One of the over-arching themes we find throughout the decentralized finance community is the desire to give access to financial tools and resources to those that have been underserved by traditional banking and finance institutions.
The need for this has come about due to the highly concentrated nature of the global financial markets, where a large percentage of the world’s wealth is held by a relatively small number of individuals and corporations.
It’s also notable that much of the world’s wealth is confined to certain geographical regions. Because of this concentration of wealth, many of the world’s citizens have not had access to the basic financial services and tools that many take for granted.
In recent years it’s been suggested that creating tokenized assets on permissionless blockchains is the way forward if we wish to give all global citizens access to financial services and markets. In addition, these decentralized finance systems are expected to improve the efficiency of current financial markets, while also providing a number of other benefits.
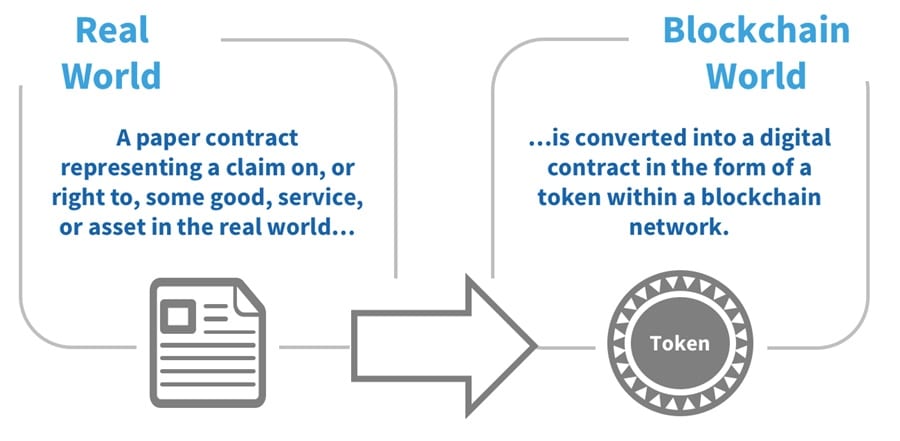
The difference between real world and digital contracts. Image via HBS Digital Initiative.
Unfortunately asset tokenization has some real issues in terms of regulatory pressures and the technology necessary to make them work properly. Because of this early projects ran into regulatory issues and problems with incompatible technologies. Some early projects have focused primarily on digitizing physical assets such as real estate and gold, and these have seen a modicum of success.
Moving into the current blockchain industry we can see a trend towards tokenizing more abstract assets such as stocks and bonds. The ongoing DeFi revolution has created a tsunami of new products, primarily in two categories: Asset-Backed Tokens and Synthetic Assets.
Anyone familiar with DeFi will be familiar with the most popular asset-backed tokens, which are backed by the physical or other asset they represent. For example, many DeFi protocols are now using an abstracted form of Bitcoin known as Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC). This is not actual Bitcoin, but is a one-to-one representation of the Bitcoin that’s held by BitGo. It’s a simple and intuitive design that is easy to understand and works so well for its purposes.
However these asset-backed tokens are not ideal. They still suffer from centralized custody risks, regulatory hurdles for the issuers, and sometimes excessive fees. However there is another way. That’s synthetic assets, and one of the projects leading the way in this area is the Mirror Protocol.

Synthetic assets created on the blockchain. Image via Mirror.finance
The Mirror Protocol promises the ability to trade equities (U.S. equities currently) 24/7 anywhere in the world by any person. The project does this by minting synthetic assets, or what they’ve named Mirror Assets (mAssets). It was created by and runs on the Terra Network, and is powered by smart contracts. The way they are designed, any mAsset created is meant to mirror the price behavior of the underlying represented real-world asset.
In this way anyone in the world could, for example, trade in synthetic mirrored shares of Tesla 24/7 from anywhere in the world, and the price would be exactly the same as the price of the actual Tesla stock. All the trading is secured by the blockchain in a permissionless system. This is an extremely powerful creation, especially considering the events seen at the Robinhood exchange in early 2021.
