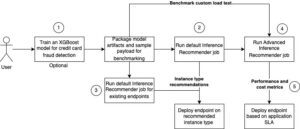
استنتاج بدون سرور Amazon SageMaker یک گزینه استنتاج هدفمند است که استقرار و مقیاسبندی مدلهای یادگیری ماشین (ML) را برای شما آسان میکند. این یک مدل پرداخت به ازای استفاده ارائه میکند، که برای خدماتی که فراخوانیهای نقطه پایانی نادر و غیرقابل پیشبینی هستند، ایدهآل است. بر خلاف یک نقطه پایانی میزبانی بلادرنگ، که توسط یک نمونه طولانی مدت پشتیبانی میشود، منابع محاسباتی برای نقاط پایانی بدون سرور بر حسب تقاضا فراهم میشوند و در نتیجه نیاز به انتخاب انواع نمونه یا مدیریت سیاستهای مقیاسبندی را از بین میبرند.
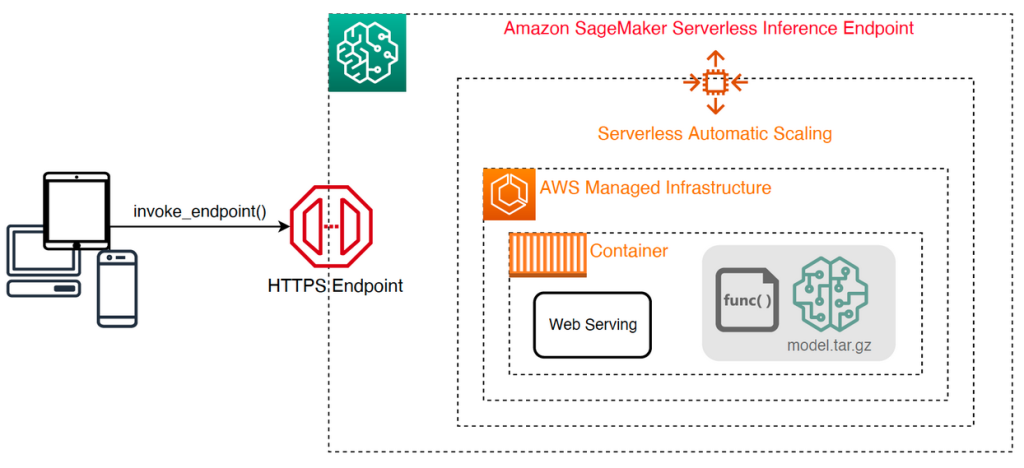
The following high-level architecture illustrates how a serverless endpoint works. A client invokes an endpoint, which is backed by AWS managed infrastructure.
However, serverless endpoints are prone to cold starts in the order of seconds, and is therefore more suitable for intermittent or unpredictable workloads.
To help determine whether a serverless endpoint is the right deployment option from a cost and performance perspective, we have developed the SageMaker Serverless Inference Benchmarking Toolkit، که پیکربندیهای نقطه پایانی مختلف را آزمایش میکند و بهینهترین آنها را با یک نمونه میزبانی بلادرنگ مقایسه میکند.
در این پست به معرفی جعبه ابزار و مروری بر پیکربندی و خروجی های آن می پردازیم.
بررسی اجمالی راه حل
You can download the toolkit and install it from the GitHub repo. Getting started is easy: simply install the library, create a مدل SageMaker, and provide the name of your model along with a JSON lines formatted file containing a sample set of invocation parameters, including the payload body and content type. A convenience function is provided to convert a list of sample invocation arguments to a JSON lines file or a pickle file for binary payloads such as images, video, or audio.
