Defi 基础设施 101 — 概述和市场格局
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is redefining the future of finance. There is a major shift going on in the underlying infrastructure powering financial applications, and it’s changing the way we think about permission and control, transparency, and risks.
DeFi 是区块链技术、数字资产和金融服务交叉领域的一个发展中的市场部门。 根据 DeFi Pulse, the value of digital assets locked into Defi applications grew 10X from less than $1 billion in 2019 to over $10 billion in 2020, and over $80 billion at its peak thus far in 2021. Yet the DeFi applications and underlying infrastructure are still in its nascent stage of development.
The goal of this report is to provide an introduction of the new emerging area of DeFi infrastructure powering DeFi apps today. While it’s easy to get caught up in the hype and speculation within the space, I’ll focus on the key components of Defi applications, their key differentiation compared to traditional finance, potential risks, and longer-term implications these Defi apps are causing.
Major Structural Commonalities Across DeFi Apps
DeFi apps are financial applications with no central counterparties. In practice, this means there is no institution (e.g. banks) you are interfacing with to access these financial applications; instead users interface directly with the programs (e.g. smart contracts) on top of the protocol itself. For more of a DeFi 101 primer, I highly recommend 本报告.
DeFi 应用程序的主要类别包括去中心化交易所、借贷平台、稳定币、合成资产、保险等。 虽然范围各不相同,但所有这些 DeFi 应用程序都有一组主要的共性,包括:
- 使用底层区块链作为核心账本
- 默认开源透明
- 互操作性和可编程性(可组合性)
- 对所有人开放和访问(无需许可)
使用底层区块链作为核心账本
Compared to traditional financial applications which use core banking systems (Fiserv, Jack Henry, FIS, etc.) as the underlying ledgers of record, Defi apps use blockchains as their underlying core ledger.
A few of the most prominent blockchains used to build Defi apps include Ethereum, Solana, and Binance Chain, etc. These underlying blockchains store the ledger state of what is deposited into the DeFi apps, what is stored within the smart contracts, all of the transactions, and withdrawals.
All of the core accounting functions to ensure matching inputs and outputs are handled by the blockchain itself, the Defi apps don’t need to create external systems to reconcile balances, because all of the transactions are queryable across the various block explorers.
此外,与传统系统相比,没有单独的结算和清算流程。 交易处理、清算和结算都在交易广播的同时发生。 尽管建议等待大约 21 个区块或更多区块以确保区块链本身的最终性。