Mirror Protocol Overview
The mAssets created by the Mirror protocol are synthetic versions of their real-life counterparts. They mimic the price of the underlying assets, and can be traded on secondary markets just like the underlying assets.
These include the Terraswap AMM from Terra and Ethereum’s Uniswap. In its current state the mAssets created mirror major U.S. equities and ETFs, but there are more assets planned for the future. You can see the platform and a full listing of the currently available assets here.
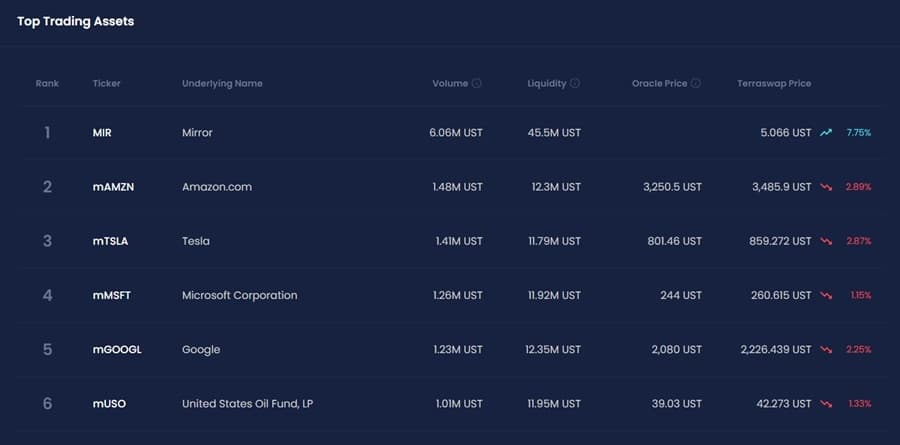
A simple trading interface. Image via Mirror Web App
The whole system is governed using the MIR token, and it is also used to incentivize staking to secure the system. There are five primary users in the Mirror ecosystem:
- Traders
- Minters
- Liquidity Providers
- Stakers
- Oracle Feeders
Traders
This is the largest group of Mirror users. They are the ones buying and selling mAssets using the Terra UST stablecoin as a peg. This is done at Terra’s Terraswap AMM or at the Uniswap AMM run on Ethereum. The entire system has significant implications for opening up access to foreign trading markets and to other asset classes normally not accessible by the vast majority of humanity.
For example, a trader in Hong Kong can now trade a derivative that gives them exposure to any U.S. stock without paying excessive capital gains taxes, without using expensive international stock brokers, and without going through an onerous KYC process. Mirror Finanace is allowing people to sidestep the stringent capital controls that have evolved over the years as a means to control the world’s wealth.
Minters
This is the group responsible for the creation and issuance of the mAssets. These mAssets are created by locking up collateral at an overcollateralization ratio that’s set by the governance parameters of Mirror. It works in a similar manner to the issuance of DAI by Maker.
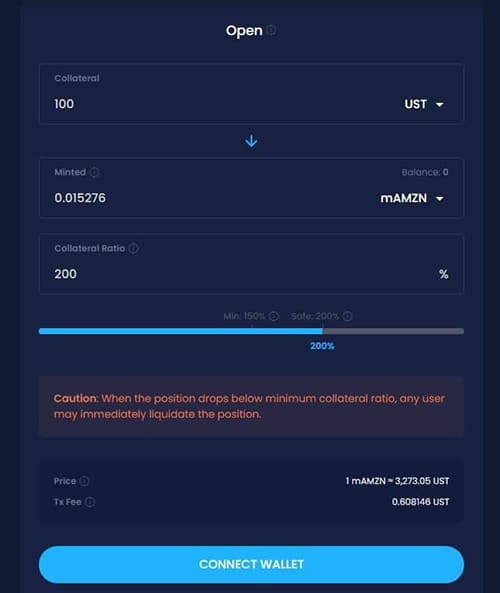
Minting on Mirror is as easy as trading. Image via Mirror Web App.
