-
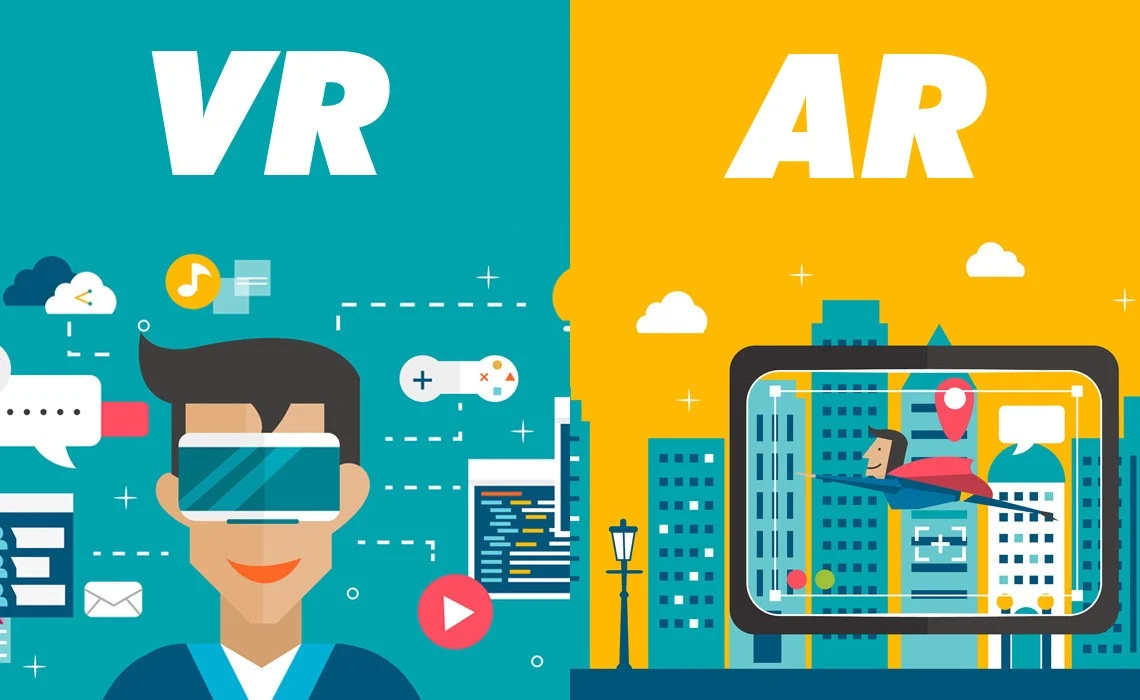
Augmented Reality overlays digital content onto the physical world, enhancing real-life experiences with virtual elements.
-
Virtual Reality immerses users in entirely simulated environments, isolating them from the physical world.
-
Ultimately, the future may not be a binary choice between AR and VR but rather a convergence of both technologies, facilitated by advancements in hardware, software, and user experience design.
A recent video by Meta founder and CEO Mark Zuckerberg in which he compared Meta’s Quest 3 headset to Apple’s Vision Pro headset had the tech community abuzz for various reasons. Amongst the discussions, it became clear that the approaches to this wearable tech will also play a big part in how well they do.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) have been rapidly evolving, promising to revolutionize how we interact with the digital world. But as they continue to advance, a pertinent question arises: which of these technologies holds the future?
To unravel this query, it’s imperative to delve into the nuances of AR and VR, exploring their applications, strengths, limitations, and the trajectories they’re carving in various industries.
Understanding AR and VR
Augmented Reality overlays digital content onto the physical world, enhancing real-life experiences with virtual elements. This technology integrates computer-generated imagery, sound, or other sensory inputs in real-time, typically viewed through smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses. AR aims to supplement and enrich the user’s environment rather than replace it entirely.
On the other hand, Virtual Reality immerses users in entirely simulated environments, isolating them from the physical world. VR headsets transport users to computer-generated worlds, enabling them to interact with and explore virtual spaces in three dimensions. Unlike AR, VR offers complete immersion, stimulating multiple senses to create a sense of presence in a virtual environment.
