Blockchain has
been at the receiving side of the humungous attention since bitcoin started becoming
known and popular. Like many news channels over hype and focuses less on the
details, a similar scenario could be said to be happening in the overall
blockchain ecosystem as well. To give a quick recap, blockchain is a complex
robust framework where transactions being executed are recorded in a
decentralized fashion. The data gets transferred in the form of blocks. Blocks encompass
information like the transaction’s date, time, who’s participating in the
transaction, and a hash in each block which helps in distinguishing all blocks.
Blockchain aims to act as a platform where digital information is recorded,
distributed, but not edited. The platform also aims to enable distinct
cryptocurrencies to be able to share data and amount without much hassle. As
it’s only recently entered the global market, few industries have started
employing it daily (BFSI, Medical, Logistics, Transportation), while some are
waiting to implement it due to various reasons. As it’s still in its initial
stage, a lot of opportunities are cropping up for the architecture to become
more adaptable, robust, and transparent as well. This piece of content will
include the functioning of blockchain, multiple facets of it, various
generations that have come to date, types of blockchains, and comparing
theoretic concepts with practical usage feasibility.
Blockchain’s
Architecture and its internal functioning.
As mentioned
above, blockchain is a platform where the motive is to record every
digital transaction in a decentralized manner and still be able to transfer
money in distinct cryptocurrency wallets. The ability to function in such a way
arises because of its blueprint. The founder of Bitcoin, “Satoshi Nakamoto”, built
a design so robust, adaptable, and transparent that blockchain is being used by
many across the world and is helping which centralized institutions weren’t
able to accomplish. As one can see from the link
that the architecture of bitcoin is very basic. The infrastructure layer is
utilized for storing data, transmitting transactions, and securing the network.
The kernel layer consists of proof of work (PoW) consensus, token rewards, and
token release data as well. From the functional architecture of the Blockchain
figure, one can figure out which layer (Cross, Infrastructure, Kernel, Service,
User) will accomplish what tasks.
Generations
of Blockchain. To date

Since the
whitepaper of Bitcoin was published online in 2008, the blockchain ecosystem has experienced three different variations of its
pros and cons. It started with the introduction of virtual currencies like
bitcoin, Ethereum, etc. Afterward, the focal point shifted towards smart
contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), applications used in financial
services, etc. The most recent up-gradation where the technological framework
is being employed in various industries like health and food to name a few. One
common link which is cropping up in almost every industry is how to integrate
it holistically and make it scalable. As companies irrespective of their size
and nature are examining the advantages of utilizing technology, curiosity is
growing gradually and exponentially. With developed nations leading the path,
it surely will get imbibed in the rest of the world as well. such a change and
transformation will only help the world live more eco-friendly, transparently,
and productively too. Like any product or service being launched into the
market, blockchain also is facing few hurdles. But with an appropriate mindset,
determination, and perseverance, the final version will surely be worthwhile to
use.
Blockchain
and IoT Devices: What’s the connection?
As mentioned
above, the most recent modification in the blockchain is integrating with
distinct industries, integrating it with the internet of things and cloud computing is another building block which has made numerous
blockchain experts start to research and experiment on. As it’s well known that
the overall functioning of blockchain intakes heavy computations, a lot of
electricity, and huge storage capacity as well. To reduce some portion, this piece of research builds a prototype where a lighter version of the
blockchain is employed that can function similar to the prior one. In short, a
Light Ethereum Subprotocol (LES) is a fresh protocol designed and developed
which minimizes the bandwidth requirement and cryptographic proofs of
consistency of data. Just like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is an
up-gradation of DES (Data Encryption Standard), similarly, LES was built
keeping in mind to ease the overall cycle of blockchain functionality at the
backend. As an appropriate mindset is a prerequisite for developing a prototype
like LES, let’s now look at how blockchain could be perceived from a philosophy
perspective.
Blockchain:
Perceived as a Philosophy
One may wonder why
to interlink technology with psychology. But with recent changes in how
algorithms are being used socio-politically, it has become a crucial factor to
ponder upon and act accordingly. Most technological experts in blockchain and recently developed sister-like frameworks also
have agreed on one aspect that is if robots are fed input with appropriate
context, the output delivered is similar to the one, one was expecting. When
the internet was launched, a set of frameworks and protocols were designed to
make it operate smoothly. Similarly, this is an act for making the current and
upcoming technologies function in a manner where the whole human society and
the rest of the living beings live harmoniously. Broadly speaking, blockchain
developers need to consider the following points:
- What’s
the purpose, function, and dimensions of the architecture? - What
kind of ethics and aesthetics would be implemented? - What
kind of fresh knowledge would be created and imbibed?