默认开源和透明
Compared to traditional financial applications which are all closed-source and built on top of proprietary systems, Defi applications are typically entirely open-sourced and built on top of open underlying blockchains.

这导致了三个有趣的特性:
- Composability — DeFi 应用程序本身可以在许多其他应用程序中进行分叉、重新混合和重用(更多内容见下文)。
- 用户评论透明 — 由于 DeFi 应用程序是开源的,因此完全可以审计来准确了解智能合约在功能、用户权限和用户数据方面的作用。
- 审计能力 — 由于底层区块链本身是开源的,所以整个资金流向是完全可审计的,包括系统中的抵押品、交易量、违约等。
与传统的金融体系(不透明)不同,它运行在部分准备金体系上,并且容易受到市场冲击——DeFi 系统是完全透明的且抵押过多——这使得 DeFi 公司能够更有效地度过低迷时期。
可互操作和可编程
为了让开发者获得用户的信任,大部分 DeFi 应用都是完全开源的——包括前端和智能合约本身。 此外,由于 DeFi 应用程序都运行在一个通用平台(底层区块链)之上,因此这些 DeFi 应用程序彼此完全可互操作,并且可以通过编程与生态系统中的任何其他 DeFi 应用程序一起使用。
这通常被称为“钱乐高“或”可组合性” DeFi 方面。 所有这些 DeFi 应用程序就像单独的乐高积木一样,可以重新混合以与其他乐高积木一起构建新的东西。
将这与传统的金融体系进行对比;
- 基础设施碎片化 — 传统金融应用程序并非建立在通用基础设施之上。
- 孤立的应用程序 — 传统金融应用程序通常由一家银行机构专有。 例如,富国银行的所有“金融科技应用程序”都可以协同工作,但不能跨不同的银行机构工作。
- 开发人员不友好 — 传统的金融应用程序不是为其他开发人员构建的服务而设计的。
传统的金融体系确实有共同的标准; 然而,要在市场参与者之间达成共识极其困难,因为金融机构将他们的软件视为他们的竞争护城河,而不是将产品作为差异化因素。
我们在 DeFi 领域看到如此多创新的最大原因之一是因为系统是可互操作的,它允许开发者生态系统对他们创建的产品和服务有更多的创造性表达。 最重要的是,开发人员不需要浪费时间重新发明轮子,而是可以建立在通用框架上并专注于使他们的产品与众不同的事情。
对所有人开放和访问
对于传统的金融应用程序,新用户通常需要经过漫长的入职流程、收入验证、信用检查,甚至是面对面的会议——只是为了能够使用给定的金融产品。
由于金融机构制定的这些任意规则,这些入职流程是 容易有偏见 如: 贷款歧视, 拒绝基本银行服务, 未经同意开设信用额度, 收取非法费用等等。
使用 DeFi 应用程序,您只需要一个钱包地址即可与这些系统进行交互。 DeFi 应用程序不需要收入验证,也不需要信用检查,而且在大多数情况下,它们甚至不需要知道您在使用的钱包地址之外是谁。
这通常被称为 DeFi 应用程序 permissionless. 如果你的钱包里有你想做的交易的资金,你就可以做到。 没有任何机构或中介机构会停止或拒绝为您提供服务。 无论您的背景是什么或来自哪个国家,DeFi 应用程序都不会歧视。
这是 DeFi 产品最不被重视的方面之一。
Traditional Fintech Architectures vs. DeFi Architecture
这是一个关于传统金融科技应用程序和 DeFi 应用程序之间主要技术差异的架构图(为简洁起见进行了简化):
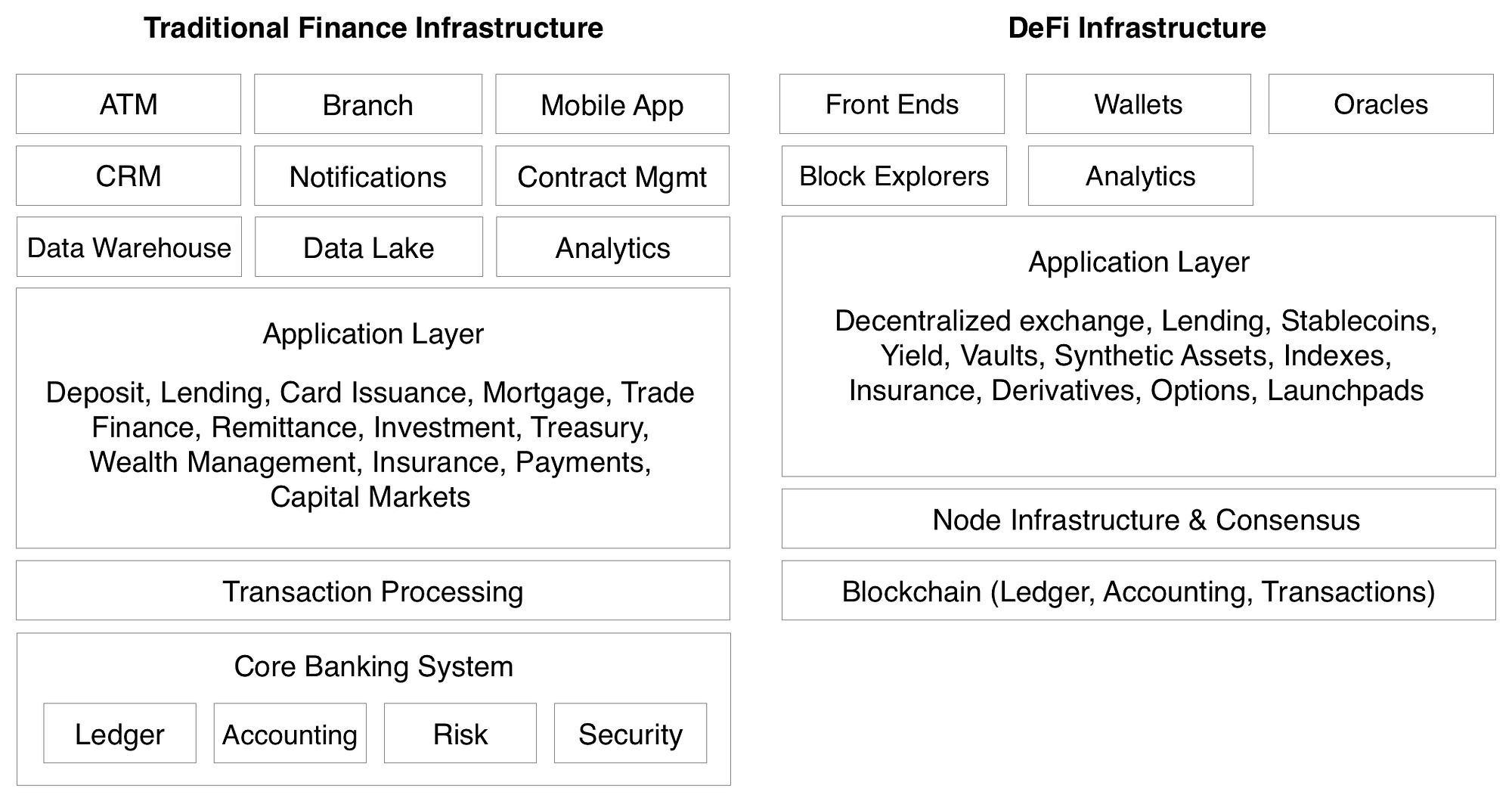
Here is a more direct comparison chart on some of the key differences between centralized and decentralized financial applications:

DeFi Infrastructure — Market Map
Below is a market map of two different DeFi ecosystems, one built on the Solana ecosystem and the other built on the Ethereum ecosystem.
The reason why I am picking these two ecosystems to focus on is to show the breadth of DeFi apps being built across two different underlying protocols. I also believe Solana is the most interesting new layer one protocol because of its high transaction throughput (50K+ transactions per second), sub second latency & transaction confirmation times, and fast growing ecosystem of developers building DeFi apps on top of the Solana protocol.