The Battle of Applications
Both AR and VR boast diverse applications across numerous sectors, ranging from entertainment and gaming to healthcare, education, retail, and beyond.
Augmented Reality Applications
AR finds extensive utility in fields like:
Retail and Commerce: AR enables virtual try-on experiences, allowing consumers to visualize products in real-world settings before making purchasing decisions.
Healthcare: Surgeons use AR overlays during complex procedures, providing real-time guidance and data visualization. Additionally, AR aids in medical training and patient education.
Education: AR enriches learning experiences by overlaying digital content onto textbooks or real-world objects, making educational content more engaging and interactive.
Virtual Reality Applications
VR applications are equally diverse, with notable examples including:
Gaming and Entertainment: VR offers immersive gaming experiences, transporting players to fantastical realms and enhancing engagement with interactive storytelling.
Training and Simulation: Industries like aviation, military, and manufacturing utilize VR for training simulations, enabling safe and cost-effective practice in high-risk scenarios.
Therapy and Rehabilitation: VR is increasingly used in mental health treatments, offering immersive environments for exposure therapy, stress reduction, and pain management.
Strengths and Limitations
Each technology, with its unique strengths and limitations, plays a critical role in determining its path towards widespread adoption and its sustainability in the long term. Augmented Reality (AR) stands out for its ability to blend digital content seamlessly with the physical environment, thereby enriching the real world with virtual elements for a more natural and intuitive user experience.
This integration finds practical applications in everyday life and is accessible through commonly available devices like smartphones, easing the way for user adoption. However, AR faces challenges in achieving the full immersion that Virtual Reality (VR) offers, as it merely overlays virtual content onto the real world instead of creating entirely virtual environments.
The evolution of dedicated AR glasses or headsets is ongoing, with issues related to cost, design, and functionality yet to be fully addressed. Moreover, the effectiveness of AR experiences is contingent upon the user’s immediate surroundings, necessitating appropriate lighting and space for optimal performance.
On the other hand, VR is celebrated for its ability to transport users to entirely simulated environments, offering an unparalleled level of immersion. This total immersion fosters deeper engagement and emotional connection, particularly beneficial in applications like gaming, education, and training.
The hardware supporting VR is constantly evolving, with improvements in high-resolution displays, motion tracking, and ergonomic designs enhancing user experience. Nonetheless, VR introduces its own set of limitations, including the potential for physical isolation from the real world, which can limit social interactions and cause discomfort or disorientation.
The requirement for powerful computing hardware and dedicated VR headsets for high-quality experiences presents a barrier in terms of cost and setup. Additionally, the issue of motion sickness or discomfort affects some users, especially in experiences characterized by rapid movement or conflicting sensory inputs, presenting a challenge to the universal acceptance and adoption of VR.
The Future Landscape
Predicting the future dominance of AR or VR requires consideration of various factors, including technological advancements, market trends, user preferences, and industry adoption.
AR’s Future
Augmented Reality (AR) is carving a significant niche for itself in the fabric of everyday life, thanks to its ability to merge seamlessly with the real world. This transformative technology is revolutionizing a wide array of daily tasks, ranging from navigation and shopping to communication and enhancing productivity.
Its integration into the routine aspects of life underscores its potential and versatility, making it an indispensable tool for the modern user.
Furthermore, the adoption of AR technology is not just limited to personal use; it is making substantial inroads into various industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and field services. These sectors are leveraging AR for a plethora of applications, including workforce training, providing remote assistance, and facilitating maintenance tasks.
This enterprise adoption highlights AR’s capability to improve efficiency and effectiveness, offering tangible benefits in professional settings.
The progression in AR hardware and software is also paving the way for the development of spatial computing platforms. These platforms represent a leap forward, enabling developers to craft immersive experiences that go beyond traditional interfaces.
By allowing for the creation of experiences that users can interact with in the three-dimensional space around them, spatial computing is set to redefine the boundaries of digital interaction, offering more intuitive and engaging ways to engage with digital content.
