- The thriving nature of the Metaverse has led to an increased number of scammers, fraudsters, zero-day attackers and crypto hacks.
- According to statistics, over 34% of businesses and systems are affected by inside threats.
- One key attribute most metaverse security and projects fail to adhere to is the element of decentralization.
The various Web3 elements, cryptocurrency, AI, NFT, the Metaverse, and blockchain technology have each promised and delivered a technological revolution. Each has worked in harmony with the other, showing how flexible, interoperable and independent each element can function.
Despite the revolutionary concept, Web3 is still a new entity within the tech world and thus has sevral loopholes. In the past year, crypto hacks have occurred regularly, and many have begun to doubt the full-proof system that blockchain technology once promised. Unfortunately, blockchain security is still in progress to mitigate any attempt. Nonetheless, the achievements of one element of Web3 overshadow its shortcomings, the Metaverse, yet individuals need to understand that Metaverse hacks are plausible.
The concept of Virtual reality has significantly gained an enormous amount f supporters. As a result, many cannot comprehend how an ever-growing virtual reality environment is vulnerable to malicious coding. Unfortunately, due to the vast nature of the Metaverse, it has one of the highest surface areas for crypto and cyber hacks. Here is a look at the crack within Metaverse’s blockchain security.
The revolutionary concept of the Metaverse
All the web3 elements are specifically designed to stand out and function independently but can also merge their different attributes. The Metaverse is the building block of two decades of effort and works from blockchain developers. In 1992, Neal Stephenson coined the term Metaverse when it was only mere science fiction. The creation of a 3-D virtual space that allowed users to interact, conduct business and connect with the world was only seen in movies then, but what was once a dream soon became a reality.
The Metaverse provides the environment necessary for blockchain applications to thrive. It’s the first iteration of a fully realized Web3 ecosystem. Granted, the merger between blockchain technology and Metaverse came relatively recently. With the ecosystem in place, NFTs serve as a form of ownership for any digital content for users. This reduces the likelihood of fraudulent activities or scams, allowing users to own virtual land.
Also, Read Blockchain Security: Lessons Learnt in 2022, expectations for 2023.
With digital ownership, one of the main hurdles of the Metaverse tackled, cryptocurrency stepped in to create a financial system for the virtual world. Developers add AI and smart contracts to govern and automate any user transaction. Metaverse became the product that could house all the Web3 elements and create an ecosystem that is eerily close to the real world.
Rise of the Metaverse applications
This concept led multiple companies such as Meta, Microsoft, IBM and other big-league organizations to nose dove into the Metaverse development project. Africa has also successfully created its Metaverse, the AFricarare and the Nandi Metaverse. Both these virtual spaces have catered to numerous African NFT artists and collectors and promoted the growth of crypto in the continent.

The metaverse has gained a considerable following given its revolutionary concept.[Photo/Medium]
Unfortunately, the massive potential and nature of the Metaverse make it a primary target for crypto hacks and cyber attacks. Many might think that the incorporation f blockchain technology could curb such attacks but keep in mind these technologies are still in their infancy stage. This means that developers make plenty of errors during its creation leading to a high rate of zero attacks.
The crumbling nature of Metaverse security
The Metaverse s a virtual space incorporating blockchain security and other security measures. Unfortunately, this has only mitigated most Web2 cases within its entire lifespan. The thriving nature of the Metaverse has led to an increased number of scammers, fraudsters, zero-day attackers and crypto hacks, each trying to bypass set blockchain security measures.
