1Zapata Computing Inc., Boston, MA 02110, USA
2Facility for Rare Isotope Beams, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA
3شعبہ کمپیوٹر سائنس، یونیورسٹی آف ٹورنٹو، ٹورنٹو، ON M5S 2E4، کینیڈا
4پیسیفک نارتھ ویسٹ نیشنل لیبارٹری، رچلینڈ، WA 99352، USA
اس کاغذ کو دلچسپ لگتا ہے یا اس پر بات کرنا چاہتے ہیں؟ SciRate پر تبصرہ کریں یا چھوڑیں۔.
خلاصہ
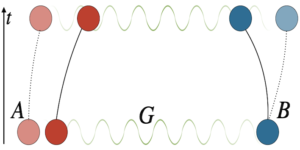
Quantum metrology allows for measuring properties of a quantum system at the optimal Heisenberg limit. However, when the relevant quantum states are prepared using digital Hamiltonian simulation, the accrued algorithmic errors will cause deviations from this fundamental limit. In this work, we show how algorithmic errors due to Trotterized time evolution can be mitigated through the use of standard polynomial interpolation techniques. Our approach is to extrapolate to zero Trotter step size, akin to zero-noise extrapolation techniques for mitigating hardware errors. We perform a rigorous error analysis of the interpolation approach for estimating eigenvalues and time-evolved expectation values, and show that the Heisenberg limit is achieved up to polylogarithmic factors in the error. Our work suggests that accuracies approaching those of state-of-the-art simulation algorithms may be achieved using Trotter and classical resources alone for a number of relevant algorithmic tasks.
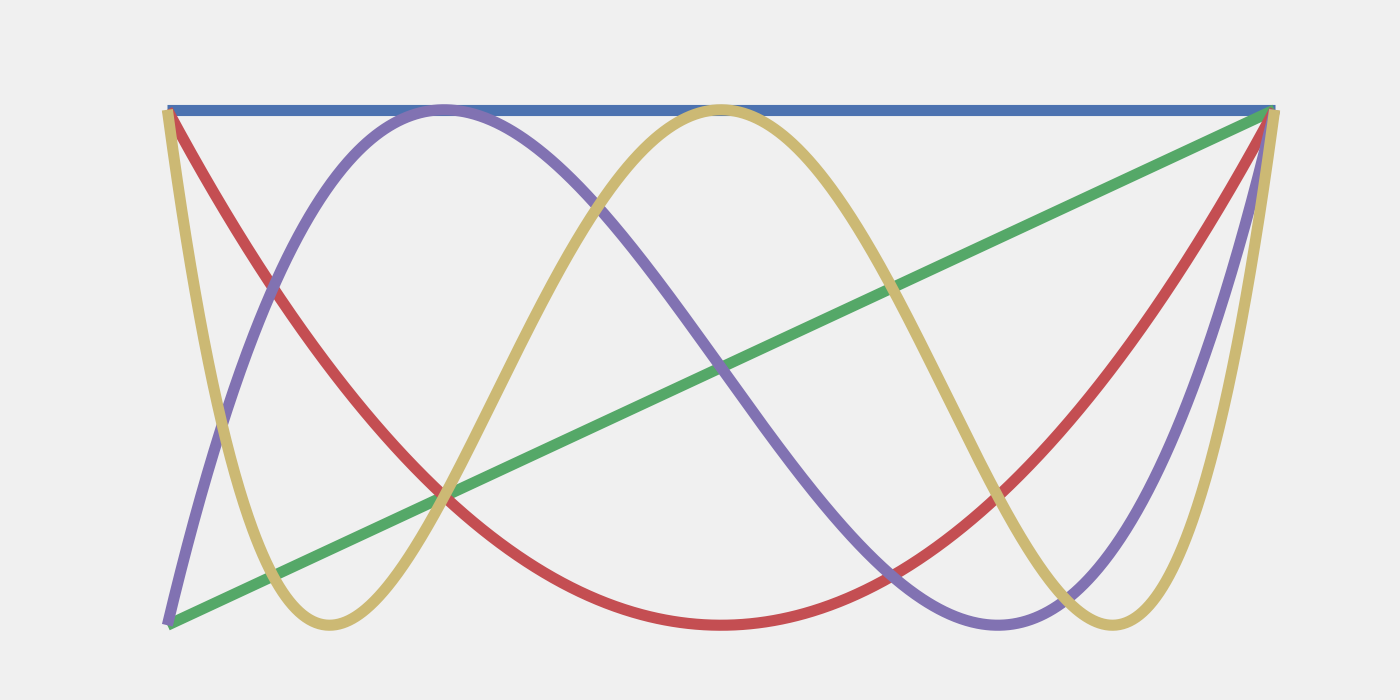
Featured image: The first five Chebyshev polynomials. Interpolation at the Chebyshev zeros serves as a robust scheme for Trotter error mitigation.