Minters lock up their collateral in a collateralized debt position (CDP) which can be backed by UST or by another mAsset. Minters need to monitor their positions and add more collateral if the ratio drops below a set minimum, otherwise they could face the liquidation of their position. Minters are also able to withdraw their position at any time, and it results in the burning of the mAsset and the return of the CDP collateral.
Liquidity Providers
This group supplies the liquidity needed by AMM pools. In a similar fashion to Uniswap, the liquidity providers put in an equivalent value of UST and the mAsset at the AMM and as a reward they receive LP tokens that are funded by the trading fees of the pool.
Stakers
There are two types of stakers found on Mirror. The first are the liquidity providers who are able to stake the LP tokens they receive and receive staking rewards in the form of native MIR tokens based on the emission schedule. The second type of staking is done by MIR token holders who stake that MIR and earn the withdrawal fees from the CDP.
Oracle Feeder
The Oracle Feeder is crucial to the Mirror ecosystem since it is the mechanism used to ensure that the mAssets retain a match with their underlying assets. The Oracle Feeder is an elected position and as of February 2021 the position is operated by the Band Protocol. The Oracle price and the exchange price create an incentive structure to trading by creating arbitrage opportunities. This also maintains the mAsset price in a tight range near the actual price of the underlying.
For example, when the price of an asset is higher on the exchange than it is from the Oracle price market participants have an incentive to mint and sell that asset on Terraswap to generate a profit. As a result they also tighten the price difference between the exchange and oracle. The same is true when the exchange price is below the oracle price. In this case there is an incentive to purchase and burn the mAsset, which brings the two prices back closer together.
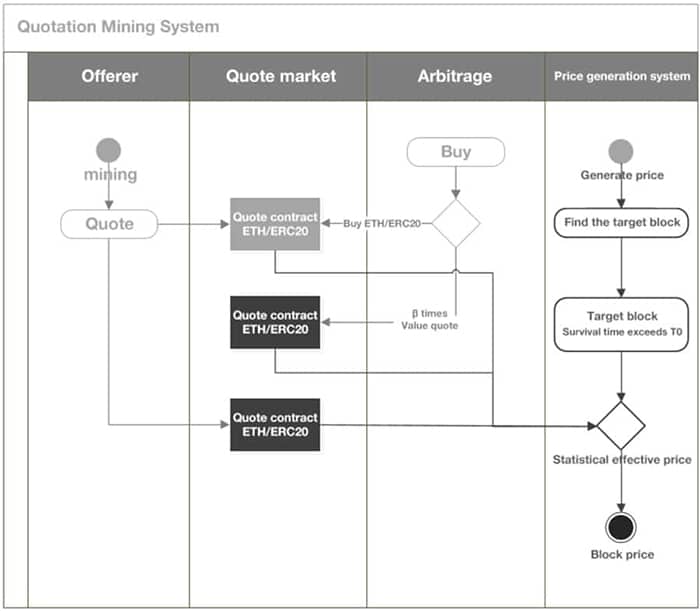
An arbitrage involving an oracle. Image via Medium
Mirror participants have their incentives balanced in such a way that value creation is promoted, and adoption is encouraged. The MIR token acts as an inventive when staked, and is also used as a governance token for potentially changing the parameters used by Mirror, such as the minimum collateral ratios. It can also be staked in polls for whitelisting mAssets.
Who are Terraform Labs
Because Mirror Finance was created by Terraform Labs and runs on the Terra Network it is important to know the background and who Terraform Labs is.
Terraform Labs is a company based in South Korea that was founded in January 2018 by Do Kwon and Daniel Shin. With $32 million backing from large venture capital firms such as Polychain Capital, Pantera Capital, and Coinbase Ventures they soon released the stablecoin LUNA.

Terraform Labs created Terra Money, which was the basis for Mirror. Image via Steemit
They also created the Terra Network, which was designed to be a decentralized global payment system. It features minimal transaction fees and is able to settle a transaction in just 6 seconds. While it hasn’t gained traction yet in Europe and the Americas it does have over 2 million monthly unique users generating over $2 billion in monthly transaction volumes.
