Looking for an electronic payment solution? Try Nanonets™ AI-based OCR solution to automate Payment Reconciliation in your organization!
For without this, there is no exchange and no partnership.
– Aristotle
The click of a button and the swipe of a card are nothing like the exchange of farm produce, but the essential principle remains the same. “Proportional exchange,“ the exchange of products for the satisfaction of a need, as described by Aristotle circa 300 BCE, has morphed into forms that the philosopher would not have dreamed of.
Electronic payments or ePayments are the norms now, driven not only by the enormous digital developments of recent decades but also spurred on by the pandemic-induced lockdowns and social distancing. The World Bank reports that two-thirds of adults worldwide make or receive a digital payment today, with the share in developing economies growing from 35% in 2014 to 57% in 2021.
With cash (or farm produce if one chooses to go that far back in history) no longer being the king, and digital payments appearing to be the transactional backbone of the future, it is important to understand what ePayments are, how they work, and how the overlap between automation and ePayment applications would fit into a future world of hyper-automation.
Table of Content
What is an electronic payment
Benefits of ePayments
Type of ePayments
Credit Cards
Bank Transfers
Digital Wallet
Others
Automation of e-Payment
Nanonets as part of the larger ePayment automation process
Take away
What is an electronic payment
Electronic payments are the systems by which consumers pay for goods and services electronically, in ways that do not involve paper either as currency or checks. ePayment methods such as credit cards and debit cards have been around for many decades now. Bank transfers and digital wallets are more recent developments that have leveraged the rapid expansion in digital data and interconnectivity.
The transition from traditional paper-based modes of payment to electronic payment systems has occurred not only in personal life but also in the business sectors. B2B and B2C transactions are moving rapidly into the ePayment domains. The pressures imposed on enterprises and individuals alike by the COVID-19 pandemic have dramatically spurred this move. According to a global study conducted by Accenture, 79 percent of Chief Financial Officers believe that the pandemic’s impacts have compelled them to resort to technology for payment processes.
The emergence of technology-enabled transactions has led to an entirely new field of operation – FinTech – the use of technology to enhance or automate financial services and processes.
Looking to automate the mundane & mechanical Payment Reconciliation process? Try Nanonets™ AI-based OCR solution to automate Payment Reconciliation in your organization!
Benefits of ePayments
The obvious benefit of electronic payments to both businesses and individuals is convenience. Less known benefits include:
- Cost and time savings: Paper-based payments, be it cash or checks, involve hidden costs such as manpower for collection and processing. The average cost of cash payment is 30 cents. While this appears small enough, it is applicable only to small transactions in geographic proximity. Further disadvantages of cash processing are that they are prone to error and fraud, and complicate accounting and bookkeeping processes. The cost of processing checks is about $3. Check processing is also slow – it can take 2-3 weeks to clear a simple check.
- Limits of payment: Cash payments are limited by the amount of cash in the wallet. Cheque payments are limited by the amount of money in the bank account. Many (not all) types of electronic payments entail a credit system, which enables payments during tough times.
- Better B2B and B2C relationships: ePayments could enable credit functionalities and convenience of payment. These, in turn, could ensure prompt payment to businesses, which can improve relationships between vendors and customers.
- Enhanced Visibility: Cash payments and check payments may be difficult to track. Maintaining the log of payment is an extra activity that must be performed when using these forms of payment. ePayment systems can provide a recorded trail of payments made, and enhanced visibility into payment statuses and financial metrics.
- Efficiency: ePayment systems do not require waiting in long queues in ATMs and banks to withdraw cash or deposit checks. Online payments are now possible for a variety of purchases, including shopping websites, which obviates visits to brick-and-mortar stores, unless by choice. ePayments offer features like contactless payments, which have their own merits – contactless payments are increasingly being practiced since the break of the pandemic in 2020.
- Cashless Economy: Beyond personal and business benefits, the use of ePayments can help the nation. A cashless economy can reduce rates of crimes involving tangible money, reduce money laundering evils, and enable international currency exchange. Furthermore, reduced cash usage in privileged sectors enables redistribution of cash among the less privileged of society.
