az előre betanított modellek finomhangolása – A JumpStart lehetővé teszi az előre betanított modellek finomhangolását anélkül, hogy saját edzési algoritmust kellene írnia. Az ML-ben az egyik tartományban tanult tudás másik tartományba való átvitelének képességét hívják transzfer tanulás. Az átviteli tanulás segítségével pontos modelleket állíthat elő kisebb adatkészletein, sokkal alacsonyabb képzési költségekkel, mint az eredeti modell betanításával kapcsolatos költségek. A JumpStart a LightGBM, CatBoost, XGBoost és Scikit-learn alapú népszerű edzési algoritmusokat is tartalmazza, amelyeket a nulláról edzhet a táblázatos regresszióhoz és osztályozáshoz.
- Használjon előre elkészített megoldásokat – A JumpStart 17 megoldást kínál a gyakori ML használati esetekre, mint például a kereslet-előrejelzés, valamint az ipari és pénzügyi alkalmazások, amelyeket néhány kattintással telepíthet. A megoldások olyan teljes körű ML-alkalmazások, amelyek különböző AWS-szolgáltatásokat kapcsolnak össze egy adott üzleti felhasználási eset megoldása érdekében. Használják AWS felhőképződés sablonok és referenciaarchitektúrák a gyors üzembe helyezés érdekében, ami azt jelenti, hogy teljes mértékben testreszabhatók.
- Tekintse meg a SageMaker algoritmusokkal kapcsolatos notebook-példákat – A SageMaker beépített algoritmusokat kínál, amelyek segítenek az adattudósoknak és az ML-gyakorlóknak az ML modellek gyors képzésében és bevezetésében. A JumpStart mintajegyzetfüzeteket biztosít, amelyek segítségével gyorsan használhatja ezeket az algoritmusokat.
- Tekintse át a képzési videókat és blogokat – A JumpStart számos blogbejegyzést és videót is kínál, amelyek megtanítják a SageMaker különböző funkcióinak használatát.
A JumpStart elfogadja az egyéni VPC beállításokat és AWS kulcskezelési szolgáltatás (AWS KMS) titkosítási kulcsokat, így biztonságosan használhatja a rendelkezésre álló modelleket és megoldásokat a vállalati környezetben. Biztonsági beállításait átadhatja a JumpStartnak a Studion belül vagy a SageMaker Python SDK-n keresztül.
Szemantikus szegmentálás
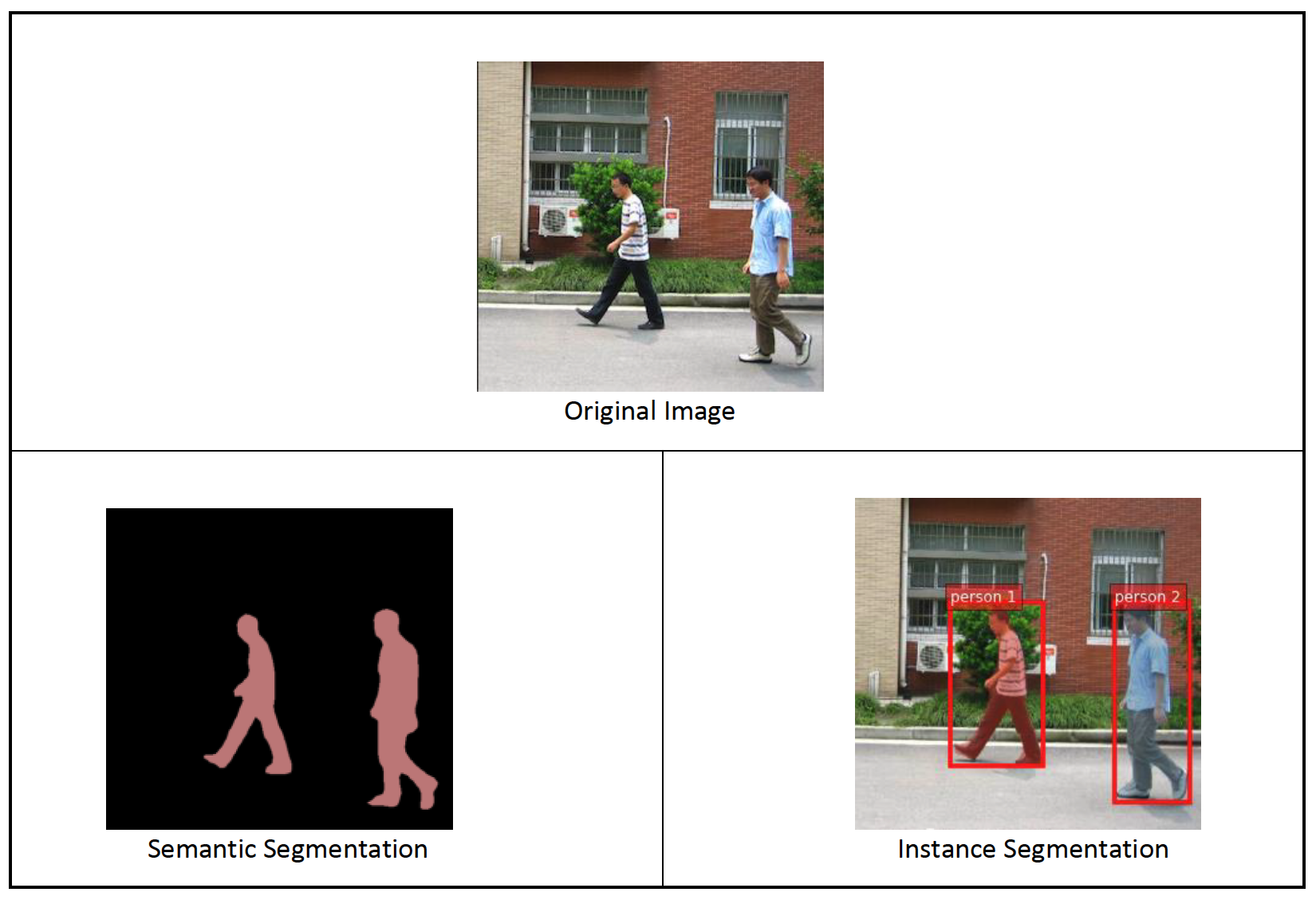
Semantic segmentation delineates each class of objects appearing in an input image. It tags (classifies) each pixel of the input image with a class label from a predefined set of classes. Multiple objects of the same class are mapped to the same mask.