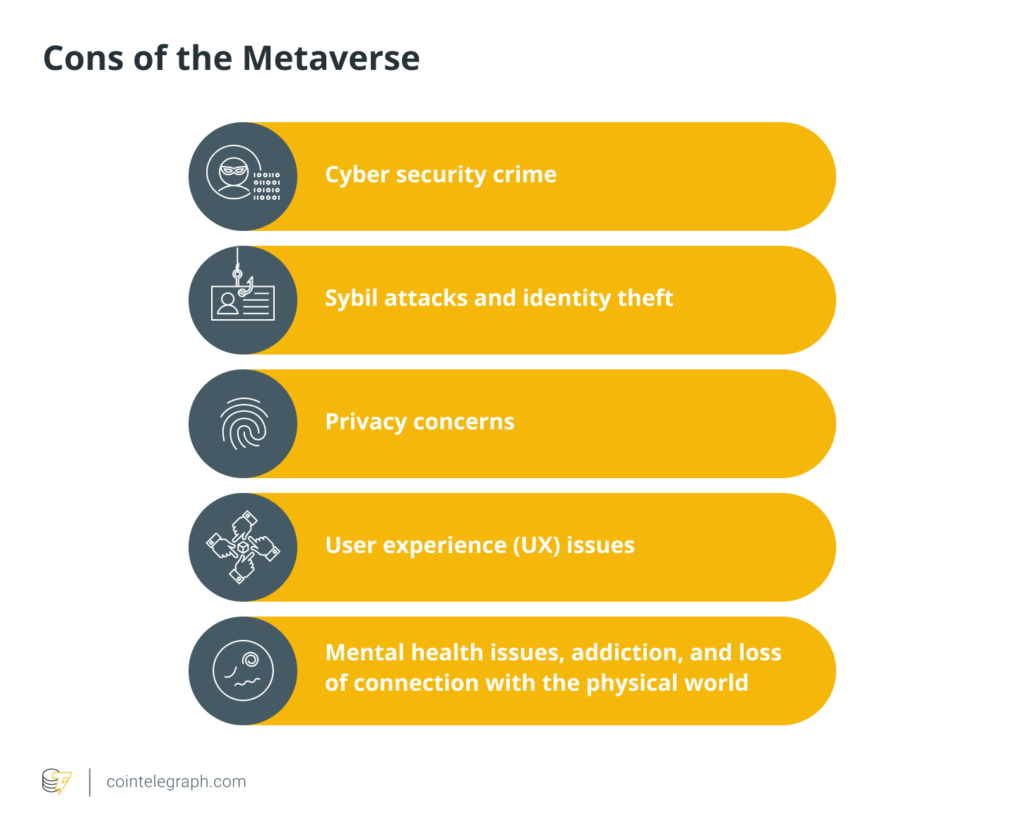
Various security issues that plague the metaverse.[Photo/CNBC]
A metaverse hack is a rare scene, but that does not mean it does not occur. Many instigators bypass metaverse security to access various NFTs and Crypto coins that have financial value. Although adding several blockchain security measures, its interactive nature is ultimately its undoing. According to statistics, over 34% of businesses and systems are affected by inside threats. In layman’s language, a user the metaverse security intends to protect might be the perpetrator.
Issues plaguing the Metaverse Security
Below are some cyber security issues that Mtetaverse projects have difficulty dealing with.
Privacy Invasion
As previously mentioned, the Metaverse mimics what Web3 is trying to do. Its interoperable nature to build a virtual space incorporating all other Web3 elements mirrors its primary goal. Unfortunately, that is as far as it goes. One key attribute most metaverse security and projects fail to adhere to is the element of decentralization.
It may incorporate crypto coins to build its financial system, but a single or a group of entities still control the overall project. This raises questions about user privacy and the protection of data. Big tech companies commonly sell or loan customer data to other corporates. Because of the interactive and vast nature of the virtual space, it can accommodate many users.
Owner companies record every action the user does, their hobbies, and their financial transactions. These data are like gold to advertising departments, so many often buy them from such corporates. Unfortunately, with the ever-growing nature of blockchain security, there are no rigid regulatory frameworks to protect user data privacy in the Metaverse. In hindsight, metaverse hacks usually occur when third parties breach owner companies to access the data.
Crypto hacks and scams
Unfortunately, with the incorporation of digital currency to build a financial system, most metaverse securities have to deal with crypto hacks and scams. The existence of in-built blockchain security might curb the sudden crash of crypto coins, but it can only do so much. Crypto hacks such as the Axie Infinity and Womhole Token bridge attacks are examples of metaverse hacks involving crypto tokens.