The bulk of these are through the South Korean payment platform CHAI and the Mongolia-based MemePay. The LUNA token is somewhat unique among stablecoins as it distributes yield back to its holders. That yield comes from the transaction fees, which are returned 100% to LUNA holders. You can learn more in the Terra Money whitepaper.
What are mAssets?
The Mirror Protocol is fully decentralized and community driven. Terraform Labs and its founders and employees have no special administrative functions on the platform, and there was no premine of the MIR tokens.
The first bridge created by the Mirror Protocol was to the Ethereum Network, which enabled trading on Uniswap. More recently the Mirror Protocol was bridged to the Binance Smart Chain (BSC), allowing the BSC community access to the tokenized synthetic assets created on Mirror.

Earn MIR for staking at mETH. Image via ETH.Mirror.Finance
Currently the assets that have been tokenized are U.S. equities, however the Mirror Protocol allows for any physical of abstract asset to be created as an mAsset. That means future use cases could see artwork, real estate, precious metals, commodities, fiat and crypto currencies, and other asset types added as mAssets. There is already interest in minting bonds, futures, and other derivatives as mAssets.
There were 14 assets that were added to the Mirror Protocol when it initially launched. These are MIR (Mirror), AMZN (Amazon), TSLA (Tesla), MSFT (Microsoft), GOOGL (Alphabet), BABA (Alibaba), AAPL (Apple), NFLX (Netflix), TWTR (Twitter), IAU (iShares Gold Trust), SLV (iShares Silver Trust), QQQ (Invesco QQQ Trust), VIXY (ProShares VIX), and USO (United States Oil Fund LP). In January 2021 a governance vote approved the addition of BTC, ETH, ABNB (Airbnb), GS (Goldman Sachs Group), and FB (Facebook) to the original 14.
In theory almost anything with value could be tokenized on Mirror and it brings all the following benefits:
- 24/7 permission-less trading anywhere in the world
- No need for intermediaries; all transactions will be on the permission less blockchain ledger.
- The tokenization allows users to trade fractions of an asset.
- For some assets, the tokenization will allow for better liquidity.
- The use of smart contracts on the blockchain will significantly cut legal and operational costs.
- Through the tokenization, assets will be more accessible; the fractional ownership will allow less liquid users to participate.

Tokenize anything with Mirror. Image via Medium.
The synthetic assets minted on the Mirror Protocol are all called mAssets since they use the prefix of “m” in the ticker for the synthetic asset. So Tesla (TSLA) becomes mTSLA and Apple (AAPL) becomes mAAPL. All of the mAssets share the following basic mechanics:
- To create an mAsset users must lock up 150% of UST’s current asset value or 200% if using other mAssets as collateral.
- If positions go under the minimum collateral ratio more collateral must be added, otherwise they will be liquidated; this measure regulates and secures the minting process.
- When redeeming any mAsset, users must burn an equal amount of mAssets issued when opening the CDP to get back the provided collateral.
- Assets are listed and can be traded on various AMM DEXs like PancakeSwap (BSC), TerraSwap (Terra), and Uniswap (Ethereum). Some of the trading fees flow back as an incentive for liquidity providers.
- A price Oracle that updates every 30 seconds ensures that the mAsset is pegged to the real asset. When oracle and exchange prices differ it incentivizes traders to arbitrage and bring the prices back to equilibrium.
mAssets can be traded in speculation, they can be held, or they can be used for other purposes such as adding collateral in creating new mAssets, creating synthetic stable pools, creating liquidity pools for decentralized exchanges, and many other uses.