One common factor
which could be seen common in the above considerations is the trust or the
reliability factor. Philosophy point-of-view helps in re-building the trust
which people at large have been declining since the financial breakdown in
2008-09.
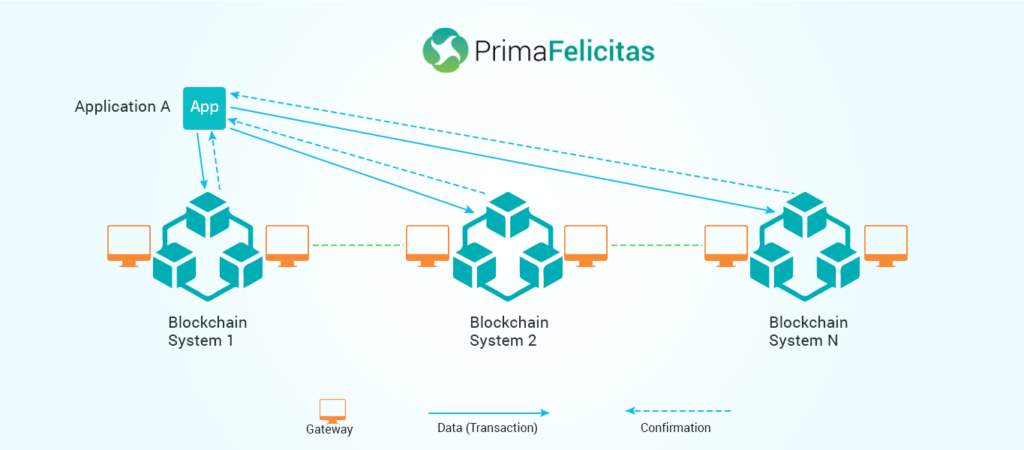
Two words ‘trust’
and ‘interoperability’ could be seen overlapping up to a great extent. It might
seem obvious, that only when one trusts another person, he/she interacts (for
personal or professional) in the future. If trust isn’t there between the two
parties (receiving side and sending side), the option of recommending it to
others or utilizing it again doesn’t come in the picture. This piece of research also indicates a couple of ways of achieving the
desired outcome by looking at the blockchain from a philosophical perspective.
Designing and building a product or a service is one part, but it wouldn’t be
of any use if it can’t be practically employed on a day to day basis. The
following part focuses on seeing and scrutinizing the theories built and their
practicality in cryptocurrency governance.
Theory VS
Reality in Cryptocurrency Governance
Coming up with
fresh ideas on how to live daily looks fascinating at the face-value, but it
could lead to a polar opposite situation when explored in depth. A similar
situation happened in financial institutions in the 19th and 20th
centuries. The result of which was financial breakdowns in many nations across
the world. Blockchain at a broader level and cryptocurrencies at the
micro-level got developed to fix the situation. A similar scenario could also
be seen in the marketing field, and almost every industry and profile. This piece of research indicates some suggestions as to how to differ
between them and then act accordingly. A figure in it shows exactly who all are
a part of the ecosystem, and what role do they play to function the overall
process effectively. The acting players consist of digital platforms, codebase,
programmers, miners, intermediaries, customers, media, and governments. As the
software behind the framework is common (open-source), everyone gets the
opportunity to propose alterations in the software where trust is established
via decentralized public ledgers. It has already been experienced that external
forces or the acting players have been able to modify the architecture as and
when required effectively. One thing seems certain that it will take some time
for the entire population to get a hang of the technology and make it the norm
of the day. Regulation is seen as the devil, as it is crucial and complex as
well while implementing on the ground. One factor which is still an issue is
alternate platforms like the Tor browser where several cases of money
laundering and illicit activities have been found to date. The following piece
will focus on the difference between the functionality of both frameworks.
