What is Diamond Traceability?
Diamond traceability refers to the ability to track the journey of the diamond from its source to the market. A comprehensive and authentic record is created by diligently documenting every stage of a diamond’s journey. This meticulous tracking allows customers to obtain complete visibility and transparency regarding the diamond’s history. Consequently, individuals purchasing diamonds can develop a profound personal connection with their chosen diamond, as they have access to its detailed narrative.
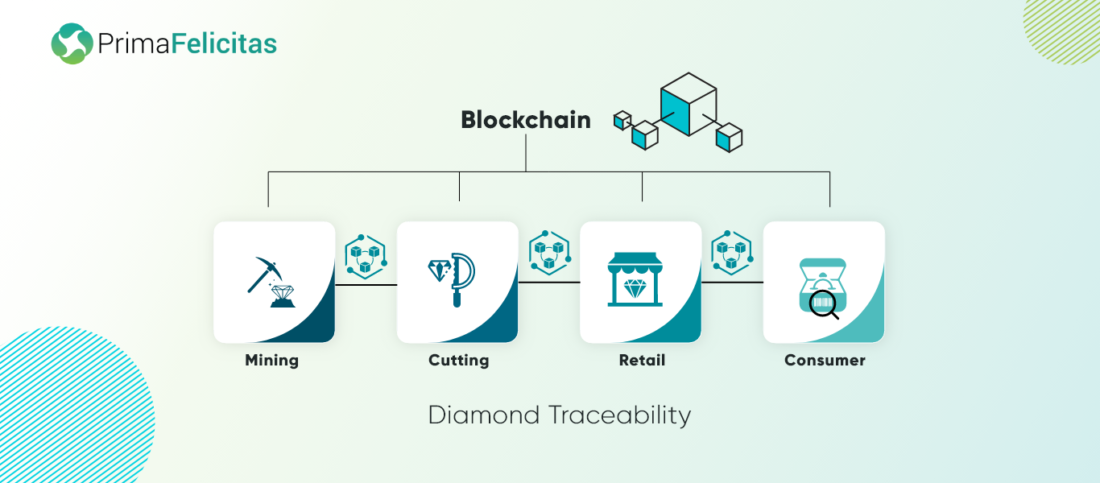

Currently, the diamond industry represents one of the most highly regulated sectors, undergoing a substantial shift from secrecy to transparency. As the industry continues to grow and transform, user perspectives and preferences are developing even more rapidly. The diamond industry, valued at approximately USD 80 billion worldwide, is infamous for its lack of transparency. However, Blockchain technology has revolutionized this industry by allowing the traceability of diamonds from their source to their final retail destination. This innovation simplifies the process of growing diamond authenticity and can potentially decrease fraudulent activities by an impressive 80%.
The Risks of Buying an Untraced Diamond
Modern buyers are more knowledgeable and socially conscious, seeking complete transparency regarding the diamond’s information from the retailer. They are even willing to pay a premium for this transparency. The diamond’s journey provides them with crucial details, including:
- The credibility of individuals or companies involved in the diamond’s purchase, sale, and processing.
- The authenticity of the diamond’s source, as tracing helps avoid supporting “Blood Diamond” scenarios involving human abuse. Consumers actively avoid direct or indirect promotion of such acts and assume responsibility.
- The diamond’s place of origin.
- Details about the cutting, shaping, and planning of the diamond.
- Information about the diamond grading process and the parameters used.
- The length of time it took for the diamond to reach the consumer.
These answers assist consumers in determining the diamond’s authenticity and assure them that their money is being spent wisely. Transparency fosters trust between the seller and the buyer. The diamond industry has certification houses and spectrography-based labs to determine color grading. However, no centralized database exists for this information and lost diamonds rely on traditional paper-based certification records.
Blockchain technology: What exactly is it?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger designed to store various types of data. It has the capability to record and store information regarding cryptocurrency transactions, ownership of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and smart contracts related to decentralized finance (DeFi).
