Defi Infrastructure 101 — Overview & Market Landscape
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is redefining the future of finance. There is a major shift going on in the underlying infrastructure powering financial applications, and it’s changing the way we think about permission and control, transparency, and risks.
DeFi é um setor de mercado em desenvolvimento dentro da intersecção de tecnologias blockchain, ativos digitais e serviços financeiros. De acordo com DeFi Pulse, the value of digital assets locked into Defi applications grew 10X from less than $1 billion in 2019 to over $10 billion in 2020, and over $80 billion at its peak thus far in 2021. Yet the DeFi applications and underlying infrastructure are still in its nascent stage of development.
The goal of this report is to provide an introduction of the new emerging area of DeFi infrastructure powering DeFi apps today. While it’s easy to get caught up in the hype and speculation within the space, I’ll focus on the key components of Defi applications, their key differentiation compared to traditional finance, potential risks, and longer-term implications these Defi apps are causing.
Major Structural Commonalities Across DeFi Apps
DeFi apps are financial applications with no central counterparties. In practice, this means there is no institution (e.g. banks) you are interfacing with to access these financial applications; instead users interface directly with the programs (e.g. smart contracts) on top of the protocol itself. For more of a DeFi 101 primer, I highly recommend este relatório.
As principais categorias de aplicativos DeFi incluem bolsas descentralizadas, plataformas de empréstimo, stablecoins, ativos sintéticos, seguros, entre outros. Embora de escopo diversificado, todos esses aplicativos DeFi compartilham um grande conjunto de pontos em comum, incluindo:
- Usando blockchains subjacentes como razão principal
- Código aberto e transparente por padrão
- Interoperável e programável (combinabilidade)
- Aberto e acessível a todos (sem permissão)
Usando Blockchains Subjacentes como o Razão Central
Compared to traditional financial applications which use core banking systems (Fiserv, Jack Henry, FIS, etc.) as the underlying ledgers of record, Defi apps use blockchains as their underlying core ledger.
A few of the most prominent blockchains used to build Defi apps include Ethereum, Solana, and Binance Chain, etc. These underlying blockchains store the ledger state of what is deposited into the DeFi apps, what is stored within the smart contracts, all of the transactions, and withdrawals.
All of the core accounting functions to ensure matching inputs and outputs are handled by the blockchain itself, the Defi apps don’t need to create external systems to reconcile balances, because all of the transactions are queryable across the various block explorers.
Além disso, em comparação com o sistema tradicional, não existe um processo separado de liquidação e compensação de transações. O processamento, compensação e liquidação da transação acontecem ao mesmo tempo quando a transação é transmitida. Embora seja aconselhável esperar cerca de 21 blocos ou mais para garantir a finalidade do próprio blockchain.
Código aberto e transparente por padrão
Compared to traditional financial applications which are all closed-source and built on top of proprietary systems, Defi applications are typically entirely open-sourced and built on top of open underlying blockchains.

Isso causa três propriedades interessantes:
- Composabilidade — O próprio aplicativo DeFi pode ser bifurcado, remixado e reutilizado em muitos outros aplicativos (mais sobre isso abaixo).
- Transparência — Como o aplicativo DeFi é de código aberto, é totalmente auditável saber exatamente o que o contrato inteligente está fazendo em termos de funções, permissões e dados do usuário.
- Auditabilidade — Como o próprio blockchain subjacente é de código aberto, todo o fluxo de fundos é completamente auditável, incluindo garantias no sistema, volume de negociação, inadimplência, etc.
Ao contrário do sistema financeiro tradicional (que é opaco), funciona num sistema de reservas fracionárias e está sujeito a choques de mercado – o sistema DeFi é completamente transparente e com garantias excessivas – o que permite às empresas DeFi resistir às crises com muito mais eficiência.
Interoperável e programável
Para que os desenvolvedores ganhem a confiança dos usuários, a maioria dos aplicativos DeFi são totalmente de código aberto – incluindo o front-end e os próprios contratos inteligentes. Além disso, como todos os aplicativos DeFi são executados em uma plataforma comum (o blockchain subjacente), esses aplicativos DeFi são completamente interoperáveis entre si e podem ser programados para funcionar com qualquer outro aplicativo DeFi no ecossistema.
Isso é comumente chamado de “dinheiro legosoucomposibilidade”aspectos do DeFi. Todos esses aplicativos DeFi são como peças individuais de Lego que podem ser remixadas para funcionar com outras peças de Lego para construir algo novo.