Type of ePayments
While there are several types of electronic payment systems available today, the most common ones are credit cards, bank transfers, and digital wallets. The workings, benefits, and drawbacks of these common ePayment methods are described below.
Credit Cards
Originally developed as “charge cards” for business travel and entertainment, credit cards now serve a plethora of purposes. With a revolving credit line, credit cards offer holders the option to pay their balance in their chosen way – in full at the end of the billing cycle, or in parts and installments. When a credit card is used at a merchant’s outlet, the money first arrives in the merchant’s account and sits in a holding zone until it is disbursed to the target bank account. Payment gateways and merchant accounts work in synergy to enable credit card payments. Payment gateways and merchant accounts may be merged into a single platform such as PayPal and Venmo.
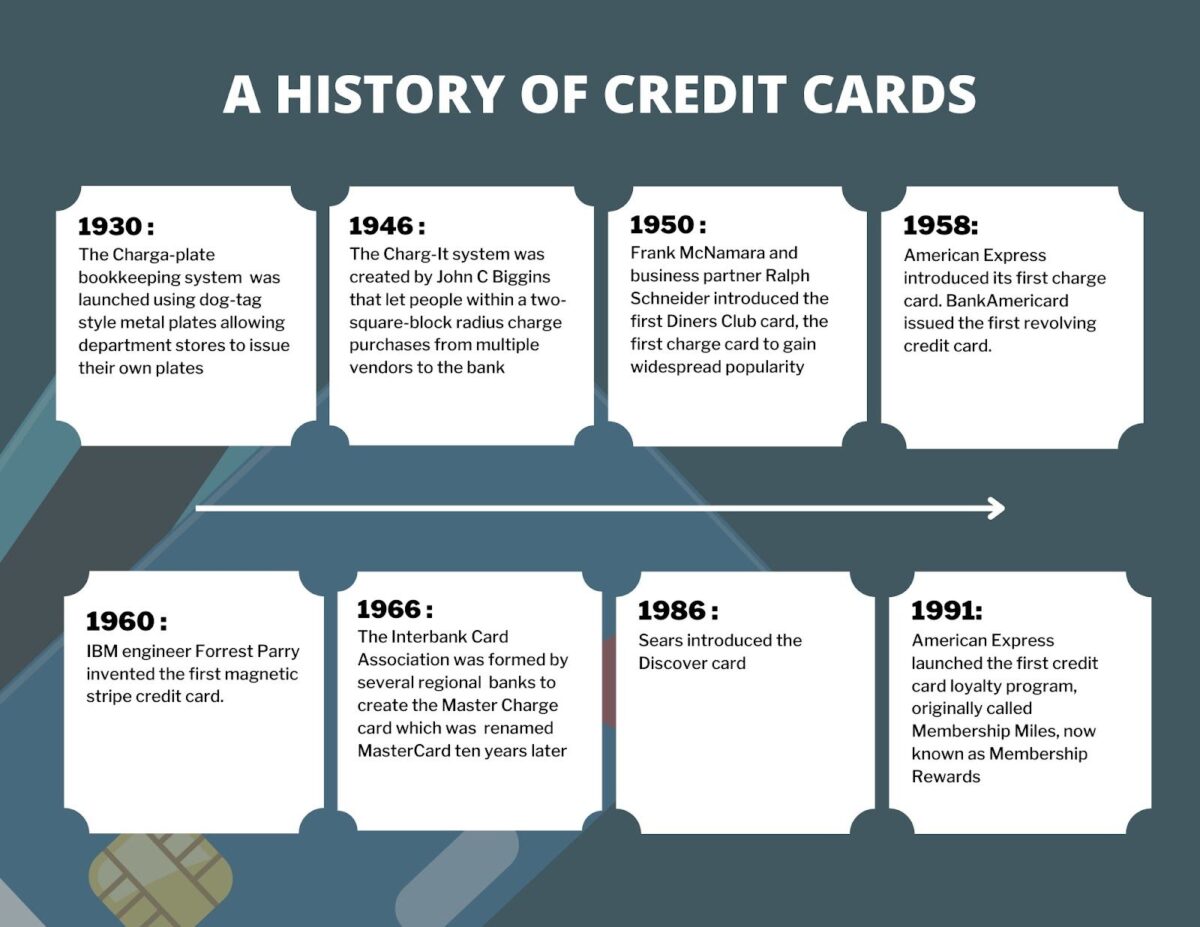
Advantages
- Credit cards are a mature FinTech. In almost all financially upward or upwardly mobile societies, credit cards have remained the preferred form of payment. This means that more people are aware of how credit cards work.