Install the toolkit
First install the benchmarking library into your Python environment using pip:
You can run the following code from an Amazon SageMaker Studio نمونه، مثال، نمونه نوت بوک SageMaker, or any instance with دسترسی برنامه ای to AWS and the appropriate هویت AWS و مدیریت دسترسی (IAM) permissions. The requisite IAM permissions are documented in the GitHub repo. For additional guidance and example policies for IAM, refer to چگونه Amazon SageMaker با IAM کار می کند. این کد یک معیار را با مجموعه ای از پارامترهای پیش فرض روی مدلی اجرا می کند که انتظار ورودی CSV با دو رکورد مثال را دارد. ارائه یک مجموعه نمونه از نمونه ها برای تجزیه و تحلیل نحوه عملکرد نقطه پایانی با بارهای ورودی مختلف، تمرین خوبی است.
Additionally, you can run the benchmark as a SageMaker Processing job, which may be a more reliable option for longer-running benchmarks with a large number of invocations. See the following code:
Note that this will incur additional cost of running an ml.m5.large SageMaker Processing instance for the duration of the benchmark.
Both methods accept a number of parameters to configure, such as a list of memory configurations to benchmark and the number of times each configuration will be invoked. In most cases, the default options should suffice as a starting point, but refer to the GitHub repo برای لیست کامل و توضیحات هر پارامتر.
Benchmarking configuration
Before delving into what the benchmark does and what outputs it produces, it’s important to understand a few key concepts when it comes to configuring serverless endpoints.
وجود دارد two key configuration options: MemorySizeInMB و MaxConcurrency. MemorySizeInMB configures the amount of memory that is allocated to the instance, and can be 1024 MB, 2048 MB, 3072 MB, 4096 MB, 5120 MB, or 6144 MB. The number of vCPUs also scales proportionally to the amount of memory allocated. The MaxConcurrency parameter adjusts how many concurrent requests an endpoint is able to service. With a MaxConcurrency of 1, a serverless endpoint can only process a single request at a time.
به طور خلاصه، MemorySizeInMB پارامتر مکانیزمی برای مقیاس پذیری عمودی فراهم می کند و به شما امکان می دهد حافظه و منابع را برای ارائه مدل های بزرگتر تنظیم کنید، در حالی که MaxConcurrency مکانیزمی برای مقیاس پذیری افقی فراهم می کند که به نقطه پایانی شما اجازه می دهد تا درخواست های همزمان بیشتری را پردازش کند.
The cost of operating an endpoint is largely determined by the memory size, and there is no cost associated with increasing the max concurrency. However, there is a per-Region account limit for max concurrency across all endpoints. Refer to SageMaker endpoints and quotas for the latest limits.
محک زدن خروجی ها
Given this, the goal of benchmarking a serverless endpoint is to determine the most cost-effective and reliable memory size setting, and the minimum max concurrency that can handle your expected traffic patterns.
By default, the tool runs two benchmarks. The first is a stability benchmark, which deploys an endpoint for each of the specified memory configurations and invokes each endpoint with the provided sample payloads. The goal of this benchmark is to determine the most effective and stable MemorySizeInMB setting. The benchmark captures the invocation latencies and computes the expected per-invocation cost for each endpoint. It then compares the cost against a similar real-time hosting instance.
When the benchmarking is complete, the tool generates several outputs in the specified result_save_path directory with the following directory structure:
La benchmarking_report دایرکتوری حاوی یک گزارش تلفیقی با تمام خروجی های خلاصه است که در این پست به آنها اشاره می کنیم. دایرکتوری های اضافی حاوی خروجی های خام و میانی هستند که می توانید از آنها برای تجزیه و تحلیل های اضافی استفاده کنید. رجوع به GitHub repo for a more detailed description of each output artifact.
بیایید چند خروجی محک زدن واقعی را برای یک نقطه پایانی که مدل TensorFlow بینایی کامپیوتر MobileNetV2 را ارائه میکند، بررسی کنیم. اگر می خواهید این مثال را تکرار کنید، به ادامه مطلب مراجعه کنید نمونه نوت بوک directory in the GitHub repo.
The first output within the consolidated report is a summary table that provides the minimum, mean, medium, and maximum latency metrics for each MemorySizeInMB successful memory size configuration. As shown in the following table, the average invocation latency (invocation_latency_mean) continued to improve as memory configuration was increased to 3072 MB, but stopped improving thereafter.