Compare isso com o sistema financeiro tradicional onde;
- Fragmentação de Infraestrutura — Os aplicativos financeiros tradicionais não são construídos sobre infraestruturas comuns.
- Aplicativos isolados — Os aplicativos financeiros tradicionais são normalmente propriedade de uma instituição bancária. Por exemplo, todas as “aplicações fintech” do Wells Fargo funcionam em conjunto, mas não em diferentes instituições bancárias.
- Desenvolvedor hostil — Os aplicativos financeiros tradicionais não são feitos para que outros desenvolvedores criem serviços.
O sistema financeiro tradicional possui padrões comuns; no entanto, é extremamente difícil chegar a um consenso entre os participantes do mercado porque as instituições financeiras vêem o seu software como o seu fosso competitivo em vez de utilizarem os produtos como um factor de diferenciação.
Uma das maiores razões pelas quais temos visto tanta inovação no espaço DeFi é porque os sistemas são interoperáveis, o que permite que o ecossistema de desenvolvedores tenha uma expressão mais criativa nos produtos e serviços que criam. Além disso, os desenvolvedores não precisam perder tempo reinventando a roda, mas podem desenvolver estruturas comuns e focar nas coisas que tornam seus produtos especiais.
Aberto e acessível a todos
Com aplicativos financeiros tradicionais, os novos usuários normalmente precisam passar por um longo processo de integração, verificações de renda, verificações de crédito ou até mesmo reuniões presenciais – apenas para poder usar um determinado produto financeiro.
Devido a estas regras arbitrárias estabelecidas pelas instituições financeiras, estes processos de integração são propenso a preconceito incluam descrição de empréstimo, negação de serviços bancários básicos, abertura de linhas de crédito sem consentimento, cobrando taxas ilegais, etc.
Com os aplicativos DeFi, tudo que você precisa é de um endereço de carteira para interagir com esses sistemas. Os aplicativos DeFi não solicitam verificação de renda, não precisam de verificações de crédito e, na maioria dos casos, nem precisam saber quem você é fora do endereço da carteira que está usando.
Isso é comumente referido como aplicativos DeFi sendo sem permissão. Se você tiver os fundos em sua carteira para a transação que deseja fazer, poderá fazê-lo. Não há instituições ou intermediários para impedir ou negar serviço a você. Não importa qual seja sua origem ou de que país você vem, os aplicativos DeFi não discriminam.
Este é um dos aspectos mais subestimados dos produtos DeFi.
Traditional Fintech Architectures vs. DeFi Architecture
Aqui está um diagrama mais arquitetônico sobre as principais diferenças técnicas entre um aplicativo fintech tradicional e um aplicativo DeFi (simplificado para fins de brevidade):
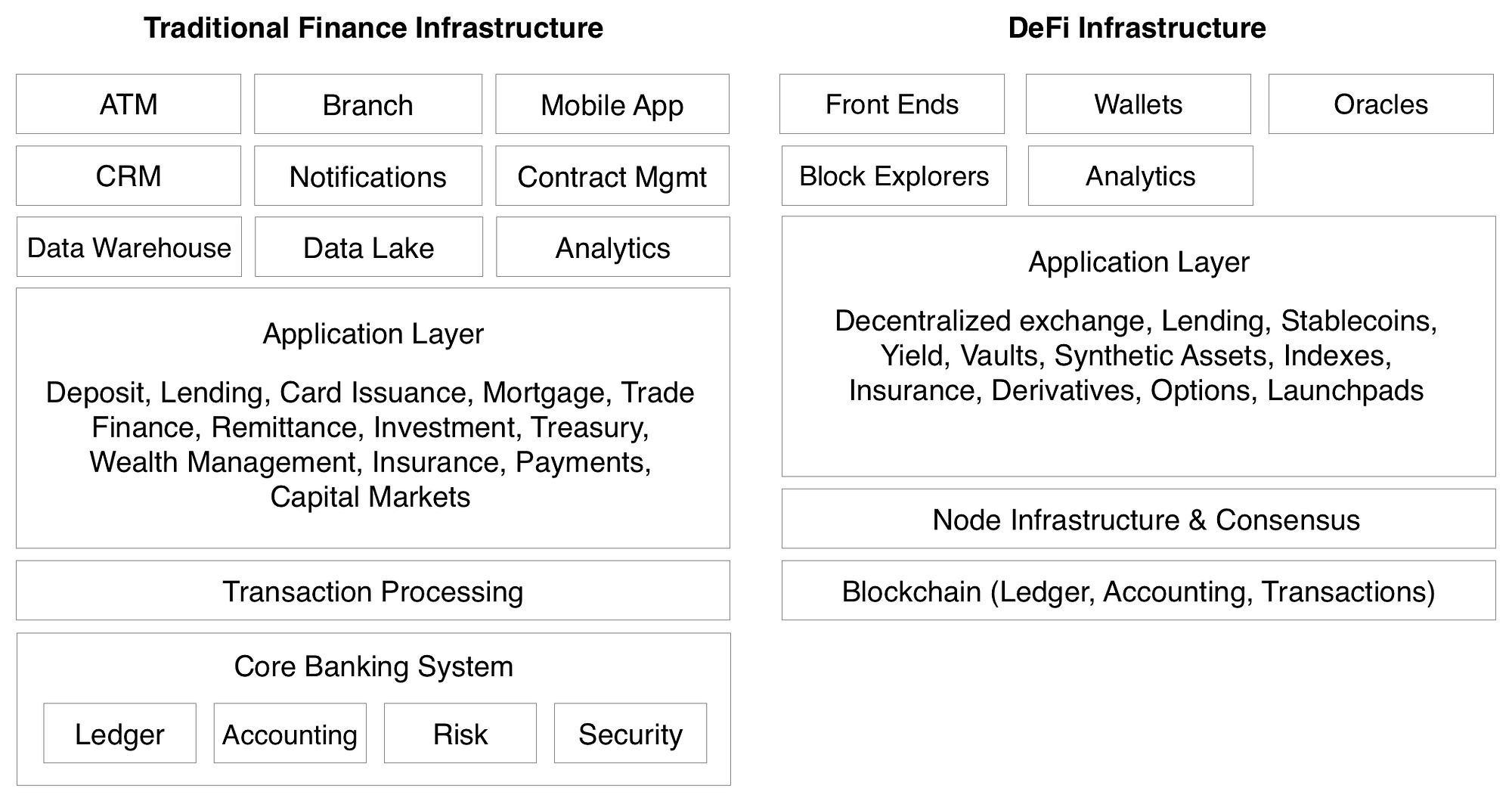
Here is a more direct comparison chart on some of the key differences between centralized and decentralized financial applications:

