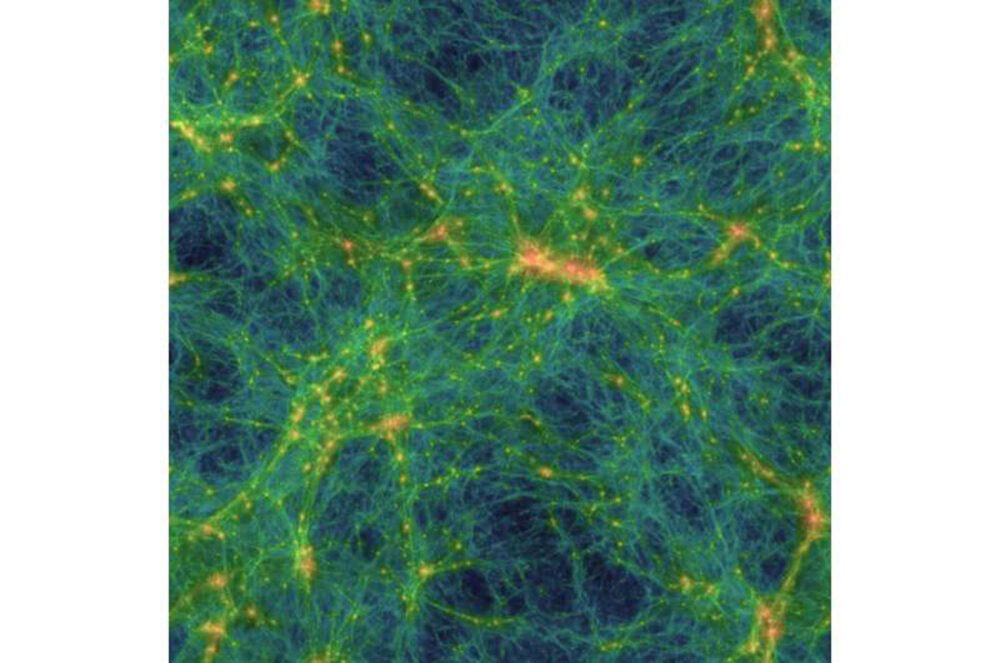
A new study proposed a scenario that dark matter could be made from ultralight dark photons that heated our universe.
The Cosmic Origin Spectrograph (COS) on board the Hubble Space Telescope, which measures the “cosmic web,” the intricate and flimsy filaments filling the space between galaxies, says that this hypothesis is in perfect agreement with observations. According to the data gathered by COS, the hydrodynamic simulations of the traditional model of structure formation indicate that the cosmic intergalactic filaments are hotter than they are.
Znanstveniki so rekli, “Since dark photons could convert into low-frequency photons and heat the cosmic structures. They could well explain the experimental information.”
Authors James S. Bolton (University of Nottingham), Andrea Caputo (CERN and Tel Aviv University), Hongwan Liu (New York University), and Matteo Viel (SISSA) explain, “Dark photons are hypothetical new particles that are the force carriers for a new force in the dark sector, much like how the photon is the force carrier for elektromagnetizem. Unlike photons, however, they can have mass. In particular, the ultralight dark photon—with a mass as small as twenty orders of magnitude less than the electron—is a good candidate for temna snov«.
Similar to how different types of neutrinos mix, dark and ordinary fotoni are also anticipated to do so, allowing ultralight dark photon dark matter to transform into low-frequency photons. The kozmični splet will be heated by these photons, but unlike other heating mechanisms based on astrophysical processes, like nastajanje zvezd and galactic winds, this heating process is more diffuse and effective even in places that are not very dense.
Matteo Viel razlaga: “Usually, cosmic filaments have been used to probe small scale properties of dark matter, while in this case, we have used for the first time the low redshift intergalactic medium data as a calorimeter, to check whether all the heating processes we are aware of are sufficient to reproduce the data. We found that this is not the case: something is missing that we model as a contribution produced by the dark photon.”
Referenca dnevnika:
- James S. Bolton, Andrea Caputo, Hongwan Liu and Matteo Viel. Comparison of Low-Redshift Lyman-α Forest Observations to Hydrodynamical Simulations with Dark Photon Dark Matter. Pisni pregledi fizike. DOI: 10.1103 / PhysRevLett.129.211102