[سرایت مواد]
مقبول خلاصہ
To mitigate errors in Trotter simulations without increasing the quantum processing time, we use polynomials to learn the relationship between error and step size. By collecting data for different choices of step size, we can interpolate, i.e. thread, the data with a polynomial, then estimate the expected behavior for very small step sizes. We prove mathematically that our approach yields asymptotic accuracy improvements over standard Trotter for two fundamental tasks: estimating eigenvalues and estimating expectation values.
Our method is simple and practical, requiring only standard techniques in quantum and classical computation. We believe our work provides a strong theoretical foothold for further investigations of algorithmic error mitigation. Extensions of this work could occur in several directions, from eliminating artificial assumptions in our analysis to demonstrating improved quantum simulations.
► BibTeX ڈیٹا
► حوالہ جات
ہے [1] S. Lloyd, Universal quantum simulators, Science 273 (1996) 1073.
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.273.5278.1073
ہے [2] M. Reiher, N. Wiebe, K.M. Svore, D. Wecker and M. Troyer, Elucidating reaction mechanisms on quantum computers, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 114 (2017) 7555.
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.161915211
ہے [3] J.D. Whitfield, J. Biamonte and A. Aspuru-Guzik, Simulation of electronic structure hamiltonians using quantum computers, Molecular Physics 109 (2011) 735.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00268976.2011.552441
ہے [4] J. Lee, D.W. Berry, C. Gidney, W.J. Huggins, J.R. McClean, N. Wiebe et al., Even more efficient quantum computations of chemistry through tensor hypercontraction, PRX Quantum 2 (2021) 030305.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PRXQuantum.2.030305
ہے [5] V. von Burg, G.H. Low, T. Häner, D.S. Steiger, M. Reiher, M. Roetteler et al., Quantum computing enhanced computational catalysis, Physical Review Research 3 (2021) 033055.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.3.033055
ہے [6] S.P. Jordan, K.S. Lee and J. Preskill, Quantum algorithms for quantum field theories, Science 336 (2012) 1130.
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1217069
ہے [7] A.F. Shaw, P. Lougovski, J.R. Stryker and N. Wiebe, Quantum algorithms for simulating the lattice schwinger model, Quantum 4 (2020) 306.
https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2020-08-10-306
ہے [8] N. Klco, M.J. Savage and J.R. Stryker, Su (2) non-abelian gauge field theory in one dimension on digital quantum computers, Physical Review D 101 (2020) 074512.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.101.074512
ہے [9] A.M. Childs and N. Wiebe, Hamiltonian simulation using linear combinations of unitary operations, Quantum Info. Comput. 12 (2012) 901–924.
https://doi.org/10.26421/QIC12.11-12-1
ہے [10] G.H. Low, V. Kliuchnikov and N. Wiebe, Well-conditioned multiproduct hamiltonian simulation, arXiv:1907.11679 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1907.11679
آر ایکس سی: 1907.11679
ہے [11] D.W. Berry, A.M. Childs, R. Cleve, R. Kothari and R.D. Somma, Simulating hamiltonian dynamics with a truncated taylor series, Physical review letters 114 (2015) 090502.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.090502
ہے [12] G.H. Low and N. Wiebe, Hamiltonian simulation in the interaction picture, arXiv:1805.00675 (2018).