Although conventional databases can store such information, Blockchain stands out due to its complete decentralization. Unlike traditional databases that are maintained in a single location by a centralized administrator, such as an Excel spreadsheet or a bank database, Blockchain operates differently. It relies on multiple computers spread across a network, known as nodes, to hold numerous identical copies of the Blockchain database.
Each transaction recorded in the ledger is verified and authorized using the owner’s digital signature, ensuring the transaction’s authenticity and protecting it against unauthorized changes. Consequently, the information stored in the digital ledger is exceptionally secure.
In essence, the digital ledger operates similarly to a shared Google spreadsheet among multiple computers in a network. It stores transactional records based on real purchases. What makes it intriguing is that anyone can view the data, but they are unable to alter or manipulate it.
The Benefits of Implementing Diamond Traceability in Your Jewelry Business
In recent years, the diamond industry has undergone powerful transformations, including the adoption of automatic sorting methods and the utilization of Blockchain technology. The possible impact of Blockchain technology on the diamond mining and trading sector is immense, promising enhanced transparency, accuracy, and security.
In the realm of mining, Blockchain technology holds the potential to boost efficiency, minimize costs, and enhance safety measures. It can simplify the authentication process for diamonds, facilitating the identification of genuine diamonds while reducing instances of fraud. Using an immutable ledger, Blockchain technology enables the recording of every transaction, ensuring comprehensive tracking of diamonds from the mining stage to the market. This has the potential to mitigate the entry of conflict diamonds into the market, improve the traceability of diamonds, and ensure their ethical sourcing.
Further, by utilizing Blockchain technology, each diamond can be designated a distinct Global Diamond ID. This digital identifier encompasses various characteristics such as clarity, carat, and color. It enables stakeholders to make informed choices by examining this data alongside other relevant information.
In what ways the Blockchain captures the unique identity of a diamond?
Blockchain can offer transparency and verification required by the user while ensuring privacy and tailored access to the ledger for different user types. This is particularly valuable for the jewelry industry, where verified supply chain solutions are essential, often requiring anonymization and privacy of information. The following are the ways using the diamond’s unique identity is captured.
- Diamond has a digital identity: Each Blockchain-enabled diamond comprises its own digital identity, which is usually called a digital twin. The digital twin involves comprehensive details regarding the diamond’s physical characteristics, place of origin, and journey since it has been mined.
Blockchain technology supports and protects the digital identity of the diamond. Additionally, this technology enables the diamond’s owner to conveniently access the files stored in the diamond’s Blockchain and facilitate ownership transfer through a diamond passport.
- Owner has digital ownership: The Blockchain provides a secure online vault where suppliers, retailers, and private owners can store the digital twins of their diamonds. This storage allows them to access and manage all their assets conveniently in one place. Furthermore, transferring ownership of a diamond is simplified by entering the recipient’s email address.
With a digital identity and proof of ownership, the diamond’s digital twin becomes a unique non-fungible token (NFT). This transformation makes the diamond a verifiable, one-of-a-kind digital asset that can be easily shared and transferred through the Blockchain.
The Impact of Diamond Traceability on the Environment and Communities
The concept of environmental sustainability revolves around ensuring fairness between generations in terms of benefiting from natural resources and environmental advantages. This subject has garnered significant attention and discourse from academia, industry, and government bodies. In the realm of supply chains, environmental sustainability concerns arise during both the initial phase, where raw materials flow from the natural environment into the production and consumption processes, and the subsequent phase, where economic activities generate pollution that affects the natural environment.
Achieving environmental sustainability within supply chains necessitates the adoption of optimal resource management practices and environmental protection policies. The unique characteristics of Blockchain technology, such as traceability, reliability, synchronized transaction processing, and cost efficiency, make it a suitable alternative to traditional corporate policies and practices in promoting environmental sustainability.