Blockchain VS
Tor Network. A comparative analysis
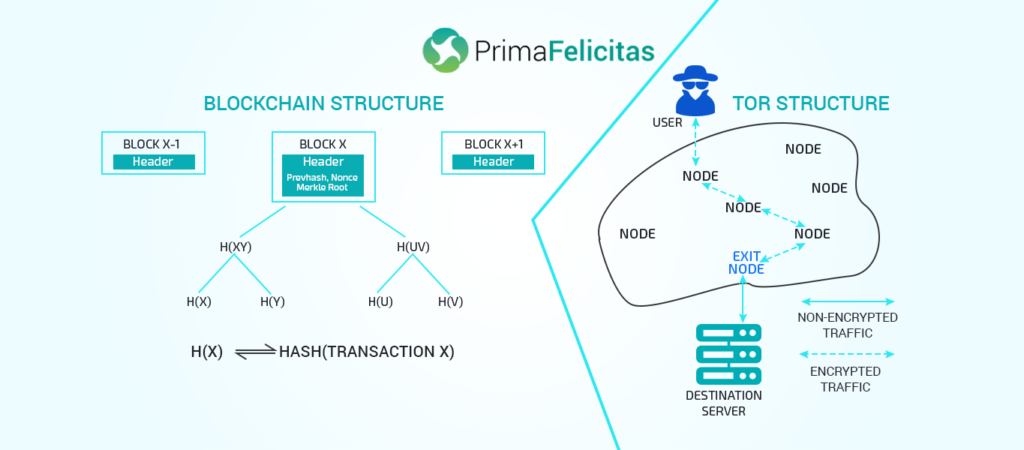
Since blockchain
came into existence, several distributed ledger technologies have been
developed for various purposes. Staring with the basic architecture, several
modified versions like Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), distributed hash table
(DHT), time to live (TTL), decentralized applications (dApps), etc have entered
the blockchain ecosystem. Based on their respective advantages and
disadvantages, newer versions were thought of and build. After constant observation, and examination from diverse point-of-views, fresh consensus models
and prototypes came into existence.
Coming to the
distinctions between Tor’s and the Blockchain’s functionalities, there’re a lot
of similarities between them (quite surprisingly). Tor is a third-generation
onion routing system which employs a TCP based services. Besides that, it runs
multiple encryption and decryption circuits with distinct session keys. Doing
so allows the user’s IP to get masked and is unable to get traced. The only
difference besides the decentralized structure, Tor doesn’t work on
incentivization, and it operates with limited resiliency. The data storage is
also not available in the tor schema. After examining the differences, the
blockchain’s framework could be upgraded in such a manner that it overtakes the
tor’s functionality completely.
Looking for help in creating a blockchain solution
To know more about
regular updates on the blockchain environment, do visit PrimaFelicitas, and subscribe to our social media platforms. To get
an idea about the applications we develop and consultations we offer, click here.
- 2019
- activities
- algorithms
- All
- applications
- architecture
- Bitcoin
- blockchain
- browser
- build
- Building
- Capacity
- cases
- change
- Common
- Companies
- Consensus
- contracts
- Couple
- Creating
- cryptocurrencies
- cryptocurrency
- Current
- Customers
- DApps
- data
- data storage
- day
- decentralized
- Decentralized Applications
- Design
- develop
- developers
- Devices
- digital
- Distributed Ledger
- electricity
- encryption
- Environment
- ethereum
- ethics
- experiment
- experts
- facing
- Fashion
- Fed
- Figure
- financial
- Financial institutions
- Fix
- Focus
- food
- form
- founder
- Framework
- fresh
- function
- future
- Global
- governance
- Governments
- great
- Growing
- hash
- Health
- How
- How To
- HTTPS
- huge
- Hurdles
- idea
- industries
- industry
- information
- Infrastructure
- institutions
- Internet
- internet of things
- iot
- iot devices
- IP
- IT
- keeping
- keys
- knowledge
- large
- lead
- leading
- Ledger
- Level
- light
- Limited
- LINK
- logistics
- Making
- Market
- Marketing
- Media
- medical
- Miners
- MIT
- money
- network
- news
- offer
- online
- Opportunity
- Option
- People
- perspective
- philosophy
- picture
- platform
- Platforms
- Popular
- population
- PoW
- Product
- Profile
- proof
- propose
- Psychology
- public
- Reality
- reasons
- recap
- reduce
- Regulation
- research
- REST
- Rewards
- Services
- set
- Share
- Short
- Size
- smart
- So
- Social
- social media
- social media platforms
- Society
- Software
- Stage
- start
- started
- storage
- system
- Technologies
- Technology
- time
- token
- Tor
- transaction
- Transactions
- Transformation
- transportation
- Trust
- Updates
- Virtual
- virtual machine
- Wallets
- What is
- Whitepaper
- WHO
- words
- Work
- world