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1805.00675
آر ایکس سی: 1805.00675
ہے [13] M. Kieferová, A. Scherer and D.W. Berry, Simulating the dynamics of time-dependent hamiltonians with a truncated dyson series, Physical Review A 99 (2019) 042314.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.99.042314
ہے [14] G.H. Low and I.L. Chuang, Hamiltonian Simulation by Qubitization, Quantum 3 (2019) 163.
https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2019-07-12-163
ہے [15] R. Babbush, C. Gidney, D.W. Berry, N. Wiebe, J. McClean, A. Paler et al., Encoding electronic spectra in quantum circuits with linear t complexity, Physical Review X 8 (2018) 041015.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.8.041015
ہے [16] D.W. Berry, G. Ahokas, R. Cleve and B.C. Sanders, Efficient quantum algorithms for simulating sparse hamiltonians, Communications in Mathematical Physics 270 (2006) 359–371.
https:///doi.org/10.1007/s00220-006-0150-x
ہے [17] N. Wiebe, D.W. Berry, P. Høyer and B.C. Sanders, Simulating quantum dynamics on a quantum computer, Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical 44 (2011) 445308.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/44/44/445308
ہے [18] A.M. Childs, Y. Su, M.C. Tran, N. Wiebe and S. Zhu, Theory of trotter error with commutator scaling, Physical Review X 11 (2021) 011020.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.11.011020
ہے [19] J. Haah, M.B. Hastings, R. Kothari and G.H. Low, Quantum algorithm for simulating real time evolution of lattice hamiltonians, SIAM Journal on Computing (2021) FOCS18.
https://doi.org/10.1137/18M12315
ہے [20] M. Hagan and N. Wiebe, Composite quantum simulations, arXiv:2206.06409 (2022).
https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2023-11-14-1181
آر ایکس سی: 2206.06409
ہے [21] G.H. Low, Y. Su, Y. Tong and M.C. Tran, On the complexity of implementing trotter steps, arXiv:2211.09133 (2022).
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PRXQuantum.4.020323
آر ایکس سی: 2211.09133
ہے [22] G.H. Low and I.L. Chuang, Optimal hamiltonian simulation by quantum signal processing, Physical Review Letters 118 (2017).
https:///doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.118.010501
ہے [23] S. Endo, Q. Zhao, Y. Li, S. Benjamin and X. Yuan, Mitigating algorithmic errors in a hamiltonian simulation, Phys. Rev. A 99 (2019) 012334.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.99.012334
ہے [24] A.C. Vazquez, R. Hiptmair and S. Woerner, Enhancing the quantum linear systems algorithm using richardson extrapolation, ACM Transactions on Quantum Computing 3 (2022).
https://doi.org/10.1145/3490631
ہے [25] A.C. Vazquez, D.J. Egger, D. Ochsner and S. Woerner, Well-conditioned multi-product formulas for hardware-friendly hamiltonian simulation, Quantum 7 (2023) 1067.
https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2023-07-25-1067
ہے [26] M. Suzuki, General theory of fractal path integrals with applications to many‐body theories and statistical physics, Journal of Mathematical Physics 32 (1991) 400.
https://doi.org/10.1063/1.529425
ہے [27] A. Gilyén, Y. Su, G.H. Low and N. Wiebe, Quantum singular value transformation and beyond: exponential improvements for quantum matrix arithmetics, in Proceedings of the 51st Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 193–204, 2019, DOI.
https://doi.org/10.1145/3313276.3316366
ہے [28] C. Yi and E. Crosson, Spectral analysis of product formulas for quantum simulation, npj Quantum Information 8 (2022) 37.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-022-00548-w
ہے [29] A. Quarteroni, R. Sacco and F. Saleri, Numerical mathematics, vol. 37, Springer Science & Business Media (2010), 10.1007/b98885.
https://doi.org/10.1007/b98885
ہے [30] F. Piazzon and M. Vianello, Stability inequalities for lebesgue constants via markov-like inequalities, Dolomites Research Notes on Approximation 11 (2018).