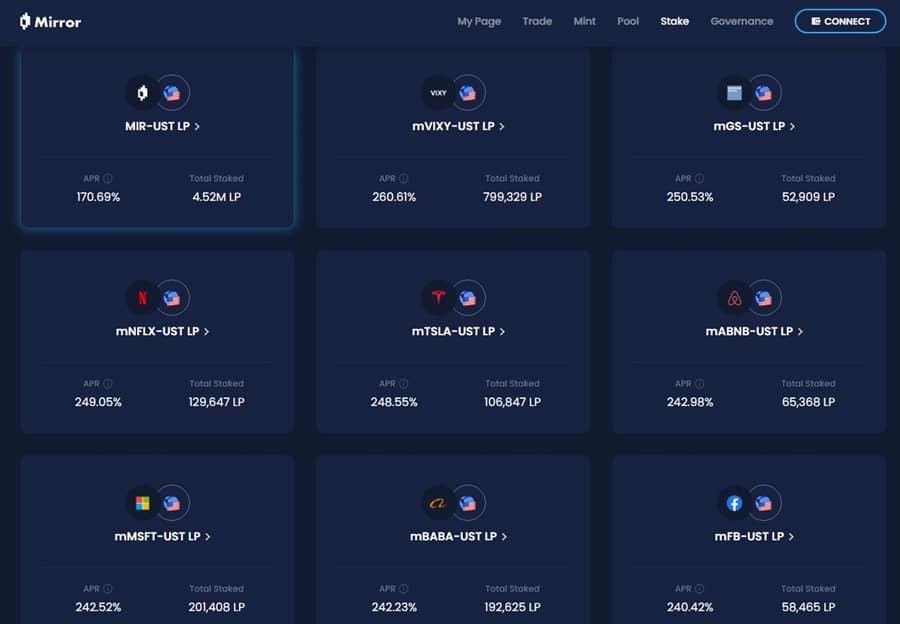
Stake coins at Mirror for some juicy yields. Image via Terra.Mirror.Finance
The smart contracts used to create the synthetic assets and hold the collateral for such have been fully audited by the cyber-security firm Cyber Unit and have been found to be secure.
Binance Smart Chain and Mirror
As mentioned above, the Binance Smart Chain is the latest network to add Mirror. On January 22, 2021 the Mirror Protocol was added to BSC, beginning with a partnership with PancakeSwap.
This is a winning move for both sides as Mirror benefits from the added user base and adoption, while Pancake Swap becomes an innovator as it adds four of the tokenized mAssets to the AMM, allowing its users to provide liquidity and to earn yield in the process.

Stake CAKE and earn UST at Pancake. Image via Medium.
Binance Smart Chain began with just a few of the Mirror contracts tradeable on the PancakeSwap platform. These four were mAMZN, mGOOGL, mNFLX, and mTSLA. More are planned for the future.
The MIR Token
The MIR token is the native token of the Mirror Protocol and it is used for governance, for staking, and to reward liquidity providers. The rewards paid out come from the fees that are paid for closing positions on mAssets, for creating polls, and trading fees.
Mir was created with a fixed supply of 370,575,000 tokens, all of which will be released over a period of four years.
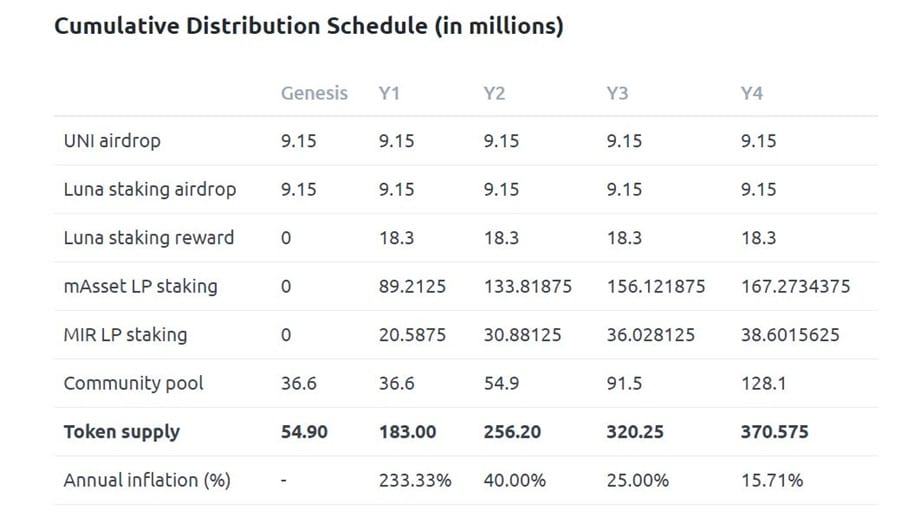
Just four years to release all the MIR tokens. Image via Mirror blog
As of February 2021 there are 33,425,682 MIR in circulation. The market capitalization of the token is nearly $165 million and the token is #241 in terms of market capitalization on Coinmarketcap.com. The token should not be confused with the Mir Coin, which uses the same ticker, but is a transactional coin with its own blockchain and ecosystem.