DeFi Infrastructure — Market Map
Below is a market map of two different DeFi ecosystems, one built on the Solana ecosystem and the other built on the Ethereum ecosystem.
The reason why I am picking these two ecosystems to focus on is to show the breadth of DeFi apps being built across two different underlying protocols. I also believe Solana is the most interesting new layer one protocol because of its high transaction throughput (50K+ transactions per second), sub second latency & transaction confirmation times, and fast growing ecosystem of developers building DeFi apps on top of the Solana protocol.
While similar in structure, each underlying protocol has its own ecosystem built on top which is largely independent of the other. Below are some of the further explanations of each layer and the tradeoffs between them.

Base Layer (Layer One)
The base layer is the blockchain in which the core ledger itself sits. Ethereum is the most dominant layer one today, and Solana is the most promising new entrant with faster transaction speeds, more throughput, and cheaper transactions.
Node Infrastructure
A never ending amount of data needs to be queried about the underlying ledger (retrieving blocks, finding transactions, syncing data, writing transactions, etc). In the Ethereum ecosystem, a whole industry sprung up to solve this need (Infura, Alchemy, etc.).
Contrast this with Solana where the underlying ledger is fast enough and in sync enough that teams can just query Solana’s RPC nodes directly (this might not last forever though).
Camada Dois
On Ethereum, there are various layer two solutions primarily used for scaling since Etheruem itself cannot handle all of the transactions on itself. Two of the promising scaling solutions include Matic, Optimism, among others.
On Solana, since there is only one layer to build upon (no layer 2 scaling solution needed) there are no specialized integrations needed and no mismatches with the underlying ledger which is processing settlement.
Order Book Aggregation
Unique to Solana, there is an additional layer occupied by a DeFi project named Sérum which provides a CLOB (Central limit order book) that is used by all of the DeFi projects built on top.
When new DeFi projects are built on top of Solana (DEX, AMM, Options, etc.), they can pull orders from Serum and push orders back into Serum, greatly reducing the cold start challenge most new financial applications face.
The best way to think about it is to think of it as “networked liquidity” and an “order management” system which is used by the majority of projects within the Solana ecosystem.
One of the more innovative examples of combining a CLOB (Serum) and an AMM is Raydium (very similar to Uniswap v3). The combining of these systems allows for passive LPs with active market making using Serum.