While similar in structure, each underlying protocol has its own ecosystem built on top which is largely independent of the other. Below are some of the further explanations of each layer and the tradeoffs between them.

Base Layer (Layer One)
The base layer is the blockchain in which the core ledger itself sits. Ethereum is the most dominant layer one today, and Solana is the most promising new entrant with faster transaction speeds, more throughput, and cheaper transactions.
Node Infrastructure
A never ending amount of data needs to be queried about the underlying ledger (retrieving blocks, finding transactions, syncing data, writing transactions, etc). In the Ethereum ecosystem, a whole industry sprung up to solve this need (Infura, Alchemy, etc.).
Contrast this with Solana where the underlying ledger is fast enough and in sync enough that teams can just query Solana’s RPC nodes directly (this might not last forever though).
第二层
On Ethereum, there are various layer two solutions primarily used for scaling since Etheruem itself cannot handle all of the transactions on itself. Two of the promising scaling solutions include Matic, Optimism, among others.
On Solana, since there is only one layer to build upon (no layer 2 scaling solution needed) there are no specialized integrations needed and no mismatches with the underlying ledger which is processing settlement.
Order Book Aggregation
Unique to Solana, there is an additional layer occupied by a DeFi project named 精華 which provides a CLOB (Central limit order book) that is used by all of the DeFi projects built on top.
When new DeFi projects are built on top of Solana (DEX, AMM, Options, etc.), they can pull orders from Serum and push orders back into Serum, greatly reducing the cold start challenge most new financial applications face.
The best way to think about it is to think of it as “networked liquidity” and an “order management” system which is used by the majority of projects within the Solana ecosystem.
One of the more innovative examples of combining a CLOB (Serum) and an AMM is Raydium (very similar to Uniswap v3). The combining of these systems allows for passive LPs with active market making using Serum.
DeFi Toolset
There are a set of common tools needed to operate most of these DeFi apps, either from the perspective of developers or end users. These services don’t have direct traditional finance analogies but they include:
- 钱包 — The main interface people use to store assets & interface with DeFi apps.