ہے [31] A.P. de Camargo, On the numerical stability of newton’s formula for lagrange interpolation, Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 365 (2020) 112369.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2019.112369
ہے [32] L. Trefethen, Six myths of polynomial interpolation and quadrature, (2011).
ہے [33] W. Gautschi, How (un)stable are vandermonde systems? asymptotic and computational analysis, in Lecture Notes in Pure and Applied Mathematics, pp. 193–210, Marcel Dekker, Inc, 1990.
ہے [34] N.J. Higham, The numerical stability of barycentric lagrange interpolation, IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis 24 (2004) 547.
https://doi.org/10.1093/imanum/24.4.547
ہے [35] J.C. Mason and D.C. Handscomb, Chebyshev polynomials, CRC press (2002), 10.1201/9781420036114.
https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420036114
ہے [36] G. Rendon, T. Izubuchi and Y. Kikuchi, Effects of cosine tapering window on quantum phase estimation, Physical Review D 106 (2022) 034503.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.106.034503
ہے [37] L.N. Trefethen, Approximation Theory and Approximation Practice, Extended Edition, SIAM (2019), 10.1137/1.9781611975949.
https://doi.org/10.1137/1.9781611975949
ہے [38] F.L. Bauer and C.T. Fike, Norms and exclusion theorems, Numer. Math. 2 (1960) 137–141.
https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01386217
ہے [39] S. Blanes, F. Casas, J.-A. Oteo and J. Ros, The magnus expansion and some of its applications, Physics reports 470 (2009) 151.
https:///doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2008.11.001
ہے [40] N. Klco and M.J. Savage, Minimally entangled state preparation of localized wave functions on quantum computers, Physical Review A 102 (2020).
https:///doi.org/10.1103/physreva.102.012612
ہے [41] J.J. García-Ripoll, Quantum-inspired algorithms for multivariate analysis: from interpolation to partial differential equations, Quantum 5 (2021) 431.
https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2021-04-15-431
ہے [42] W. Górecki, R. Demkowicz-Dobrzański, H.M. Wiseman and D.W. Berry, $pi$-corrected heisenberg limit, Physical review letters 124 (2020) 030501.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.030501
ہے [43] D. Grinko, J. Gacon, C. Zoufal and S. Woerner, Iterative quantum amplitude estimation, npj Quantum Information 7 (2021) 52 [1912.05559].
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-021-00379-1
آر ایکس سی: 1912.05559
ہے [44] N. Wiebe, D. Berry, P. Høyer and B.C. Sanders, Higher order decompositions of ordered operator exponentials, Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical 43 (2010) 065203.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/43/6/065203
ہے [45] R.A. Horn and C.R. Johnson, Matrix analysis, Cambridge university press (2012), 10.1017/CBO9780511810817.
https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511810817
ہے [46] M. Chiani, D. Dardari and M.K. Simon, New exponential bounds and approximations for the computation of error probability in fading channels, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2 (2003) 840.
https:///doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2003.814350
ہے [47] J.M. Borwein and P.B. Borwein, Pi and the AGM: a study in the analytic number theory and computational complexity, Wiley-Interscience (1987).
ہے [48] B.L. Higgins, D.W. Berry, S.D. Bartlett, H.M. Wiseman and G.J. Pryde, Entanglement-free Heisenberg-limited phase estimation, Nature 450 (2007) 393.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06257
ہے [49] R.B. Griffiths and C.-S. Niu, Semiclassical Fourier Transform for Quantum Computation, Physical Review Letters 76 (1996) 3228.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.76.3228
ہے [50] A.Y. Kitaev, Quantum measurements and the abelian stabilizer problem, quant-ph/9511026 (1995).
https:///doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.quant-ph/9511026
arXiv:quant-ph/9511026
ہے [51] D.S. Abrams and S. Lloyd, Quantum Algorithm Providing Exponential Speed Increase for Finding Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, Physical Review Letters 83 (1999) 5162.
https:///doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.83.5162
ہے [52] J. Watkins, N. Wiebe, A. Roggero and D. Lee, Time-dependent hamiltonian simulation using discrete clock constructions, arXiv:2203.11353 (2022).