Those who wish to earn MIR tokens can do so in three different ways:
- By staking $LUNA, this requires the use of the Station Wallet desktop app.
- By providing liquidity to MIR/UST pair.
- By providing liquidity to any mAsset/UST pool pairs (non-BNB)
There was no pre-mine or ICO involved with the MIR token and the initial 18.3 million MIR tokens were airdropped to holders of LUNA and UNI. On November 23, 2020 each user with LUNA staked received MIR on a pro-rata basis and each UNI holder with at least 100 UNI received 220 MIR.
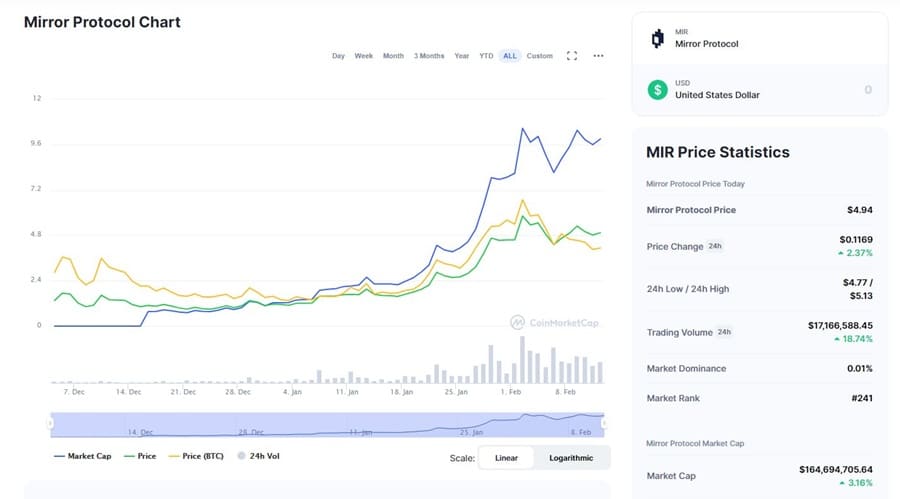
MIR is up significantly in just two months time. Image via Coinmarketcap.com
As you can see from the chart above the price of MIR closed on its first day of trading on December 4, 2020 at $1.41 and declined initially, probably as some of those early airdrop recipients cashed in, but by late December 2020 the coin had hit a bottom and began recovering.
Since then it has surged higher alongside the broader crypto markets and as of mid-February 2021 it is trading around $5.00. That’s a pretty good return for an airdropped token, and those who’ve held on are likely quite pleased.
Mirror Protocol Future
The Mirror Protocol went live on December 3, 2021 and has seen excellent adoption in the short time it’s been in existence. In addition to the web app that allows for trading, minting, staking, and governance, there’s also a mobile app for trading. Additionally, Mirror has created bridges to Ethereum and to Binance Smart Chain that allows for seamless porting of mAssets between the chains. The Ethereum bridge was the first ever cross-chain bridge for synthetic assets.
Mirror has been very active in creating partnerships during its first two months of existence, and we would expect that they will continue spreading the availability of mAssets to as many platforms as possible, increasing liquidity and the user base as they go.