Specifically, Blockchain technology can enhance the following two key aspects:
- Environmental emission reduction: Through Blockchain, supply chain participants can track the location and quantity of emissions, particularly carbon emissions, wastewater, or harmful pollutants, at each step of the chain. This enables them to take necessary measures to comply with environmental policies. Moreover, participants can ensure that their upstream partners adhere to environmental laws and regulations. The collective pressure exerted by the entire supply chain encourages intentional reductions in environmental emissions.
- Resource management: Blockchain technology enables monitoring of raw materials’ origins, mitigating excessive extraction and utilization of natural resources. This aids in preventing issues such as salinization or deforestation.
Final Thoughts
The adoption of Blockchain technology in supply chains is steadily increasing. By leveraging distributed ledger technology, the Blockchain platform offers a digital
system and database for recording transactions across the supply chain. All involved parties reach a consensus on the information, which is then shared among them. This decentralized transaction database enhances transparency, reliability, traceability, and efficiency in supply chain management.
Blockchain technology plays a key role in promoting ethical practices within the diamond industry. By enabling the traceability of diamonds, Blockchain ensures that their origin can be verified, thereby ensuring they are sourced from legitimate and ethical channels, free from any association with unethical practices or conflicts. As a result, the implementation of Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize the supply chain of the diamond industry. With the continued growth of this technology, it is expected to have a significant and positive impact on the traceability system of diamonds.
Looking for help here?
Connect with Our Expert for a detailed discussion
Post Views: 12
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Automotive / EVs, Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- BlockOffsets. Modernizing Environmental Offset Ownership. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.primafelicitas.com/Insights/diamond-traceability-using-blockchain-why-is-it-important/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=diamond-traceability-using-blockchain-why-is-it-important
- :has
- :is
- :where
- 80
- a
- ability
- About
- abuse
- Academia
- access
- accuracy
- across
- actively
- activities
- acts
- Additionally
- address
- adhere
- Adoption
- advantages
- against
- aids
- All
- Allowing
- allows
- alongside
- alternative
- among
- an
- and
- answers
- any
- anyone
- approximately
- ARE
- arise
- around
- AS
- aspects
- asset
- Assets
- assist
- Association
- assume
- At
- attention
- Authentic
- Authentication
- authenticity
- authorized
- Automatic
- avoid
- Bank
- based
- BE
- becomes
- been
- being
- benefiting
- benefits
- between
- Billion
- blockchain
- blockchain database
- blockchain platform
- blockchain technology
- bodies
- boost
- both
- but
- BUYER..
- buyers
- Buying
- by
- called
- CAN
- capability
- captured
- captures
- carbon
- carbon emissions
- centralized
- Certification
- chain
- chains
- Changes
- channels
- characteristics
- choices
- chosen
- clarity
- Collective
- color
- Companies
- complete
- comply
- comprehensive
- comprises
- computers
- concept
- Concerns
- conflict
- connection
- conscious
- Consensus
- Consequently
- consumer
- Consumers
- consumption
- continued
- continues
- contracts
- conventional
- Corporate
- Cost
- Costs
- created
- Credibility
- crucial
- cryptocurrency
- Customers
- cutting
- data
- Database
- databases
- Decentralization
- decentralized
- Decentralized Finance
- decentralized finance (DeFi)
- decrease
- DeFi
- deforestation
- designated
- designed
- destination
- detailed
- details
- Determine
- determining
- develop
- developing
- Diamond
- different
- digital
- Digital Asset
- digital identity
- digital ledger
- digital twin
- Digital twins
- diligently