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.11353
آر ایکس سی: 2203.11353
ہے [53] T.D. Ahle, Sharp and simple bounds for the raw moments of the binomial and poisson distributions, Statistics & Probability Letters 182 (2022) 109306.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spl.2021.109306
ہے [54] T. Rivlin, Chebyshev Polynomials, Dover Books on Mathematics, Dover Publications (2020).
کی طرف سے حوالہ دیا گیا
[1] Dean Lee, “Quantum techniques for eigenvalue problems”, یورپی فزیکل جرنل A 59 11, 275 (2023).
[2] Tatsuhiko N. Ikeda, Hideki Kono, and Keisuke Fujii, “Trotter24: A precision-guaranteed adaptive stepsize Trotterization for Hamiltonian simulations”, آر ایکس سی: 2307.05406, (2023).
[3] Hans Hon Sang Chan, Richard Meister, Matthew L. Goh, and Bálint Koczor, “Algorithmic Shadow Spectroscopy”, آر ایکس سی: 2212.11036, (2022).
[4] Sergiy Zhuk, Niall Robertson, and Sergey Bravyi, “Trotter error bounds and dynamic multi-product formulas for Hamiltonian simulation”, آر ایکس سی: 2306.12569, (2023).
[5] Zhicheng Zhang، Qisheng Wang، اور Mingsheng Ying، "Hamiltonian Simulation کے لیے متوازی کوانٹم الگورتھم"، کوانٹم 8, 1228 (2024).
[6] Lea M. Trenkwalder, Eleanor Scerri, Thomas E. O'Brien, and Vedran Dunjko, "کمپیلیشن آف پروڈکٹ فارمولہ Hamiltonian simulation via reinforcement Learning"، آر ایکس سی: 2311.04285, (2023).
[7] گومارو رینڈن اور پیٹر ڈی جانسن، "کم گہرائی گاوسی ریاستی توانائی کا تخمینہ"، آر ایکس سی: 2309.16790, (2023).
[8] گریگوری بوائیڈ، "کموٹنگ آپریٹرز کے ذریعے LCU کا کم اوور ہیڈ متوازی"، آر ایکس سی: 2312.00696, (2023).
مذکورہ بالا اقتباسات سے ہیں۔ SAO/NASA ADS (آخری بار کامیابی کے ساتھ 2024-02-27 02:40:25)۔ فہرست نامکمل ہو سکتی ہے کیونکہ تمام ناشرین مناسب اور مکمل حوالہ ڈیٹا فراہم نہیں کرتے ہیں۔
On Crossref کی طرف سے پیش خدمت کاموں کے حوالے سے کوئی ڈیٹا نہیں ملا (آخری کوشش 2024-02-27 02:40:24)۔
یہ مقالہ کوانٹم میں کے تحت شائع کیا گیا ہے۔ Creative Commons انتساب 4.0 انٹرنیشنل (CC BY 4.0) لائسنس کاپی رائٹ اصل کاپی رائٹ ہولڈرز جیسے مصنفین یا ان کے اداروں کے پاس رہتا ہے۔
- SEO سے چلنے والا مواد اور PR کی تقسیم۔ آج ہی بڑھا دیں۔
- پلیٹو ڈیٹا ڈاٹ نیٹ ورک ورٹیکل جنریٹو اے آئی۔ اپنے آپ کو بااختیار بنائیں۔ یہاں تک رسائی حاصل کریں۔
- پلیٹوآئ اسٹریم۔ ویب 3 انٹیلی جنس۔ علم میں اضافہ۔ یہاں تک رسائی حاصل کریں۔
- پلیٹو ای ایس جی۔ کاربن، کلین ٹیک، توانائی ، ماحولیات، شمسی، ویسٹ مینجمنٹ یہاں تک رسائی حاصل کریں۔