Also, Read The Metaverse and the evolution of modern technology.
In addition, the Metaverse is an interactive platform. Despite being an element of web3, it still advocated for social development among users. Unfortunately, this could lead to severe intervention hacks through social engineering. Since users interact with avatars, trust builds through daily interaction with other users.
In most cases, everyone within a single metaverse project uses alias names, and hiding a user’s true identity protects and causes harm simultaneously. Hackers and Scammers thrive in such an environment and use various social engineering techniques to gain access. This led to massive crypto hacks, and despite its incorporation of decentralized crypto coins, it is still a long way to go.
Difficulty with smart contracts
Most metaverse projects associated with Web3 have integrated various smart contracts to deal with the daily transactions of users. Its automation has rapidly increased the efficiency of crypto transactions and digital ownership selection. The incorporation of it has built the reputation of the Metaverse. Unfortunately, a fundamental problem arose quickly over the years. One such element is the ever-expanding nature of the Metaverse.
The main goal of every metaverse security measure is to provide the necessary control measures to ensure cyber security n an ever-expanding environment. To achieve this, security analysts have revised and added various new regulations to the system. Unfortunately, changing smart contracts is more complex than many think.
Its fundamental attribute, blockchain technology, makes it immutable and only changeable through the consensus of the entire network. Many metaverse hacks can occur through the exploitation of this rigid system. With more users expanding the domain of the Metaverse, new inventions and ways of interaction are also invented. This creates a zero attack that many security analysts cannot detect.
Conclusion
For an honorary mention, identity theft is also a significant factor contributing to metaverse hacks known today. The use of avatars is one of the significant vulnerabilities in metaverse security. Hackers could find a way o compromise and bypass its blockchain security and take the identity of another user.
This allows hackers to carry out crypto hacks while masquerading as other individuals. The ramification of identifying heft in the metaverse security goes beyond an individual victim. Hackers are known for using other avatars t conduct social engineering and fraudulent activity. Fortunately, the establishment of NFT can curb this dilemma. Its digital ownership properties can provide legal evidence against an individual unless a user gives out their details.
Also, Read Examining the Progress of the African Metaverse.
Metaverse Security is still in progress as developers find newer ways to improve the experiences of its users. Developers can curb metaverse hacks by redefining their blockchain security without needing third-party security analyses.
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- Platoblockchain. Web3 Metaverse Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- Minting the Future w Adryenn Ashley. Access Here.
- Source: https://web3africa.news/2023/04/18/news/metaverse-security-unable-to-defend-from-attackers/
- :has
- :is
- 2022
- a
- About
- access
- accommodate
- According
- Achieve
- achievements
- Action
- activities
- activity
- added
- addition
- adhere
- Advertising
- africa
- African
- African NFT artists
- Africarare
- against
- AI
- All
- Allowing
- allows
- Although
- among
- amount
- Analyses
- Analysts
- and
- Another
- any
- applications
- ARE
- areas
- Artists
- AS
- associated
- At
- attack
- Attacks
- attributes
- automate
- Automation
- Avatars
- Axie
- Axie Infinity
- BE
- because
- being
- between
- Beyond
- Big
- big tech
- Block
- blockchain
- blockchain applications
- Blockchain security
- blockchain technology
- breach
- BRIDGE
- build
- Building
- builds
- built
- business
- businesses
- buy
- by
- CAN
- cannot
- carry
- cases
- causes
- changing
- Close
- Coding
- coined
- Coins