- Cards allow credit and often offer cash-back incentives, installment payments, and discounts.
- Cards are convenient to carry and have an extra layer of protection – even no-swipe, tap-based cards have the option to be swiped with OTP approvals.
- Cards also come with built-in security and fraud prevention which is an added benefit.
Disadvantages
- There is often a merchant fee for credit card transactions. Credit card processing fees may range between 2.8 and 4.3 percent. The merchant may add this to the product price, to avoid loss, which means, this fee is transferred to the customer.
- Credit cards may encourage impulsive and unnecessary purchases
- They may charge high-interest rates for balances not paid in full by the due date
- Fees and fines may be charged for late payments
Bank Transfers
Bank transfer is the movement of funds from one bank account to another using recipient data like account number, bank routing number etc. While this was performed non-digitally at the customer’s side, in the past, i.e. a form for fund transfer was filled and turned in manually by the customer, bank transfers can now be performed online directly by the customer.
Advantages
- Transactions are secure and quick. Both payer and payee receive notifications of funds transfer, which makes it a dependable process.
- There is no possibility of bounced checks or payment reversals because payment can only be made if there is a sufficient balance in the payer’s account.
Disadvantages
- Bank transfers may be associated with a fee, especially when performed between countries.
- Bank transfers are also irreversible. It is a hassle to reverse wrong payments
- Bank transfers do not allow credit. Hence, the bank from which the money is being transferred must have sufficient funds.
Digital Wallet
Boku, a FinTech company conducted a survey that showed that half the population of the world – 4.8 billion people worldwide will use digital wallets by 2025. Digital wallets such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay are being increasingly used to make payments using a hand-held smart device such as a mobile phone or tablet. Digital wallets may be of the form of e-wallets that can be used from any digital medium like computers, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices, m-wallets are specific to mobile devices. It is a money management app that enables payments to retailers or other people from bank accounts or credit cards.

Advantages
- Digital wallets are built using encryption software, which means that the financial information encoded in them is secure and cannot be hacked. Digital wallets don’t store the actual account number or credit card details but only a personal token and can be used only by the holder of the mobile phone because it is protected by passwords and OTPs.
- More and more merchants are accepting digital wallet payments. Payment is as easy as scanning a QR code and transferring the money after multiple levels of security checks.
- The need to have a stuffed wallet and bottomless purse into which one must root to get out the cash is eliminated. Almost everyone carries a smartphone, and that is pretty much the only tool necessary to make the payment.
Disadvantages
- Digital wallets can be platform-dependent and company dependent. Merchants may accept different kinds of digital wallets, and one wallet may not fit all.
- While digital wallets are secure as long as they are in the hands of the owner of the device that holds the wallet, safety is always compromised if the device is stolen. Risks of cyberattacks also exist as with all forms of e-Payment options. However, most digital wallets come with security features that protect them from hacks and cyberattacks. Losing the phone, however, is a more personal risk to using digital wallets.
- Ease of use may encourage impulsive and unnecessary purchases
Others
A subsect of the digital wallet is the virtual card. It is a plastic-free card that allows customers to generate single-use 16-digit numbers authorized for a specific payment amount. Virtual cards are just gaining a foothold in many countries.
There are also country-specific ePayment methods such as the Automated Clearing House (ACH) in the US. ACH is the bank-to-bank transfers that are aggregated and processed in batches through the Automated Clearing House network, run by NACHA. They are used in the US for bulk payments such as salaries.
Looking to automate the mundane & mechanical Payment Reconciliation process? Try Nanonets™ AI-based OCR solution to automate Payment Reconciliation in your organization!