- پلیٹو ہیلتھ۔ بائیوٹیک اینڈ کلینیکل ٹرائلز انٹیلی جنس۔ یہاں تک رسائی حاصل کریں۔
- ماخذ: https://quantum-journal.org/papers/q-2024-02-26-1266/
- : ہے
- : نہیں
- ][p
- $UP
- 001
- 1
- 10
- 11
- 114
- 118
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15٪
- 16
- 17
- 19
- 1995
- 1996
- 1999
- 20
- 2006
- 2008
- 2009
- 2011
- 2012
- 2015
- 2017
- 2018
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2022
- 2023
- 2024
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26٪
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 35٪
- 36
- 39
- 40
- 400
- 41
- 43
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 54
- 7
- 700
- 8
- 9
- a
- ہوں
- کی صلاحیت
- اوپر
- خلاصہ
- اکیڈمی
- تک رسائی حاصل
- درستگی
- حاصل کیا
- ACM
- انکولی
- وابستگیاں
- ماخوذ
- AL
- یلگورتم
- الگورتھم
- یلگوردمز
- تمام
- کی اجازت دیتا ہے
- اکیلے
- کے درمیان
- تجزیہ
- تجزیاتی
- اور
- سالانہ
- ایپلی کیشنز
- اطلاقی
- نقطہ نظر
- قریب
- کیا
- مصنوعی
- AS
- مفروضے
- At
- کرنے کی کوشش
- مصنف
- مصنفین
- دستیاب
- BE
- بن
- رویے
- یقین ہے کہ
- بنیامین
- کے درمیان
- سے پرے
- کتب
- بوسٹن
- حد
- توڑ
- کاروبار
- by
- حساب
- کیمبرج
- کر سکتے ہیں
- کیونکہ
- چین
- چینل
- کیمسٹری
- انتخاب
- گھڑی
- جمع
- کے مجموعے
- تبصرہ
- عمومی
- کموینیکیشن
- سفر
- مقابلے میں
- حریف
- مکمل
- پیچیدگی
- حساب
- کمپیوٹیشنل
- گنتی
- کمپیوٹر
- کمپیوٹر سائنس
- کمپیوٹر
- کمپیوٹنگ
- مواد
- کاپی رائٹ
- اخراجات
- سکتا ہے
- CRC
- ڈی سی
- اعداد و شمار
- de
- مظاہرین
- کے الات
- مختلف
- ڈیجیٹل
- طول و عرض
- مضامین
- بات چیت
- تقسیم
- ڈولومائٹس
- دو
- متحرک
- حرکیات
- e
- ای اینڈ ٹی
- وسطی
- ایڈیشن
- اثرات
- ہنر
- الیکٹرانک
- ختم کرنا
- ایمبیڈڈ
- انکوڈنگ
- توانائی
- بڑھانے کے
- بہتر
- بڑھانے
- مساوات
- خرابی
- نقائص
- تخمینہ
- بھی
- ارتقاء
- توسیع
- امید
- توقع
- ظالمانہ
- توسیع
- ملانے
- عوامل
- فروری
- میدان
- تلاش
- پہلا
- پانچ
- کے لئے
- فارمولا
- ملا
- سے
- افعال
- بنیادی
- مزید
- گیج
- جنرل
- ہنس
- ہارڈ ویئر
- ہارورڈ
- ہے
- مدد
- اعلی
- ہولڈرز
- کس طرح
- تاہم
- HTTPS
- i
- IEEE
- تصویر
- پر عمل درآمد
- بہتر
- بہتری
- in
- غلط
- انکارپوریٹڈ
- اضافہ
- اضافہ
- اسماتایں
- معلومات
- معلومات
- اداروں
- بات چیت
- دلچسپ
- بین الاقوامی سطح پر
- تحقیقات
- میں
- جیکب
- جاوا سکرپٹ
- جانسن
- اردن
- جرنل
- تجربہ گاہیں
- آخری
- جانیں
- سیکھنے
- چھوڑ دو
- لیکچر
- لی
- Li
- لائسنس
- LIMIT
- لمیٹڈ
- لکیری
- لسٹ
- لانگ
- لو
- میسن
- مواد
- ریاضی
- ریاضیاتی
- ریاضی طور پر
- ریاضی
- میٹرکس
- میٹھی
- زیادہ سے زیادہ چوڑائی
- مئی..