The model available for fine-tuning builds a fully convolutional network (FCN) “head” on top of the base network. The fine-tuning step fine-tunes the FCNHead while keeping the parameters of the rest of the model frozen, and returns the fine-tuned model. The objective is to minimize per-pixel softmax cross entropy loss to train the FCN. The model returned by fine-tuning can be further deployed for inference.
The input directory should look like the following code if the training data contains two images. The names of the .png files can be anything.
The mask files should have class label information for each pixel.
Példányszegmentálás
Instance segmentation detects and delineates each distinct object of interest appearing in an image. It tags every pixel with an instance label. Whereas semantic segmentation assigns the same tag to pixels of multiple objects of the same class, instance segmentation further labels pixels corresponding to each occurrence of an object on the image with a separate tag.
Currently, JumpStart offers inference-only models for instance segmentation and doesn’t support fine-tuning.
The following images illustrate the difference between the inference in semantic segmentation and instance segmentation. The original image has two people in the image. Semantic segmentation treats multiple people in the image as one entity: Person. However, instance segmentation identifies individual people within the Person kategória.
Megoldás áttekintése
The following sections provide a step-by-step demo to perform semantic segmentation with JumpStart, both via the Studio UI and via JumpStart APIs.
A következő lépéseket járjuk végig:
- A JumpStart elérése a Studio felhasználói felületén keresztül:
- Futtasson következtetést az előre betanított modellen.
- Finomhangolja az előre betanított modellt.
- A JumpStart programozott használata a SageMaker Python SDK-val:
- Futtasson következtetést az előre betanított modellen.
- Finomhangolja az előre betanított modellt.
We also discuss additional advanced features of JumpStart.
A JumpStart elérése a Studio felhasználói felületén keresztül
Ebben a részben bemutatjuk, hogyan lehet betanítani és telepíteni a JumpStart modelleket a Studio felhasználói felületén keresztül.