As Mirror heads into its third month of existence its TVL has more than tripled, currently at $330 million within two months of launch. On average, 30,000 transactions are conducted and $36 million in assets are traded on a 24 hour basis. Liquidity (the total value of all mAssets and UST in liquidity pools) stands at $160 million.
Those only interested in the trading feature of Mirror have several options. Besides the web app there’s also a mobile app released by ATQ Capital and available for Android devices (there’s a link for an iOS version on the Mirror website, but it is a dead link and we couldn’t locate an iOS version of the app).
There’s also a partnership with Mask Network that allows users to purchase mAssets right on Twitter.

Trade mAssets right from Twitter. Image via Mirror blog
It’s also been good to see the governance feature working quite well in the early days of the project. The first vote saw five new assets added to Mirror, and over 60 on-chain proposals for the community to consider. It’s an excellent start, and eventually the goal is to create a list that spans hundreds, if not thousands of assets and combine it with a sleek user interface that rivals even the best of the online brokers.
One of the highly anticipated additions to Mirror is the Anchor Protocol product, a savings protocol on the Terra blockchain that offers yield powered by block rewards of major Proof-of-Stake blockchains. Anchor offers a principal-protected stablecoin savings product that pays depositors a stable interest rate.
It achieves this by stabilizing the deposit interest rate with block rewards accruing to assets that are used to borrow stablecoins. Anchor will thus offer DeFi’s benchmark interest rate, determined by the yield of the PoS blockchains with highest demand. Ultimately, the Terra team envisions Anchor to become the gold standard for passive income on the blockchain.
While the workings under the hood are no doubt complex, there’s no denying it’s well worth creating. The synthetic assets being offered by Mirror are extremely powerful. Future use cases could dramatically level the playing field when it comes to wealth creation across the globe, especially when a user-friendly interface like Mirror is part of the process. Perhaps Mirror is the beginning of a new generation of traders who will know nothing more than mAssets and their like.
Mirror Protocol Governance
Governance in the Mirror Protocol is controlled by the MIR token. Anyone who is staking MIR tokens can participate in the governance of the system. The voting power of the user is determined by the amount of MIR that is being staked, and the more MIR staked, the greater the voting power.
It’s possible for anyone to create a new governance proposal, known as a poll, and in the first month of its operation Mirror saw 50 forum proposals and 60 on-chain proposals put forward. Note that in order to make a proposal it is necessary to stake a deposit of MIR tokens and if the proposal is not adopted that deposit is forfeit.
In the event a proposal meets all the necessary threshold and quorum parameters and is then voted “yes” by the community, the Mirror Governance Contract automatically executes the parameters specified in the proposal. This governance contract is able to invoke any of the functions that are defined for use in the Mirror smart contracts. So, there is no need to update the core protocol to implement proposals.
There is no outside influence in any of this, and no third-party, not even the Terra Labs founders, has any special administrative privileges over the protocol. It is fully permissionless and decentralized, working solely on a community governed principle.
Conclusion
Having the ability to tokenize any asset and trade it freely from anywhere in the world at any time of the day or night is an amazing lead forward for finance. It allows people to enter markets they otherwise would never have access to, and it levels the playing field in terms of financial freedom. As the usage of mAssets grows we will become freed from the constraints that have been placed on trading, investing, and saving. This is the power of decentralized finance.
The Mirror platform is also quite generous in terms of incentives paid out to those who stake or provide liquidity for the platform. As the reach of the mAssets grows these incentives can only increase in value.
The dedication of the Terraform Labs team to the project, and their selflessness in releasing it without a pre-mine, and without some hold on the project is admirable. And with the strong community that’s building around the project it is fairly certain it is facing an exciting future.
Young traders have little trust or faith in Wall Street and the institutions that form our modern financial systems. Mirror Finance gives them an excellent alternative, and as the platform grows, so too will the number, breadth and range of assets available as mAssets.
Overall the Mirror Protocol is an innovative and needed service that’s come along at exactly the right time. You can stay up to date on Mirror Protocol’s progress by following them on Twitter and in their Telegram group.