- mcclean
- پیمائش
- پیمائش
- نظام
- میڈیا
- طریقہ
- میٹرولوجی
- مشی گن
- تخفیف کریں
- تخفیف کرنا
- تخفیف
- ماڈل
- آناخت
- لمحات
- مہینہ
- زیادہ
- زیادہ موثر
- خرافات کا ترک کرنا
- قومی
- فطرت، قدرت
- نئی
- نیا
- نہیں
- معیارات
- نوٹس
- جوہری
- نیوکلیئر فزکس
- تعداد
- واقع
- of
- اکثر
- on
- ایک
- صرف
- کھول
- آپریشنز
- آپریٹر
- آپریٹرز
- زیادہ سے زیادہ
- or
- حکم
- اصل
- دیگر
- ہمارے
- پر
- صفحات
- کاغذ.
- متوازی
- راستہ
- انجام دیں
- پیٹر
- مرحلہ
- جسمانی
- طبعیات
- تصویر
- پلاٹا
- افلاطون ڈیٹا انٹیلی جنس
- پلیٹو ڈیٹا
- ممکنہ
- عملی
- پریکٹس
- کو ترجیح دی
- تیاری
- تیار
- پریس
- مسئلہ
- مسائل
- کارروائییں
- پروسیسنگ
- مصنوعات
- خصوصیات
- ثابت کریں
- فراہم
- فراہم کرتا ہے
- فراہم کرنے
- مطبوعات
- شائع
- پبلیشر
- پبلشرز
- پاک
- کوانٹم
- کوانٹم الگورتھم
- کوانٹم کمپیوٹر
- کوانٹم کمپیوٹرز
- کمانٹم کمپیوٹنگ
- کوانٹم معلومات
- جلدی سے
- R
- Rare
- خام
- رد عمل
- اصلی
- اصل وقت
- حوالہ جات
- تعلقات
- نسبتا
- متعلقہ
- باقی
- رپورٹیں
- تحقیق
- وسائل
- کا جائزہ لینے کے
- رچرڈ
- سخت
- مضبوط
- s
- سینڈرز
- سکیلنگ
- سکیم
- سائنس
- سائنس
- سائنسی
- سیریز
- کام کرتا ہے
- کئی
- شیڈو
- تیز
- شا
- دکھائیں
- سیم
- اشارہ
- سائمن
- سادہ
- سادگی
- تخروپن
- نقوش
- واحد
- چھ
- سائز
- سائز
- چھوٹے
- کچھ
- بہتر
- سپیکٹرا
- سپیکٹروسکوپی۔
- تیزی
- spl
- استحکام
- معیار
- حالت
- ریاستی آرٹ
- امریکہ
- شماریات
- کے اعداد و شمار
- مرحلہ
- مراحل
- حکمت عملی
- مضبوط
- ساخت
- مطالعہ
- کامیابی کے ساتھ
- اس طرح
- پتہ چلتا ہے
- موزوں
- سمپوزیم
- کے نظام
- سسٹمز
- ٹاسک
- کاموں
- تکنیک
- کہ
- ۔
- ان
- تو
- نظریاتی
- نظریہ
- وہاں.
- یہ
- اس
- تھامس
- ان
- اگرچہ؟
- کے ذریعے
- وقت
- عنوان
- کرنے کے لئے
- آج
- ٹورنٹو
- معاملات
- تبدیل
- تبدیلی
- دو
- UN
- کے تحت
- افہام و تفہیم
- بدقسمتی سے
- بے حد
- یونیورسل
- یونیورسٹی
- اپ ڈیٹ
- URL
- استعمال کی شرائط
- کا استعمال کرتے ہوئے
- قیمت
- اقدار
- بہت
- کی طرف سے
- حجم
- کے
- W
- وانگ
- چاہتے ہیں
- تھا
- لہر
- we
- جب
- گے
- ونڈو
- وائرلیس
- ساتھ
- بغیر
- کام
- کام کرتا ہے
- X
- سال
- پیداوار
- ینگ
- یو ٹیوب پر
- یوآن
- زیفیرنیٹ
- صفر
- زو