- Cross-chain interoperability is the process of operation that enables two or more blockchain networks to communicate
- Decentralized open-source technology allows the creation of interoperable products across chains, enabling more users, businesses and institutions to stay interconnected
- A critical challenge of interoperability is the fundamental functioning of the consensus mechanisms
A critical and common factor among successful crypto hacks is the exploitation of blockchain weaknesses discovered that are caused by cross-chain interoperability. Indeed among the fundamental weaknesses that blockchain technology has is found within the challenges of interoperability, but it’s generally not the developers’ fault. Blockchain alone has proven to have numerous functions. Unfortunately, like every invention out there, developers sought to improve it. Then the idea of blockchain interoperability came to mind, but it had various hick-ups along the way.
Developers had to think outside the box to make this “cliche” concept of a merge happen. After years of consistent trial and error, they created an operational cross-chain between blockchain networks. Unfortunately, the hype did not last because this bridge became a source of both benefits and tragedies within the crypto ecosystem.
Understanding Blockchain Interoperability
From the word items, blockchain interoperability or cross-chain interoperability is a merge of the combination of two stand-alone concepts. Blockchain technology is the decentralized and immutable ledger that runs the crypto ecosystem and the entire Web3 concept. On the other hand, interoperability combines several different operations to appear as a single entity.
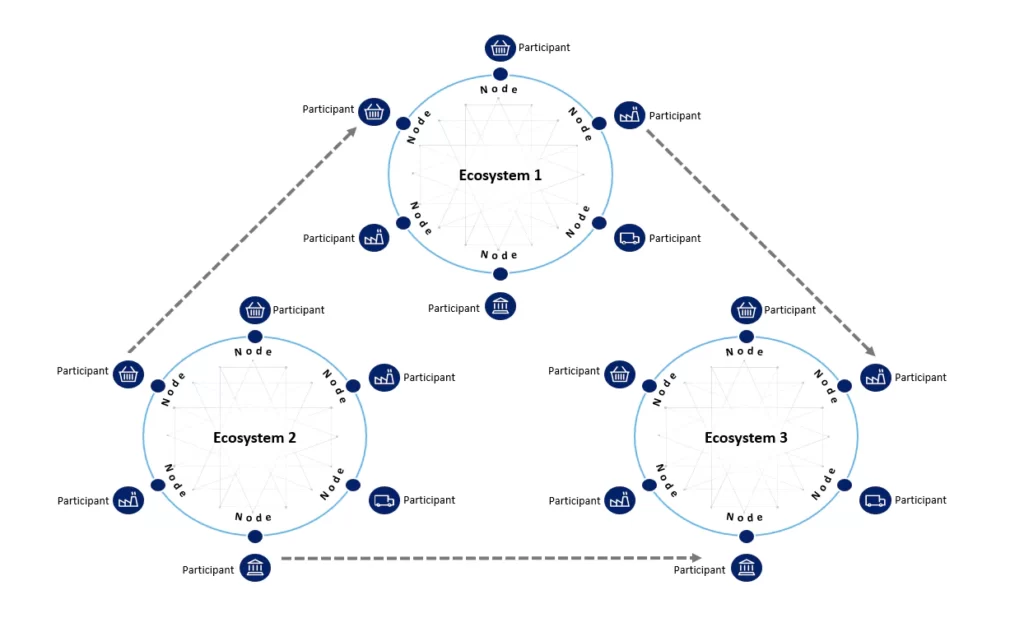
The entire workflow of Blockchain interoperability.[Photo/CENGN]
Cross-chain interoperability is the process of operations that enables two or more blockchain networks to communicate. This makes it possible for one blockchain network to communicate or transact with an entirely different blockchain network. According to Marcel Harmann, CEO of THORWallet DEX, interoperability is the freedom of data exchange.
Also, Read Blockchain Security: Lessons learnt in 2022, expectations for 2023.
It establishes successful cross-chain interoperability and creates improved blockchain technology in terms of scalability. Many experts have stated that interoperability is the missing element to address various blockchain weaknesses in global adoption.
Why is Blockchain Interoperability necessary
For blockchain technology to fully realize its true potential and finally implement Web3, it is necessary to have a vast interconnected network system similar to Web2. Having a single consensus mechanism running an entire global network is bound to cause plenty of trouble.
As such, it is necessary to attain cross-chain interoperability to enable individuals to participate in more than one blockchain network but still has access to another. Having each network running a different consensus mechanism but still linked to a single protocol is the ideal nature for Web3. The current nature of many blockchain networks is a severe challenge to interoperability.
Cross-chain interoperability has significantly boosted blockchain efficiency but also resulted in being one of the most significant blockchain weaknesses known.[Photo/CBInsights]
Users need access to the benefits of another blockchain network, making it difficult to experience the possibilities of blockchain networks truly. Cross-chain interoperability can fix this problem by allowing users to use one token across multiple blockchains.
Also, Read MasterCard launches CryptoSecure, a new addition to blockchain security.
Step back for a minute and think about the possibilities of using the Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism from Bitcoin, then advance its progression from Proof-of-Stake from Ethereum. The possibilities would open new domain users and mitigate various Blockchain weaknesses.