- 甲骨文 — On-chain data feeds DeFi apps use to reference prices and execute transactions against (example: liquidations).
- Block Explorers & Analytics — Tools like Block Explorers were created to allow people to query the blockchain ledger itself directly. These are used most often when verifying transactions.
- Stablecoins — The two main assets used in DeFi ecosystems include the underlying native protocol token (ETH or SOL) and ideally on-chain stablecoins (USDC, Dai, or Pai).
- Front-Ends — A new emerging layer which creates easy to use front-end applications to interact with multiple DeFi projects at once, or to simplify transactions. This includes both Zapper.fi within the Ethereum Ecosystem or Step Finance within the Solana ecosystem.
DeFi 应用
The DeFi apps themselves are composed of all of the core financial applications which can be used directly, or embedded into other various apps within the crypto ecosystem.

Potential Missing Pieces of DeFi Infrastructure
When comparing and contrasting DeFi infrastructure with traditional financial infrastructure, there were a few pieces that don’t exist yet in the decentralized world that could be interesting to explore.
A few to highlight below:
- 消费者应用 — In the traditional financial world, consumers typically act with consumer apps (ex. Robinhood, Chime, Transferwise) not the underlying protocols themselves. The front-ends of the DeFi space could be greatly improved and intermediate much more of the total consumer experience. In general, the UI/UX of most DeFi apps are still very difficult to use from a consumer perspective.
- 客户关系管理 — The DeFi space doesn’t really have a concept of customer relationship management nor typically collects any amount of consumer data. While great from a privacy perspective, there is great value in understanding the customer better.
- 通知 — Notifications or alerts don’t really exist at all in the DeFi space at all. On a more broader level there aren’t any great methods to communicate with users either.
- 产品分析 — There are tools to measure blockchain activity, but not to measure engagement within DeFi applications.
- 安全性 DeFi products do typically conduct security audits; however, none of the security audits guarantee the most common protections consumers are accustomed to in the traditional financial world. On top of this, the demand for security auditors outstrips the supply, so it’s a big bottleneck.
- Transaction Rollbacks — In traditional finance, if you make a mistake, a financial institution can initiate a rollback of the transaction. This does not yet exist in DeFi.
- 保管 — Right now, most DeFi projects need to be interacted with from an individual wallet perspective. None of the custodians allow you to interact with DeFi apps.
- 开发者平台 — Most of the developers in the crypto space are building right on top of the layer one protocol itself. There are no concepts of developer platforms or middleware just yet.
- Embeddable Wallets — Wallets are seen as these external services, there aren’t any offerings of white-label wallets to embed these directly into the DeFi apps themselves. There are several initiatives such as 花托, but these are still in its infancy.
- 身分 — One of the biggest complaints from the traditional finance world about DeFi is the pseudonymity of users. Ideally there needs to be a way to keep out the bad actors while persevering consumer privacy.
Future of Financial Applications
After meeting hundreds of founders and seeing progress teams are making, one thing is very clear — the pace of innovation in DeFi is 10x faster vs. that of traditional fintech apps.
In traditional finance:
- The underlying ledgers are not open source nor developer friendly.
- There are a whole host of “banking as a service” applications just to wrap underlying partner banks in developer friendly platforms.
- Fintech apps are very challenging regulatory wise and typically take years of development before releasing a single product.
Contrast that to DeFi where:
- Everything is open source including the ledger itself.
- All of the transactions are public.
- Everything is built from the perspective of developers building applications on top of protocols.
- New DeFi apps are built and released in weeks, not years.
We at Race Capital believe that DeFi developers will forever change how the finance world works. We are incredibly bullish about the DeFi infrastructure stack and community.
If you are building the horizontal infrastructure layers of the new open source financial stack including: trading, lending, borrowing, and/or any horizontal tools all new DeFi projects will rely upon in the future, we want to chat with you. Send me a message > chris@race.capital
谢谢!
A big thank you to Bartosz Lipinski, Kas Vardhanabhuti, George Harrap, Dylan Macalinao, Anmol Singh, Edith Yeung, and Kim McCann for helping to review and provide feedback on this post.
Disclaimer: I’m a proud seed investor in 索拉纳实验室.