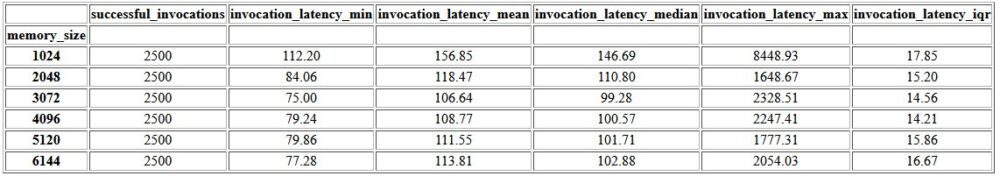
In addition to the high-level descriptive statistics, a chart is provided showing the distribution of latency as observed from the client for each of the memory configurations. Again, we can observe that the 1024 MB configuration isn’t as performant as the other options, but there isn’t a substantial difference in performance in configurations of 2048 and above.
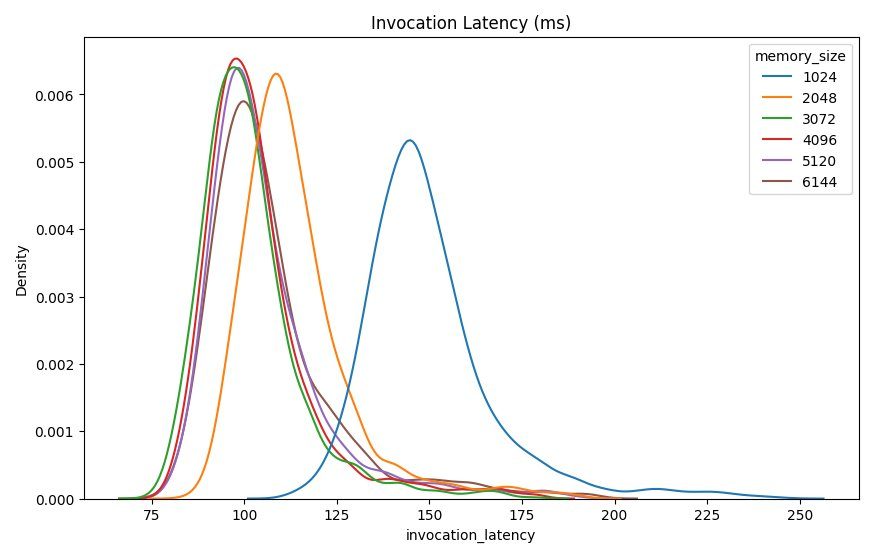
CloudWatch آمازون metrics associated with each endpoint configuration are also provided. One key metric here is ModelSetupTime, which measures how long it took to load the model when the endpoint was invoked in a cold state. The metric may not always appear in the report as an endpoint is launched in a warm state. A cold_start_delay parameter is available for specifying the number of seconds to sleep before starting the benchmark on a deployed endpoint. Setting this parameter to a higher number such as 600 seconds should increase the likelihood of a cold state invocation and improve the chances of capturing this metric. Additionally, this metric is far more likely to be captured with the concurrent invocation benchmark, which we discuss later in this section.
The following table shows the metrics captured by CloudWatch for each memory configuration.
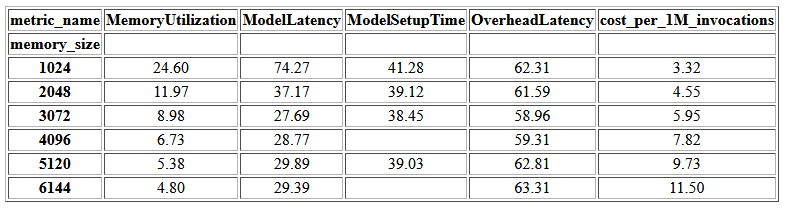
The next chart shows the performance and cost trade-offs of different memory configurations. One line shows the estimated cost of invoking the endpoint 1 million times, and the other shows the average response latency. These metrics can inform your decision of which endpoint configuration is most cost-effective. In this example, we see that the average latency flattens out after 2048 MB, whereas the cost continues to increase, indicating that for this model a memory size configuration of 2048 would be most optimal.