Automation of e-Payment
The Accounts Payable Network reports that replacing paper checks by ePayments would save the $5.14 per check avoided. The automation of ePayments, especially in the B2B area can help companies save considerable time and money. While there are already many accounts payable software and tools available and being used by enterprises, the incorporation of vendor pay automation into the system would result in fully automated procure-to-pay processes.
Some benefits of ePayment automation are:
- Time savings: Automation makes ePayment processes faster when combined with automated invoice processing, and enables the achievement of the optimum Days Payable Outstanding – a powerful metric that reflects the financial health of the company.
- Money savings: Automated payments are cost-effective when compared to paper transactions as seen in the above statistic of $5.14 per check.
- Security: Automatic ePayment software is equipped with high levels of security and encryption, which makes it easier to detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Error elimination: Automated ePayments can eliminate duplication and overpayment errors because they can be connected to automated invoice management.
- Better relationships between enterprises: Setting up automated payment processes can provide the recipients with real-time data on the status of the payment. This can enhance trust and improve customer-supplier relationships.
The choice of an automation tool for ePayments must entail detailed research into the options available vis-à-vis the needs of the business. The automation tool for the ePayment process is not a stand-alone entity but is an extension of the larger AP automation process. Thus, the payment automation solution must be capable of being integrated with the larger AP automation or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
Nanonets as part of the larger ePayment automation process
The automation of the ePayment process is a part of the larger Accounts Payable automation. Nanonets is an AI-enabled OCR software that is ideally suited for the automated extraction of financial data from a variety of sources, to be used in an automated AP process. Accounts Payable Automation or AP Automation is the process by which Accounts Payable Processes are handled digitally rather than manually. It basically comprises three sub-processes:
- Invoice Receipt and Data Extraction
This is the first step where the business owner receives Invoices and ideally uses an OCR tool to convert electronically scanned invoices to digital form. Nanonets can handle this workflow end-to-end in a completely automated fashion. We can integrate with your email inboxes to directly import attachments as Invoices, import Invoices from Cloud Storage, such as G-Drive, One Drive, Dropbox, etc., integrate with databases such as Amazon S3, Integrate via APIs and build any other integrations using Zapier. - Matching and Approval Workflow
This is the second step, where Invoices that are received and processed, are matched with the Purchase Orders and goods Receipts, to ensure accuracy. They can also be manually verified by the relevant team within the organization. Nanonets with their revolutionary AI-powered engines can perform 2-way and 3-way matching between Invoices and Purchase Orders or Invoices, Purchase Orders, and Goods Receipts eliminating up to 90% manual labor and making the process more efficient, reliable, and accurate. - Payments and Recordkeeping for Audit Purposes
The third and final step in this process is when one needs to pay out these Invoices and record these entries in their Accounts Payable Systems for Audit purposes. We, at Nanonets, have pre-built Integrations with popular Accounting Software, such as Quickbooks, Xero, Sage, Netsuite, etc., and can handle integrations with any other Accounting Software swiftly.
Now you know how we, at Nanonets, can automate the entire electronic payments system for an organization end-to-end.
Take away
Electronic payment systems come with compelling benefits such as time and cost savings, streamlined accounts payable processes, and ultimately better bottom lines. Automated ePayment solutions will enable human employees to concentrate on less mundane, higher-value tasks such as business development and other activities that contribute to enterprise value. The choice of an ePayment automation tool depends on the level of automation that the business warrants, and the ability of the software to blend with the company’s larger AP automation processes.
Nanonets online OCR & OCR API have many interesting use cases that could optimize your business performance, save costs and boost growth. Find out how Nanonets’ use cases can apply to your product.
- AI
- AI & Machine Learning
- ai art
- ai art generator
- ai robot
- artificial intelligence
- artificial intelligence certification
- artificial intelligence in banking
- artificial intelligence robot
- artificial intelligence robots
- artificial intelligence software
- blockchain
- blockchain conference ai
- coingenius
- conversational artificial intelligence
- crypto conference ai
- dall-e
- deep learning
- electronic payment
- google ai
- machine learning
- payment reconciliation
- plato
- plato ai
- Plato Data Intelligence
- Plato Game
- PlatoData
- platogaming
- scale ai
- syntax
- zephyrnet