Fabrice Cheng, CEO of Quadrate, stated, “Cross-chain interoperability is crucial because it’s one of the key benefits of blockchain technology. Decentralized open-source technology allows the creation of interoperable products across chains, enabling more users, businesses and institutions to stay interconnected.”
Blockchain interoperability is applied directly to its fundamental functionalities, such as Protocols and Smart contracts. Interoperable intelligent contracts make it easier for developers to create cross-chain applications for users to run cross-chain transfers. This also makes it easier for users to access multiple users to use different decentralized applications without changing networks. This makes work efficient and much more accessible by reducing the time it takes to change between blockchain networks.
Challenges in blockchain interoperability
Unfortunately, the central fact is that blockchain technology is independent. Thus, achieving cross-chain interoperability became cumbersome during the first trials. According to Hug Philion, CEO of Flare, the lack of adequate cross-chain interoperability has constrained the size, participation and efficiency of blockchain technology.
The absence and presence of interoperability are critical blockchain weaknesses that developers are currently trying to address. There have been numerous successes in creating cross-chain interoperability, but their design needs to be revised. The main proof of this statement is the number of successful crypto hacks in 2022 alone. Crypto hackers have successfully identified the interoperability challenges and have designed various tools and exploits to take advantage of the “rocky bridge” known as blockchain interoperability.
Also, Read Cryptocurrency mixer Tornado Cash creates fodder for crypto hackers.
One of the first few instances is the Ronin hack which resulted in a loss of over $540 million worth of Ether and USDC. As many of you have probably guessed, it was through exploiting a critical blockchain weakness in the network, the Ronin bridge, a cross-chai interoperable feature. Ronin developers initially designed this blockchain bridge to allow crypto traders to transfer their funds between different blockchain networks. Unfortunately, many noticed this flaw. This resulted in one of the largest successful crypto hacks of all time.

Numerous interoperability challenges make cross-chain difficult to achieve and result in numerous successful crypto hacks.[Photo/Developer-on-Rent]
Another critical challenge of interoperability is the fundamental functioning of the consensus mechanisms. One of the few facts that have empowered blockchain networks with their decentralized nature is the ability of a single protocol to determine the validation method of an entire network.
This removed the importance of a centralized system since once the validation method is confirmed, the user needs to abide by its rule to receive some form of authority over the network. Unfortunately, its native functionality makes it nearly impossible to govern any outside entity since once the transition goes beyond the boundaries of its blockchain network, there is no way of verifying it through its rules.
Finally, cross-chain interoperability should satisfy three significant components:
- Trustless
- Extensibility/Scalability
- Data Agnostics
Trustless
Blockchain interoperability should maintain the same level of security as the base chain. Take a step back and think for a minute. If the developer’s goal is to build decentralized, uncensorable transactions truly, then they have to consider that mighty adversaries could attack their system.
Also, Read Crypto Coins vs Crypto Token: Are they the same?
Unfortunately, given the successful crypto hacks over the years, many should have considered this. It is crucial to remember that generally, consensus mechanisms cannot govern past their boundaries; hence to ensure maximum security, a set of validators are to be incorporated to curb this crucial blockchain weakness.
Extensibility
Blockchain interoperability aims to connect as many blockchain networks as efficiently as possible. This factor has proven doable, although it requires some alteration to the blockchain network. Ethereum currently uses the concept of Wrapped tokens, which allows other cryptocurrencies to run efficiently in its blockchain network as Ether would.
Unfortunately, getting this right has proven to task one of the few successful crypto hacks in 2022, the Wormhole Defi project, which involves hackers exploiting the cross-chain interoperable nature of wrapped tokens allowing them to transact without the developers knowing. Unfortunately, they made haste with 120000 wETH, caused by a vulnerability within their interoperable features.
Data Agnostics
This is the ability of a blockchain network to transfer any data supported by cross-chain interoperable devices. This is the most fundamental aspect of cross-chain interoperability. This feature allows interoperable devices or entities to transverse between different blockchain networks.
Achieving all three feats is still a goal for blockchain interoperability. The concept of wrapped tokens appeared as a solution, but a successful crypto hack, unfortunately, shattered it. There are various solutions to interoperability challenges, and some, such as native verification to achieve trustless verification, are utilized.
Wrapping up
There is the concept of introducing a new foundation layer on which multiple blockchains can reside. It’s essentially an “I have what you don’t” ruling mechanism that allows blockchain interoperability to function.
Also, Read Africa’s crypto ecosystem affected by FTX collapse.
Experts have called it layer 0, and one such blockchain network is; Polkadot. Polkadot uses a concept called heterogeneous sharding, which enables ross-chain interoperability. It allows multiple blockchain networks to be customized to exchange data in parallel for unique use cases. Its foundation layer is the Realy Chain which governs and supports the entire cross-chain ecosystem. The Relay Chain supports blockchain interoperability through its designs called Parachains.
Parachain build slots on the Realy Chain through scheduled auctions. This provides seamless interoperability across multiple chains, each having its allocated slot.