- direct
- distinct
- distributed
- Distributed Ledger
- distributed ledger technology
- due
- during
- each
- easily
- Economic
- efficiency
- emission
- Emissions
- enables
- enabling
- encompasses
- encourages
- enhance
- enhanced
- Enhances
- ensure
- ensures
- ensuring
- entering
- Entire
- entry
- Environment
- environmental
- Environmental Sustainability
- essence
- essential
- ethical
- Even
- Every
- exactly
- Examining
- Excel
- exists
- expected
- expert
- facilitate
- facilitating
- fairness
- Files
- final
- finance
- flow
- following
- For
- fosters
- fraud
- fraudulent
- Free
- from
- Furthermore
- generate
- generations
- genuine
- Global
- Government
- Grow
- Growing
- Growth
- harmful
- Have
- help
- helps
- here
- highly
- history
- hold
- holds
- houses
- However
- HTTPS
- human
- ID
- identical
- Identification
- identifier
- Identity
- immense
- immutable
- immutable ledger
- Impact
- implementation
- implementing
- important
- impressive
- improve
- in
- Including
- increasing
- individuals
- industry
- infamous
- information
- informed
- initial
- Innovation
- Intentional
- into
- intriguing
- involved
- involving
- issues
- IT
- ITS
- jewelry
- journey
- Key
- known
- Labs
- Lack
- Laws
- Laws and regulations
- Ledger
- legitimate
- Length
- leveraging
- location
- lost
- make
- MAKES
- manage
- management
- Market
- materials
- max-width
- measures
- methods
- mined
- Mining
- Mitigate
- mitigating
- money
- monitoring
- more
- Moreover
- most
- multiple
- NARRATIVE
- Natural
- Navigation
- necessary
- necessitates
- network
- NFT
- NFTs
- no
- nodes
- non-fungible
- non-fungible token
- Non-Fungible Token (NFT)
- non-fungible tokens
- NON-FUNGIBLE TOKENS (NFTS)
- numerous
- obtain
- of
- offer
- Offers
- often
- on
- ONE
- One-of-a-Kind
- online
- operates
- optimal
- or
- origin
- Other
- our
- out
- own
- owner
- owners
- ownership
- paper-based
- parameters
- participants
- particularly
- parties
- partners
- passport
- Pay
- personal
- perspectives
- phase
- physical
- Place
- planning
- platform
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- plays
- policies
- Pollution
- positive
- possible
- Posts
- potential
- potentially
- powerful
- practices
- preferences
- Premium
- pressure
- preventing
- PrimaFelicitas
- privacy
- private
- process
- processes
- processing
- Production
- profound
- promising
- promoting
- promotion
- proof
- protecting
- protection
- provides
- purchase
- purchases
- purchasing
- quantity
- rapidly
- Raw
- reach
- real
- realm
- recent
- record
- recorded
- recording
- records
- reducing
- refers
- regarding
- regulated
- regulations
- related
- relevant
- reliability
- rely
- represents
- required
- resource
- Resources
- responsibility
- result
- retail
- retailer
- retailers
- revolutionize
- revolutionized
- revolves
- risks
- Role
- Safety
- sale
- scenarios
- sector
- Sectors
- secure
- security
- seeking
- shaping
- shared
- shift
- significant
- Similarly
- simplified
- simplify
- since
- single
- smart
- Smart Contracts
- socially
- Solutions
- Source
- sourced
- Sourcing
- spent
- spread
- Spreadsheet
- Stage
- stakeholders
- stands
- Step
- storage
- store
- stored
- stores
- subject
- subsequent
- substantial
- such
- suitable
- suppliers
- supply
- supply chain
- supply chain management
- Supply chains
- Supporting
- Supports
- Sustainability
- system
- tailored
- Take
- Technology
- terms
- that
- The
- the information
- their
- Them
- then
- thereby
- they
- this
- Through
- time
- to
- token
- Tokens
- took
- Traceability
- Tracing
- track
- Tracking
- Trading
- traditional
- transaction
- transactional
- Transactions
- transfer
- transferred
- Transferring
- Transform
- Transformation
- transformations
- Transparency
- Trust
- twin
- Twins
- two
- types
- unable
- undergoing
- undergone
- unique
- unlike
- USD
- used
- User
- using
- usually
- Utilizing
- Valuable
- valued
- various
- Vault
- verifiable
- Verification
- verified
- View
- views
- visibility
- ways
- What
- which
- while
- why
- willing
- with
- within
- worldwide
- years
- Your
- zephyrnet