VR’s Future
The immersive storytelling capabilities of Virtual Reality (VR) have proven to be a significant source of inspiration for content creators across various domains. This has led to the emergence of innovative experiences in gaming, film, and interactive media, where the immersive nature of VR brings stories and environments to life in ways previously unimaginable.
Beyond entertainment, VR is making substantial inroads into enterprise settings, providing training, simulation, and remote collaboration solutions. These applications offer industries cost-effective, scalable ways to enhance efficiency and learning, demonstrating VR’s versatility beyond its traditional confines.
Moreover, the landscape of digital communication and social interaction is transforming thanks to collaborative and social VR experiences. These platforms are creating virtual communities and enabling shared experiences that bridge geographic boundaries, fostering a new era of digital socialization.
Through VR, users can engage in communal activities, attend virtual events, and interact in shared spaces, heralding a future where virtual interactions are as meaningful as those in the physical world.
Maybe both AR and VR
In the ongoing debate between AR and VR, it’s clear that both technologies have significant roles to play in shaping the future of digital experiences. While AR’s seamless integration with the real world offers practical utility and widespread accessibility, VR’s unparalleled immersion and transformative potential in gaming, training, and social interaction cannot be overlooked.
Ultimately, the future may not be a binary choice between AR and VR but rather a convergence of both technologies, facilitated by advancements in hardware, software, and user experience design. This is being referred to as Mixed Reality (MR).
As AR continues to augment our physical surroundings and VR transports us to new realms of imagination, the boundaries between the real and virtual worlds will blur, ushering in an era of truly immersive computing where the possibilities are limited only by our imagination.
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- PlatoHealth. Biotech and Clinical Trials Intelligence. Access Here.
- Source: https://web3africa.news/2024/03/14/news/augmented-reality-virtual-reality/
- :has
- :is
- :not
- :where
- a
- ability
- acceptance
- accessibility
- accessible
- achieving
- across
- activities
- Additionally
- addressed
- Adoption
- advance
- advancements
- aids
- aims
- Allowing
- also
- amongst
- an
- and
- applications
- approaches
- appropriate
- AR
- AR experiences
- AR Glasses
- ar hardware
- ARE
- around
- Array
- AS
- aspects
- Assistance
- attend
- augment
- augmented
- Augmented Reality
- augmented reality (ar)
- available
- aviation
- barrier
- Battle
- BE
- became
- been
- before
- being
- beneficial
- benefits
- between
- Beyond
- Big
- Blend
- blur
- both
- boundaries
- BRIDGE
- Brings
- but
- by
- CAN
- cannot
- capabilities
- capability
- carving
- Cause
- celebrated
- ceo
- challenge
- challenges
- characterized
- choice
- clear
- collaboration
- collaborative
- Commerce
- commonly
- communal
- Communication
- Communities
- community
- compared
- complete
- complex
- computer-generated
- computing
- Conflicting
- connection
- consideration
- constantly
- Consumers
- content
- content creators
- continue
- continues
- Convergence
- Cost
- cost-effective
- craft
- create
- Creating
- creation
- creators
- critical
- daily
- data
- data visualization
- debate
- decisions
- dedicated
- deeper
- delve
- demonstrating
- Design
- designs
- determining
- developers
- Development
- Devices
- digital
- Digital Content
- digital world
- dimensions
- discussions
- displays
- diverse
- do
- domains
- Dominance
- during
- easing
- Education
- educational
- effectiveness
- efficiency
- elements
- emergence
- enables
- enabling
- engage
- engagement
- engaging
- enhance
- enhancing
- enrich
- enriching
- Enterprise
- enterprise adoption
- Entertainment
- entirely
- Environment
- environments
- equally
- Era
- especially
- events
- everyday
- evolution
- evolving
- examples
- experience
- Experiences
- explore
- Exploring
- Exposure
- extensive
- fabric
- faces
- facilitated
- facilitating
- factors
- fantastical
- field
- Fields
- Film
- finds
- For
- Forward
- fostering
- fosters
- founder
- Founder and CEO
- from
- full
- fully
- functionality
- future
- gaming
- geographic
- Go
- guidance
- had
- hand
- Hardware
- Have
- he
- Headset
- headsets
- Health
- healthcare
- heralding
- high-quality
- high-resolution
- high-risk
- highlights
- holds
- How
- However
- HTTPS
- imagination
- immediate
- immersion
- immersive
- Immersive Storytelling
- imperative
- improve
- improvements
- in
- Including
- increasingly
- indispensable
- industries
- industry
- innovative
- inputs
- Inspiration
- instead
- Integrates
- integration
- interact
- interaction
- interactions
- interactive
- interactive media
- interfaces
- into
- Introduces
- intuitive
- isolation
- issue
- issues
- IT
- ITS
- itself
- just
- landscape
- Leap
- learning
- Led
- Level
- leveraging
- Life
- Lighting
- like
- LIMIT
- limitations
- Limited
- logistics
- Long
- maintenance
- Making
- management
- manufacturing
- mark
- mark zuckerberg
- Market
- Market Trends
- May..
