By Kenna Hughes-Castleberry postat pe 07 octombrie 2022
Many equations within quantum physics can be helpful for guiding researchers that are looking at chemical interactions. As both quantum physics and chimie work on the same atomic levels, they are often used in tandem with each other to achieve new results. Recently, researchers at the Laboratorul Național Los Alamos (LANL) took this pairing one step further by adding masina de învățare processes to help predict biochemical interaction in molecular simulations. This in turn could help accelerate steps in drug design and other industry scenarios, making drugs safer and quicker in the long term.
Using Machine Learning for Data Sets
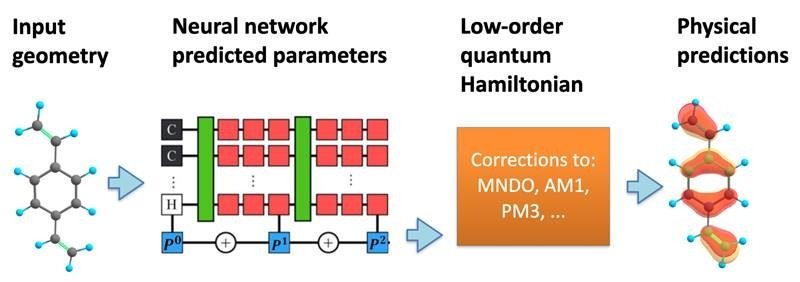
Already machine learning processes are being aplicat to quantum computing and quantum physics. Because machine learning predicts and creates patterns from large groups of data, it is beneficial for fields like quantum physics or chemistry, which have a lot of moving pieces. According to LANL researcher Benjamin Nebgen: “before the advent of machine learning (ML) methods in the fields of chemistry and materials science, the largest practical simulation of chemistry and material systems was capped at a few thousand atoms. This is much too small to accurately capture many effects that dictate chemical or material properties such as grain pathways or rare reactive pathways.” Thanks to the benefits of machine learning, researchers can study more complicated scenarios in simulations, including those focused on quantum physics and chemistry.
For scientists designing new medicamente or studying chemical reactions, it’s important to fully understand what is happening with the electrons at the quantum level. “The motion of electrons and atomic nuclei controls nearly all the chemical and material properties that define our modern existence,” Nebgen said. “This includes the chemistry of everything from the drugs we take, the household cleaners we use daily, to the fuels in our own cars and trucks. Further, the properties of materials that make up our cars, houses, tools, aircraft, and nearly everything we interact with day-to-day are controlled by the same underlying physics.” This enables researchers to probe deeper into a molecule’s interactions at a fundamental level. However, once this level is reached, more complicated math ensues. “The forces acting on individual atoms which go into Newton’s equations derive from the motion of electrons, which are inherently quantum in nature,” Nebgen explained. “Thus, the electrons must be treated with the Schrodinger equation, which is a much more challenging mathematical problem to solve.”
LANL Uses Machine Learning to Create Models
To overcome these difficult equations, researchers like Nebgen are utilizing machine learning tools. These tools can accelerate a chemical simulation by focusing on only a few of the most important electrons in the system, Nebgen added. Using a machine learning tool called a neural network, Nebgen and his team were able to make a model predictiv of the possible electron states and their associated energies within a molecule. From there the team could predict with accuracy some of the possible outcomes of the simulation given different inputs. For biotech companies spending millions of dollars to design and test new drugs, predictive models like this one could give many cost-effective benefits. While using machine learning in the drug industry is not new, combining it with the power of quantum computing may create the next generation of technology needed to launch future drugs.
Kenna Hughes-Castleberry este scriitoare la Inside Quantum Technology și Science Communicator la JILA (un parteneriat între Universitatea din Colorado Boulder și NIST). Bataile ei de scris includ tehnologia profundă, metaversul și tehnologia cuantică.