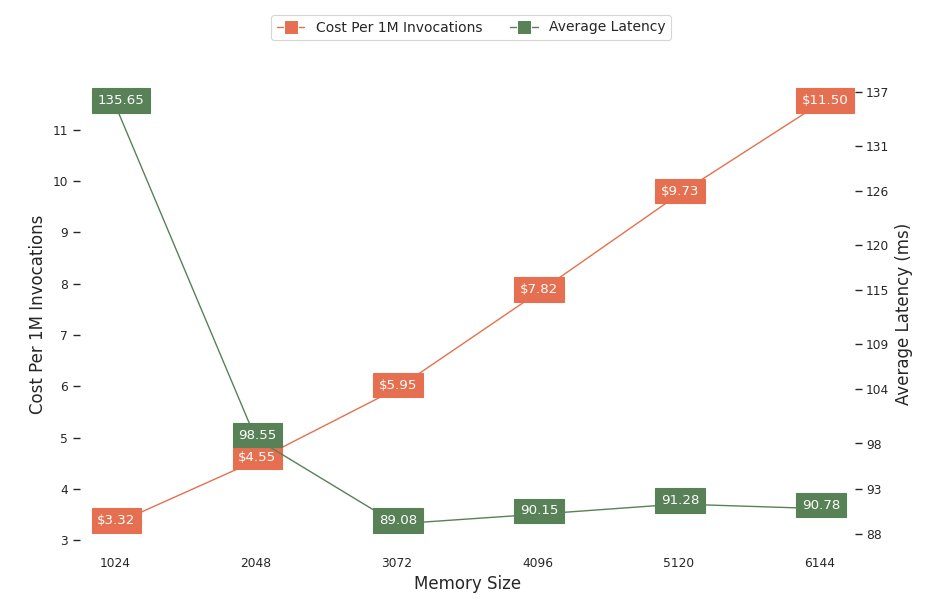
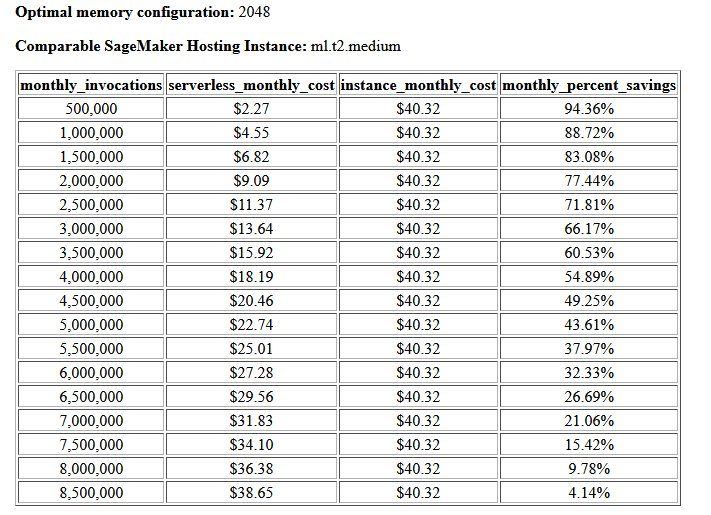
The final output of the cost and stability benchmark is a recommended memory configuration, along with a table comparing the cost of operating a serverless endpoint against a comparable SageMaker hosting instance. Based on the data collected, the tool determined that the 2048 MB configuration is the most optimal one for this model. Although the 3072 configuration provides roughly 10 milliseconds better latency, that comes with a 30% increase in cost, from $4.55 to $5.95 per 1 million requests. Additionally, the output shows that a serverless endpoint would provide savings of up to 88.72% against a comparable real-time hosting instance when there are fewer than 1 million monthly invocation requests, and breaks even with a real-time endpoint after 8.5 million requests.