Featured Image via Shutterstock
Disclaimer: These are the writer’s opinions and should not be considered investment advice. Readers should do their own research.
Source: https://www.coinbureau.com/review/mirror-protocol-mir/
- &
- 000
- 100
- 2020
- access
- active
- Adoption
- advice
- airdrop
- All
- All Transactions
- Allowing
- Alphabet
- Amazon
- Americas
- among
- android
- app
- Apple
- arbitrage
- AREA
- around
- asset
- Assets
- availability
- Banking
- Benchmark
- BEST
- Billion
- binance
- Bitcoin
- BitGo
- blockchain
- Bonds
- BRIDGE
- BTC
- Building
- Buying
- capital
- cases
- closed
- closer
- Coin
- coinbase
- Coinbase Ventures
- CoinMarketCap
- Coins
- Commodities
- community
- company
- concentration
- continue
- contract
- contracts
- Corporations
- Costs
- Creating
- crypto
- Crypto Markets
- currencies
- Current
- Current state
- Custody
- cyber
- DAI
- dapp
- data
- day
- dead
- Debt
- decentralized
- Decentralized Finance
- DeFi
- Demand
- Derivatives
- Design
- Devices
- digital
- driven
- Early
- ecosystem
- efficiency
- emission
- employees
- estate
- ETFs
- ETH
- ethereum
- ethereum network
- Europe
- Event
- events
- exchange
- Exchanges
- Face
- facing
- farm
- Fashion
- Feature
- Features
- Fees
- Fiat
- finance
- financial
- financial services
- Firm
- First
- flow
- form
- Forward
- founders
- Freedom
- full
- fund
- funded
- future
- Futures
- Global
- Gold
- goldman
- Goldman Sachs
- good
- governance
- Group
- hold
- Hong Kong
- HTTPS
- Hundreds
- Hurdles
- ICO
- image
- Income
- Increase
- industry
- influence
- institutions
- interest
- International
- investing
- investment
- involved
- iOS
- issues
- IT
- korea
- Korean
- KYC
- Labs
- large
- latest
- launch
- lead
- leading
- LEARN
- Ledger
- Legal
- Level
- LINK
- Liquid
- Liquidation
- Liquidity
- liquidity providers
- List
- listing
- LP
- major
- Majority
- maker
- Market
- Market Capitalization
- Markets
- mask
- Match
- measure
- medium
- Microsoft
- million
- mirror
- Mobile
- Mobile app
- money
- months
- Most Popular
- move
- Near
- Netflix
- network
- new products
- offer
- Offers
- Oil
- online
- Opinions
- Options
- oracle
- order
- Other
- pantera capital
- Partnership
- partnerships
- payment
- payment system
- People
- platform
- Platforms
- poll
- pool
- Pools
- Popular
- PoS
- power
- Precious Metals
- price
- Product
- Products
- Profit
- project
- projects
- Proof-of-Stake
- proposal
- purchase
- range
- readers
- real estate
- research
- Resources
- Results
- review
- Rewards
- Robinhood
- Run
- saving
- seamless
- secondary
- sell
- Services
- set
- Share
- Shares
- Short
- Silver
- Simple
- small
- smart
- Smart Contracts
- So
- South
- South Korea
- stablecoin
- Stablecoins
- stake
- Staking
- start
- State
- States
- stay
- stock
- Stocks
- street
- success
- supply
- system
- Systems
- Taxes
- Technologies
- Technology
- Terra
- Tesla
- time
- token
- Tokenization
- Tokens
- trade
- trader
- Traders
- Trading
- traditional banking
- transaction
- Transactions
- Trust
- u.s.
- Uniswap
- United
- United States
- Update
- Updates
- users
- value
- venture
- venture capital
- venture capital Firms
- Ventures
- Vote
- Voting
- Wall Street
- Wallet
- wBTC
- Wealth
- web
- Website
- WHO
- within
- Work
- works
- world
- worth
- years
- Yield