Despite the on-standing interoperability challenges, Polkadot has successfully curbed one of the few blockchain weaknesses known. Unfortunately, blockchain, let alone cross-chain interoperability, is still an unchartered concept, and the more its applied, the better it improves. However, one thing is clear: its numerous and complete global applications might happen sooner than people think.
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- Platoblockchain. Web3 Metaverse Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- Source: https://web3africa.news/2023/01/15/news/blockchain-interoperability-its-successes-and-failures/
- 2022
- a
- ability
- About
- access
- accessible
- According
- Achieve
- achieving
- across
- addition
- address
- Adoption
- advance
- ADvantage
- After
- aims
- All
- allocated
- Allowing
- allows
- alone
- Although
- among
- and
- Another
- appear
- appeared
- applications
- applied
- aspect
- attack
- Auctions
- authority
- back
- base
- because
- being
- benefits
- Better
- between
- Beyond
- Bitcoin
- blockchain
- Blockchain Interoperability
- Blockchain network
- Blockchain networks
- blockchain technology
- blockchains
- Boosted
- Bound
- boundaries
- Box
- BRIDGE
- build
- businesses
- called
- cannot
- cases
- Cash
- Cause
- caused
- central
- centralized
- ceo
- chain
- chains
- challenge
- challenges
- change
- changing
- Cheng
- clear
- Coins
- combination
- combines
- Common
- communicate
- complete
- components
- concept
- concepts
- CONFIRMED
- Connect
- Consensus
- consensus mechanism
- Consider
- considered
- consistent
- contracts
- could
- create
- created
- creates
- Creating
- creation
- critical
- Cross-Chain
- crucial
- crypto
- Crypto ecosystem
- Crypto Hack
- crypto hacks
- crypto traders
- cryptocurrencies
- Current
- Currently
- data
- Data Exchange
- decentralized
- Decentralized Applications
- DeFi
- Design
- designed
- designs
- Determine
- developers
- Devices
- DID
- different
- difficult
- directly
- discovered
- domain
- during
- each
- easier
- ecosystem
- efficiency
- efficient
- efficiently
- empowered
- enable
- enables
- enabling
- ensure
- Entire
- entirely
- entities
- entity
- error
- essentially
- establishes
- Ether
- ethereum
- exchange
- expectations
- experience
- experts
- exploits
- Feature
- Features
- few
- Finally
- First
- Fix
- flaw
- form
- found
- Foundation
- Freedom
- from
- FTX
- fully
- function
- functionalities
- functionality
- functioning
- functions
- fundamental
- funds
- generally
- getting
- given
- Global
- global network
- goal
- Goes
- governs
- guessed
- hack
- hackers
- hacks
- happen
- having
- However
- HTTPS
- Hype
- idea
- ideal
- identified
- immutable
- implement
- importance
- impossible
- improve
- improved
- in
- Incorporated
- independent
- individuals
- initially
- institutions
- Intelligent
- interconnected
- Interoperability
- interoperable
- introducing
- Invention
- IT
- items
- Key
- Knowing
- known
- Lack
- largest
- Last
- launches
- layer
- Ledger
- Lessons
- Level
- linked
- loss
- made
- Main
- maintain
- make
- MAKES
- Making
- many
- max-width
- maximum
- mechanism
- Merge
- method
- might
- million
- mind
- missing
- Mitigate
- mixer
- more
- most
- multiple
- multiple chains
- native
- Nature
- nearly
- necessary
- Need
- needs
- network
- network system
- networks
- New
- number
- numerous
- ONE
- open
- open source
- operation
- operational
- Operations
- Other
- outside
- parachains
- Parallel
- participate
- participation
- past
- People
- Philion
- PHP
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- Plenty
- Polkadot
- PoS
- possibilities
- possible
- potential
- presence
- probably
- Problem
- process
- Products
- progression
- project
- proof
- Proof-of-Work
- protocol
- protocols
- proven
- provides
- Read
- realize
- receive
- reducing
- remember
- Removed
- requires
- result
- Robinhood
- RONIN
- ronin hack
- Rule
- rules
- ruling
- Run
- running
- same
- Scalability
- scheduled
- seamless
- security
- set
- several
- should
- significant
- significantly
- similar
- since
- single
- Size
- slots
- smart
- Smart Contracts
- solution
- Solutions
- some
- Source
- stated
- Statement
- stay
- Step
- Still
- successful
- Successfully
- such
- Supported
- Supports
- system
- Take
- takes
- Task
- Technology
- terms
- The
- their
- thing
- three
- Through
- time
- to
- token
- Tokens
- tools
- tornado
- Tornado Cash
- Traders
- transact
- Transactions
- transfer
- transfers
- transition
- trial
- trials
- trouble
- true
- unique
- USDC
- use
- User
- users
- utilized
- validation
- validators
- various
- various blockchain
- Vast
- Verification
- verifying
- vulnerability
- weakness
- Web3
- webp
- wETH
- What
- which
- within
- without
- Word
- Work
- wormhole
- worth
- would
- Wrapped
- years
- You
- zephyrnet