- meaningful
- Media
- medical
- mental
- Mental health
- merely
- Merge
- Meta
- Military
- mixed
- mixed reality
- Modern
- more
- Moreover
- motion
- movement
- mr
- multiple
- Natural
- Nature
- Navigation
- necessitating
- New
- niche
- notable
- nuances
- numerous
- objects
- of
- offer
- offering
- Offers
- ongoing
- only
- onto
- optimal
- or
- Other
- our
- out
- own
- Pain
- pain management
- part
- particularly
- path
- patient
- Paving
- performance
- personal
- physical
- Platforms
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- Play
- players
- plays
- plethora
- possibilities
- potential
- powerful
- Practical
- practice
- preferences
- presence
- presenting
- presents
- previously
- Pro
- procedures
- productivity
- Products
- professional
- progression
- promising
- proven
- providing
- purchasing
- query
- quest
- quest 3
- question
- ranging
- rapid
- rapidly
- rather
- real
- real world
- real-time
- Reality
- realms
- reasons
- recent
- redefine
- reduction
- referred
- related
- remote
- remote assistance
- replace
- represent
- requirement
- requires
- retail
- revolutionize
- Revolutionizing
- Rise
- Role
- roles
- routine
- safe
- scalable
- scenarios
- seamless
- seamlessly
- Sectors
- sense
- Services
- set
- settings
- setup
- shaping
- shared
- Shopping
- significant
- simulation
- simulations
- smartphones
- Social
- social vr
- socialization
- Software
- Solutions
- some
- Sound
- Source
- Space
- spaces
- Spatial
- spatial computing
- stands
- Stories
- storytelling
- strengths
- stress
- substantial
- such
- supplement
- Supporting
- Sustainability
- tablets
- tangible
- tasks
- tech
- technological
- Technologies
- Technology
- term
- terms
- than
- Thanks
- that
- The
- The Future
- The Landscape
- their
- Them
- therapy
- thereby
- These
- they
- this
- those
- three
- three-dimensional
- Through
- to
- tool
- Total
- towards
- Tracking
- traditional
- Training
- transformative
- transforming
- transport
- treatments
- Trends
- truly
- try-on
- typically
- underscores
- unimaginable
- unique
- Universal
- unlike
- unparalleled
- unravel
- unstoppable.
- upon
- us
- use
- used
- User
- User Adoption
- User Experience
- User Experience Design
- users
- ushering
- utility
- utilize
- various
- versatility
- Virtual
- Virtual reality
- virtual worlds
- vision
- visualization
- visualize
- vr
- VR Experiences
- VR headsets
- Way..
- ways
- we
- wearable
- webp
- WELL
- which
- while
- wide
- widespread
- will
- with
- Workforce
- world
- world’s
- yet
- zephyrnet
- Zuckerberg