- collectors
- commonly
- Companies
- complex
- comprehend
- compromise
- concept
- Conduct
- Connect
- Consensus
- considerable
- content
- continent
- contracts
- contributing
- control
- corporates
- could
- crack
- Crash
- create
- created
- creates
- creation
- crypto
- Crypto Coins
- crypto hacks
- CRYPTO TOKENS
- crypto transactions
- cryptocurrency
- Currency
- customer
- customer data
- cyber
- Cyber Attacks
- cyber security
- daily
- daily transactions
- data
- data privacy
- deal
- dealing
- decades
- Decentralization
- decentralized
- delivered
- departments
- designed
- Despite
- details
- developers
- Development
- different
- Difficulty
- digital
- Digital Content
- digital currency
- digital ownership
- domain
- doubt
- dove
- dream
- during
- each
- ecosystem
- efficiency
- effort
- element
- elements
- Engineering
- enormous
- ensure
- Entire
- entities
- entity
- Environment
- Errors
- establishment
- ever-growing
- Every
- everyone
- evidence
- evolution
- examples
- expanding
- expectations
- Experiences
- exploitation
- FAIL
- Fiction
- financial
- financial system
- Find
- First
- flexible
- following
- For
- form
- Fortunately
- fraudsters
- fraudulent
- fraudulent activity
- from
- fully
- function
- fundamental
- Gain
- given
- gives
- Go
- goal
- Goes
- Gold
- granted
- Group
- Growth
- hack
- hackers
- hacks
- Harmony
- Have
- here
- High
- highest
- hindsight
- House
- How
- HTTPS
- Hurdles
- IBM
- identifying
- Identity
- immutable
- improve
- in
- incorporate
- incorporating
- increased
- independent
- independently
- individual
- individuals
- Infinity
- integrated
- intends
- interact
- interaction
- interactive
- interoperable
- intervention
- Into the Metaverse
- Invented
- inventions
- issues
- IT
- iteration
- ITS
- jpg
- Kaspersky
- Keep
- Key
- known
- Land
- language
- lead
- leading
- Led
- Legal
- Lessons
- lifespan
- like
- loan
- Long
- Look
- loopholes
- Main
- make
- MAKES
- many
- massive
- max-width
- May..
- means
- measure
- measures
- mentioned
- Merge
- Merger
- Meta
- Metaverse
- metaverse development
- metaverse project
- metaverse projects
- metaverse security
- Microsoft
- might
- mind
- Mitigate
- Modern
- more
- most
- Movies
- multiple
- names
- Nature
- Neal Stephenson
- necessary
- Need
- needing
- network
- New
- NFT
- NFT Artists
- NFTs
- nose
- number
- numerous
- occurred
- of
- ONE
- organizations
- Other
- over
- overall
- own
- owner
- ownership
- parties
- past
- Place
- Plague
- platform
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- plausible
- Plenty
- potential
- previously
- primary
- privacy
- Problem
- Product
- Progress
- project
- projects
- promised
- Promoted
- properties
- protect
- protection
- provide
- provides
- Questions
- quickly
- raises
- rapidly
- RARE
- Rate
- Read
- real
- real world
- Reality
- realized
- recently
- record
- Redefining
- reduces
- regularly
- regulations
- regulatory
- relatively
- reputation
- result
- Revolution
- revolutionary
- rigid
- s
- Scammers
- scams
- scene
- Science
- Science Fiction
- Securities
- security
- Security Measures
- selection
- sell
- serve
- set
- several
- severe
- significant
- significantly
- simultaneously
- since
- single
- smart
- Smart Contracts
- So
- Social
- Social Engineering
- some
- Space
- spaces
- specifically
- Stage
- stand
- statistics
- Still
- Successfully
- such
- sudden
- supporters
- Surface
- system
- Systems
- Take
- Target
- tech
- tech companies
- techniques
- technological
- Technologies
- Technology
- that
- The
- The african metaverse
- the metaverse
- the world
- theft
- their
- Them
- These
- Third
- third parties
- third-party
- threats
- Thrive
- thriving
- Through
- to
- today
- token
- Tokens
- transaction
- Transactions
- true
- Trust
- Ultimately
- understand
- use
- User
- user privacy
- users
- usually
- value
- various
- Vast
- Victim
- Virtual
- virtual land
- Virtual reality
- Virtual space
- virtual world
- Vulnerabilities
- Vulnerable
- Way..
- ways
- Web2
- Web3
- Web3 Ecosystem
- webp
- What
- while
- with
- within
- without
- worked
- works
- world
- year
- years
- zephyrnet
- zero