Futtasson következtetést az előre betanított modellen
The following video shows you how to find a pre-trained semantic segmentation model on JumpStart and deploy it. The model page contains valuable information about the model, how to use it, expected data format, and some fine-tuning details. You can deploy any of the pre-trained models available in JumpStart. For inference, we pick the ml.g4dn.xlarge instance type. It provides the GPU acceleration needed for low inference latency, but at a lower price point. After you configure the SageMaker hosting instance, choose Telepítése. 5–10 percbe telhet, amíg az állandó végpont elindul és fut.
After a few minutes, your endpoint is operational and ready to respond to inference requests.
Similarly, you can deploy a pre-trained instance segmentation model by following the same steps in the preceding video while searching for instance segmentation instead of semantic segmentation in the JumpStart search bar.
Finomhangolja az előre betanított modellt
The following video shows how to find and fine-tune a semantic segmentation model in JumpStart. In the video, we fine-tune the model using the PennFudanPed adatkészlet, provided by default in JumpStart, which you can download under the Apache 2.0 licenc.
Fine-tuning on your own dataset involves taking the correct formatting of data (as explained on the model page), uploading it to Amazon egyszerű tárolási szolgáltatás (Amazon S3), and specifying its location in the data source configuration. We use the same hyperparameter values set by default (number of epochs, learning rate, and batch size). We also use a GPU-backed ml.p3.2xlarge as our SageMaker training instance.
You can monitor your training job running directly on the Studio console, and are notified upon its completion. After training is complete, you can deploy the fine-tuned model from the same page that holds the training job details. The deployment workflow is the same as deploying a pre-trained model.
A JumpStart programozott használata a SageMaker SDK-val
In the preceding sections, we showed how you can use the JumpStart UI to deploy a pre-trained model and fine-tune it interactively, in a matter of a few clicks. However, you can also use JumpStart’s models and easy fine-tuning programmatically by using APIs that are integrated into the SageMaker SDK. We now go over a quick example of how you can replicate the preceding process. All the steps in this demo are available in the accompanying notebooks Bevezetés a JumpStartba – Példányszegmentálás és a Bevezetés a JumpStartba – Szemantikus szegmentáció.
Futtasson következtetést az előre betanított modellen
In this section, we choose an appropriate pre-trained model in JumpStart, deploy this model to a SageMaker endpoint, and run inference on the deployed endpoint.
A SageMaker egy Docker konténereken alapuló platform. A JumpStart a rendelkezésre álló keretrendszer-specifikusat használja SageMaker Deep Learning tárolók (DLC-k). Lekérünk minden további csomagot, valamint szkripteket, amelyekkel kezelhetjük a képzést és a következtetéseket a kiválasztott feladathoz. Végül az előre betanított modelltermékeket külön lekérjük model_uris, amely rugalmasságot biztosít a platform számára. Tetszőleges számú, ugyanarra a feladatra előre betanított modellt használhat egyetlen betanítási vagy következtetési szkripttel. Lásd a következő kódot:
For instance segmentation, we can set model_id nak nek mxnet-semseg-fcn-resnet50-ade. The is in the identifier corresponds to instance segmentation.
Ezután az erőforrásokat a SageMaker modell példány és telepítsen egy végpontot:
Néhány perc múlva a modellünk bevetésre kerül, és valós időben kaphatunk előrejelzéseket belőle!
The following code snippet gives you a glimpse of what semantic segmentation looks like. The predicted mask for each pixel is visualized. To get inferences from a deployed model, an input image needs to be supplied in binary format. The response of the endpoint is a predicted label for each pixel in the image. We use the query_endpoint és a parse_response helper functions, which are defined in the kísérő jegyzetfüzet:
Finomhangolja az előre betanított modellt
To fine-tune a selected model, we need to get that model’s URI, as well as that of the training script and the container image used for training. Thankfully, these three inputs depend solely on the model name, version (for a list of the available models, see JumpStart Available Model Table), and the type of instance you want to train on. This is demonstrated in the following code snippet:
Visszaszerezzük a model_id corresponding to the same model we used previously. You can now fine-tune this JumpStart model on your own custom dataset using the SageMaker SDK. We use a dataset that is publicly hosted on Amazon S3, conveniently focused on semantic segmentation. The dataset should be structured for fine-tuning as explained in the previous section. See the following example code:
A kiválasztott modellünkhöz ugyanazokat az alapértelmezett hiperparamétereket kapjuk, mint amelyeket az előző részben láttunk, használatával sagemaker.hyperparameters.retrieve_default(). We then instantiate a SageMaker estimator and call the .fit method to start fine-tuning our model, passing it the Amazon S3 URI for our training data. The entry_point script provided is named transfer_learning.py (the same for other tasks and models), and the input data channel passed to .fit meg kell nevezni training.