The second type of benchmark is optional and tests various MaxConcurency settings under different traffic patterns. This benchmark is usually run using the optimal MemorySizeInMB configuration from the stability benchmark. The two key parameters for this benchmark is a list of MaxConcurency settings to test along with a list of client multipliers, which determine the number of simulated concurrent clients that the endpoint is tested with.
For example, by setting the concurrency_benchmark_max_conc parameter to [4, 8] and concurrency_num_clients_multiplier to [1, 1.5, 2], two endpoints are launched: one with MaxConcurency از 4 و دیگری 8. سپس هر نقطه پایانی با یک (MaxConcurency x multiplier) number of simulated concurrent clients, which for the endpoint with a concurrency of 4 translates to load test benchmarks with 4, 6, and 8 concurrent clients.
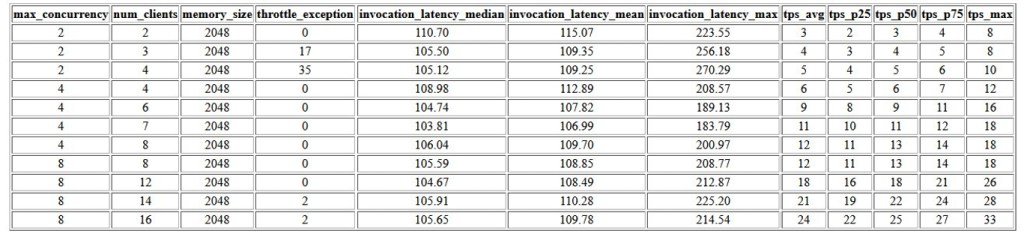
The first output of this benchmark is a table that shows the latency metrics, throttling exceptions, and transactions per second metrics (TPS) associated with each MaxConcurrency configuration with different numbers of concurrent clients. These metrics help determine the appropriate MaxConcurrency setting to handle the expected traffic load. In the following table, we can see that an endpoint configured with a max concurrency of 8 was able to handle up to 16 concurrent clients with only two throttling exceptions out of 2,500 invocations made at an average of 24 transactions per second.
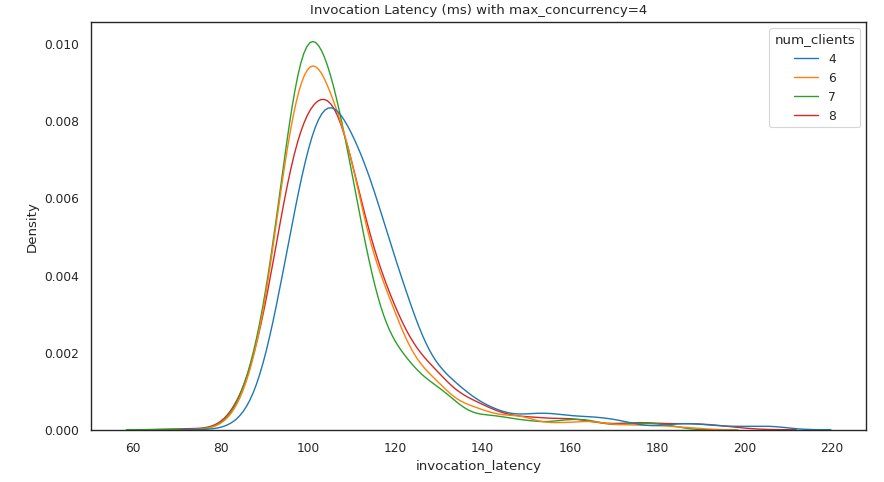
The next set of outputs provides a chart for each MaxConcurrency setting showing the distribution of latency under different loads. In this example, we can see that an endpoint with a MaxConcurrency setting of 4 was able to successfully process all requests with up to 8 concurrent clients with a minimal increase in invocation latency.
خروجی نهایی جدولی با معیارهای CloudWatch برای هر کدام ارائه می دهد MaxConcurrency configuration. Unlike the previous table showing the distribution of latency for each memory configuration, which may not always display the cold start ModelSetupTime متریک، این معیار به دلیل تعداد بیشتر درخواستهای فراخوانی و بیشتر بودن، به احتمال زیاد در این جدول ظاهر میشود. MaxConcurrency.