DeFi Toolset
There are a set of common tools needed to operate most of these DeFi apps, either from the perspective of developers or end users. These services don’t have direct traditional finance analogies but they include:
- Carteiras — The main interface people use to store assets & interface with DeFi apps.
- Oráculos — On-chain data feeds DeFi apps use to reference prices and execute transactions against (example: liquidations).
- Block Explorers & Analytics — Tools like Block Explorers were created to allow people to query the blockchain ledger itself directly. These are used most often when verifying transactions.
- Stablecoins — The two main assets used in DeFi ecosystems include the underlying native protocol token (ETH or SOL) and ideally on-chain stablecoins (USDC, Dai, or Pai).
- Front-Ends — A new emerging layer which creates easy to use front-end applications to interact with multiple DeFi projects at once, or to simplify transactions. This includes both Zapper.fi within the Ethereum Ecosystem or Step Finance within the Solana ecosystem.
Apps DeFi
The DeFi apps themselves are composed of all of the core financial applications which can be used directly, or embedded into other various apps within the crypto ecosystem.

Potential Missing Pieces of DeFi Infrastructure
When comparing and contrasting DeFi infrastructure with traditional financial infrastructure, there were a few pieces that don’t exist yet in the decentralized world that could be interesting to explore.
A few to highlight below:
- Aplicativos de consumo — In the traditional financial world, consumers typically act with consumer apps (ex. Robinhood, Chime, Transferwise) not the underlying protocols themselves. The front-ends of the DeFi space could be greatly improved and intermediate much more of the total consumer experience. In general, the UI/UX of most DeFi apps are still very difficult to use from a consumer perspective.
- CRM — The DeFi space doesn’t really have a concept of customer relationship management nor typically collects any amount of consumer data. While great from a privacy perspective, there is great value in understanding the customer better.
- Notificações — Notifications or alerts don’t really exist at all in the DeFi space at all. On a more broader level there aren’t any great methods to communicate with users either.
- Análise de Produto — There are tools to measure blockchain activity, but not to measure engagement within DeFi applications.
- Segurança - DeFi products do typically conduct security audits; however, none of the security audits guarantee the most common protections consumers are accustomed to in the traditional financial world. On top of this, the demand for security auditors outstrips the supply, so it’s a big bottleneck.
- Transaction Rollbacks — In traditional finance, if you make a mistake, a financial institution can initiate a rollback of the transaction. This does not yet exist in DeFi.
- Custódia — Right now, most DeFi projects need to be interacted with from an individual wallet perspective. None of the custodians allow you to interact with DeFi apps.
- Plataformas de desenvolvedor — Most of the developers in the crypto space are building right on top of the layer one protocol itself. There are no concepts of developer platforms or middleware just yet.
- Embeddable Wallets — Wallets are seen as these external services, there aren’t any offerings of white-label wallets to embed these directly into the DeFi apps themselves. There are several initiatives such as Toro, but these are still in its infancy.
- Dados de identificação: — One of the biggest complaints from the traditional finance world about DeFi is the pseudonymity of users. Ideally there needs to be a way to keep out the bad actors while persevering consumer privacy.
Future of Financial Applications
After meeting hundreds of founders and seeing progress teams are making, one thing is very clear — the pace of innovation in DeFi is 10x faster vs. that of traditional fintech apps.
In traditional finance:
- The underlying ledgers are not open source nor developer friendly.
- There are a whole host of “banking as a service” applications just to wrap underlying partner banks in developer friendly platforms.
- Fintech apps are very challenging regulatory wise and typically take years of development before releasing a single product.
Contrast that to DeFi where:
- Everything is open source including the ledger itself.
- All of the transactions are public.
- Everything is built from the perspective of developers building applications on top of protocols.
- New DeFi apps are built and released in weeks, not years.
We at Race Capital believe that DeFi developers will forever change how the finance world works. We are incredibly bullish about the DeFi infrastructure stack and community.
If you are building the horizontal infrastructure layers of the new open source financial stack including: trading, lending, borrowing, and/or any horizontal tools all new DeFi projects will rely upon in the future, we want to chat with you. Send me a message > chris@race.capital
Obrigado!
A big thank you to Bartosz Lipinski, Kas Vardhanabhuti, George Harrap, Dylan Macalinao, Anmol Singh, Edith Yeung, and Kim McCann for helping to review and provide feedback on this post.
Disclaimer: I’m a proud seed investor in Laboratórios Solana.