Amíg az algoritmus edz, nyomon követheti a folyamatát a SageMaker notebookban, ahol magát a kódot futtatja, vagy amazonfelhőóra. When training is complete, the fine-tuned model artifacts are uploaded to the Amazon S3 output location specified in the training configuration. You can now deploy the model in the same manner as the pre-trained model.
Jellemzők
In addition to fine-tuning and deploying pre-trained models, JumpStart offers many advanced features.
Az első az automatic model tuning. This allows you to automatically tune your ML models to find the hyperparameter values with the highest accuracy within the range provided through the SageMaker API.
A második fokozatos képzés. This allows you to train a model you have already fine-tuned using an expanded dataset that contains an underlying pattern not accounted for in previous fine-tuning runs, which resulted in poor model performance. Incremental training saves both time and resources because you don’t need to retrain the model from scratch.
Következtetés
In this post, we showed how to fine-tune and deploy a pre-trained semantic segmentation model, and how to adapt it for instance segmentation using JumpStart. You can accomplish this without needing to write code. Try out the solution on your own and send us your comments.
Ha többet szeretne megtudni a JumpStartról és arról, hogyan használhatja a nyílt forráskódú, előre betanított modelleket számos más ML-feladathoz, tekintse meg a következőt AWS re:Invent 2020 videó.
A szerzőkről
 Dr. Vivek Madan az Amazon SageMaker JumpStart csapatának alkalmazott tudósa. PhD fokozatát az Illinoisi Egyetemen szerezte, az Urbana-Champaign-ben, és a Georgia Tech posztdoktori kutatója volt. Aktív kutatója a gépi tanulásnak és az algoritmustervezésnek, és publikált előadásokat EMNLP, ICLR, COLT, FOCS és SODA konferenciákon.
Dr. Vivek Madan az Amazon SageMaker JumpStart csapatának alkalmazott tudósa. PhD fokozatát az Illinoisi Egyetemen szerezte, az Urbana-Champaign-ben, és a Georgia Tech posztdoktori kutatója volt. Aktív kutatója a gépi tanulásnak és az algoritmustervezésnek, és publikált előadásokat EMNLP, ICLR, COLT, FOCS és SODA konferenciákon.
 Santosh Kulkarni az Amazon Web Services vállalati megoldások építésze, aki sportügyfelekkel dolgozik Ausztráliában. Szenvedélyesen épít nagyszabású elosztott alkalmazásokat üzleti problémák megoldására, felhasználva tudását az AI/ML, a big data és a szoftverfejlesztés terén.
Santosh Kulkarni az Amazon Web Services vállalati megoldások építésze, aki sportügyfelekkel dolgozik Ausztráliában. Szenvedélyesen épít nagyszabású elosztott alkalmazásokat üzleti problémák megoldására, felhasználva tudását az AI/ML, a big data és a szoftverfejlesztés terén.
 Leonardo Bachega is a senior scientist and manager in the Amazon SageMaker JumpStart team. He’s passionate about building AI services for computer vision.
Leonardo Bachega is a senior scientist and manager in the Amazon SageMaker JumpStart team. He’s passionate about building AI services for computer vision.
- AI
- ai művészet
- ai art generátor
- van egy robotod
- Amazon SageMaker
- mesterséges intelligencia
- mesterséges intelligencia tanúsítás
- mesterséges intelligencia a bankszektorban
- mesterséges intelligencia robot
- mesterséges intelligencia robotok
- mesterséges intelligencia szoftver
- AWS gépi tanulás
- blockchain
- blokklánc konferencia ai
- coingenius
- társalgási mesterséges intelligencia
- kriptokonferencia ai
- dall's
- mély tanulás
- google azt
- gépi tanulás
- Plató
- plato ai
- Platón adatintelligencia
- Platón játék
- PlatoData
- platogaming
- skála ai
- szintaxis
- zephyrnet