نتیجه
در این پست، SageMaker Serverless Inference Benchmarking Toolkit را معرفی کردیم و یک نمای کلی از پیکربندی و خروجی های آن ارائه کردیم. این ابزار می تواند به شما کمک کند تا با بارگیری پیکربندی های مختلف با الگوهای ترافیک واقعی، تصمیم آگاهانه تری در مورد استنتاج بدون سرور بگیرید. جعبه ابزار محک را با مدلهای خود امتحان کنید تا خودتان عملکرد و صرفهجویی در هزینهای را که با استقرار یک نقطه پایانی بدون سرور انتظار دارید، ببینید. لطفا به GitHub repo برای اسناد اضافی و نمونه نوت بوک.
منابع اضافی
درباره نویسندگان
 سیمون زامارین یک معمار راه حل های AI/ML است که تمرکز اصلی آن کمک به مشتریان برای استخراج ارزش از دارایی های داده خود است. سایمون در اوقات فراغت خود از گذراندن وقت با خانواده، خواندن علمی تخیلی و کار بر روی پروژه های مختلف خانه DIY لذت می برد.
سیمون زامارین یک معمار راه حل های AI/ML است که تمرکز اصلی آن کمک به مشتریان برای استخراج ارزش از دارایی های داده خود است. سایمون در اوقات فراغت خود از گذراندن وقت با خانواده، خواندن علمی تخیلی و کار بر روی پروژه های مختلف خانه DIY لذت می برد.
 داوال پاتل یک معمار اصلی یادگیری ماشین در AWS است. او با سازمانهایی از شرکتهای بزرگ گرفته تا استارتآپهای متوسط در زمینه مشکلات مربوط به محاسبات توزیعشده و هوش مصنوعی کار کرده است. او بر یادگیری عمیق، از جمله NLP و حوزه های بینایی کامپیوتر تمرکز می کند. او به مشتریان کمک می کند تا به استنباط مدل با عملکرد بالا در SageMaker دست یابند.
داوال پاتل یک معمار اصلی یادگیری ماشین در AWS است. او با سازمانهایی از شرکتهای بزرگ گرفته تا استارتآپهای متوسط در زمینه مشکلات مربوط به محاسبات توزیعشده و هوش مصنوعی کار کرده است. او بر یادگیری عمیق، از جمله NLP و حوزه های بینایی کامپیوتر تمرکز می کند. او به مشتریان کمک می کند تا به استنباط مدل با عملکرد بالا در SageMaker دست یابند.
 ریشابه ری چاودری is a Senior Product Manager with Amazon SageMaker, focusing on machine learning inference. He is passionate about innovating and building new experiences for machine learning customers on AWS to help scale their workloads. In his spare time, he enjoys traveling and cooking. You can find him on لینک.
ریشابه ری چاودری is a Senior Product Manager with Amazon SageMaker, focusing on machine learning inference. He is passionate about innovating and building new experiences for machine learning customers on AWS to help scale their workloads. In his spare time, he enjoys traveling and cooking. You can find him on لینک.
- پیشرفته (300)
- AI
- آی هنر
- مولد هنر ai
- ربات ai
- آمازون SageMaker
- Amazon SageMaker Serverless Inference Benchmarking Toolkit
- هوش مصنوعی
- گواهی هوش مصنوعی
- هوش مصنوعی در بانکداری
- ربات هوش مصنوعی
- ربات های هوش مصنوعی
- نرم افزار هوش مصنوعی
- آموزش ماشین AWS
- بلاکچین
- کنفرانس بلاک چین ai
- coingenius
- هوش مصنوعی محاوره ای
- کنفرانس کریپتو ai
- دل-ه
- یادگیری عمیق
- گوگل ai
- فراگیری ماشین
- افلاطون
- افلاطون آی
- هوش داده افلاطون
- بازی افلاطون
- PlatoData
- بازی پلاتو
- مقیاس Ai
- نحو
- زفیرنت